Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Marketing
on Mar 3rd, 2014 | 0 comments
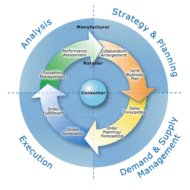
Product Forecasting – An Analogy What is Product Forecasting: It is the science of predicting the degree of success a new product will enjoy in the marketplace. Forecasting is said to be the first and foremost step in the planning process. One of the requirements for effective long-term planning by managers is to assess the changes in technology and environmental conditions that could affect the firm. This is termed as environmental scanning which facilitates the firm to benchmark its performance as against the top industry standards. Technological forecasting involves anticipating development of new products and processes and the time taken for such kind of innovations to be accepted and absorbed in the market. External Environmental Scanning: Environmental forecasts focus on factors such as population growth, availability of resources, social and political trends that may affect the firm’s future. Business firms become more informative on, The percentage of market share for existing products of the firm Future demand for its product range Decline in sales proportions Consumer feedback about product performance Customer satisfaction Sales team performance level Pitfalls in marketing strategies Need for new product development Unidentified customer needs and so on All predictive activity is subject to error, but technological and environmental forecasting is particularly different because they often involve assessing ideas and relationship that do not exist at the time the analysis is being performed. These forecasts are best suited for predicting performance a year or two in the future. Plan of Future Course of Action: Based on forecasting, the firm decides the future course of action. Sales forecasts help the firm to decide on the volume of production for the next few months and aid in aggregate capacity planning. Labor productivity is a crucial factor in determining the success of a business environment, especially a production environment. Manpower planning is purely based on production forecasts where in, the labor hour productivity is also taken into consideration. Forecasting Techniques: In the absence of empirical data, the forecasts must be based on expert opinions. Techniques like Delphi method can be used for this purpose. A group of experts is asked to assess a particular situation, presented with the judgments of others in the group, and then asked to reevaluate their individual positions based on what they have heard. The process continues until a consensus is arrived or until it is apparent that there will be no consensus. This helps the firm to consolidate its position with respect to specific problem situations. The Delphi method has been successfully used to forecast the nature and timing of technological change. Techniques like Delphi and Brain storming also help in the process of identification of bottlenecks, the current business trend, the firm’s future prospects, range of estimates for the desired breakthroughs etc. Although the pattern of a business cycle or a product cycle for the most part, follows a fairly predictable pattern, the firm cannot overlook probabilities, upon which the firm has to capitalize on. The firm has to become alert and employ some innovations at that point of time, when the market becomes saturated. Or else, the rate of growth declines and the firm has to decide whether to continue with the operations which calls for additional investment or close down the...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Decision Making, Principles of Management, Productivity
on Feb 26th, 2014 | 0 comments
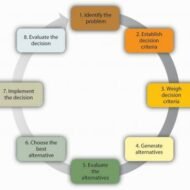
The Process of Decision Making There is a need to broaden our understanding about decision-making process. Decision making is not an independent entity and relies upon many other factors like precedence, social processes and random eventualities. It has three components; identification of the issue, the possible course of action and choosing the best amongst the choices of action available. The decision-making process is continuous since the business environment is dynamic and constantly poses challenges to the decision makers. Organizations are viewed as “Garbage can models” of decision making, in which actions, decisions and outcome are randomly mixed in the flow of events. With this introduction let us proceed to know more about the nature and types of decision making. NATURE OF DECISION-MAKING: 1. It is closely related to solving problems and issues 2. It is associated with all the important management functions like planning, organizing and controlling 3. Fayol and Urwick feels that decision-making is concerned only to the extent that it affects delegation and authority 4. Chester I Bernard in his “Functions of the Executive” says that the process is nothing but narrowing down of choice 5. Herbert A Simon considers decision-making as a process of intelligence, design and choice activities 6. According to Peter Drucker, it is a central part of the management process THE DECISION-MAKING PROCESS: The following steps are involved in the process of decision-making Recognizing the problem: Think about this; if there is a decline in the sales volume of your company or say if the value of your stock decreases, you are forced to make decisions to manage the contingency. In such situations, the first step would be to recognize or identify the problem area. A problem identified is half done. In this instance, the reason might be competitor strength or lack of necessary investment in the key strategic business units. Deciding priorities among the problems: A manager need not and cannot look after all the problems prevailing in the organization. He should know how to delegate authority and the responsibility that goes along with it. Subordinates can be entrusted with the handling of small and trivial problems while the manager can handle very important ones that might affect the functioning of the firm. He should ask the following questions to diagnose the situation. 1. What is the real problem? 2. What are the causes and effects of the problem? 3. Is this problem very important? 4. Can sub-ordinates handle this problem? 5. Which is the most pressing problem to be solved? Diagnosing the problem: Now the manager must start diagnosing the problem. Each and every individual has a different perspective and perceive the problem from a different angle. This depends upon the background orientations and training. The right way of approach for any manager would be to systematically analyze the problem for identifying the alternative courses of action. Developing alternative courses of action: This step involves creativity and innovative capabilities as the manager has to think from all possible angles and directions. Managers holding senior corporate positions are exposed to more of this kind of atmosphere where they are forced to make quick decisions in accordance with what the situation demands. Outside expert consultants are also put into use by some companies for developing choice alternatives. The following are the five PSYCHOLOGICAL STEPS for developing alternatives: 1. Saturation– A manager must be thoroughly familiar with the problem 2. Deliberation– Analyzing the problem from several points of view 3. Incubation– Temporarily switching off the conscious search to relax for the purpose of clear thinking 4. Illumination– A flash of light may occur after sometime giving him the right insights and ideas. 5. Accommodation– The ideas are made into a concrete proposal Evaluating the alternatives: The pros and cons of each and every choice is thoroughly subjected to scrutiny in terms of cost, time, risk, results expected, deviations anticipated...




