Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Decision Making, Principles of Management, Strategy
on Mar 24th, 2014 | 0 comments
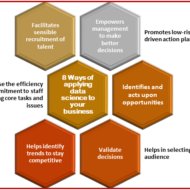
Growth Strategies In Business What are Growth Strategies? The means by which an organization plans to achieve its objective to grow in volume and turnover. The dynamic business environment calls for periodical changes in the business definitions, in terms of customer groups, customer functions and alternative technologies to broaden their scope for expansion. Growth can never be achieved by a business enterprise, if there is no proper planning for diversification of its business activities across a broad spectrum. Expansion strategies are followed when an organization aims at high growth, by improving its overall performance. A Small Note on Data Science and Analytics Data analytics help companies improve operational efficiency, drive new revenue and gain competitive advantages. To leverage this technology, companies need to understand the core of their data and determine the outputs that they are looking for. In fact, data-driven companies that utilize Business Analytics achieve a competitive advantage. The companies can improve their strategies by keeping in mind the customer focus. Big data analytics efficiently helps operations to become more effective. Expansion Strategy: Expansion strategies have a profound impact on the internal configuration as well as internal functioning of an organization. The business firms bear the risk of moving in an entirely new direction, where there is an equal chance for failure as that of success. If only a manufacturer plans to diversify or expand in a field that complements his present business activity, does it make any sense. What is the fun in venturing into a business activity about which you have no knowledge or scope? Expansion through concentration: This involves investment of resources in a product line for an identified market with the help of proven technology. A firm may attempt to intensify its focus on existing markets through market penetration strategies. Or new users may be targeted for existing products or alternatively it may introduce new products in existing markets by concentrating on product development. Concentration policy relies on the principle of “A known devil is far better than an unknown angel.” It is a very difficult task for firms to capture new markets or to gain acceptance for new products in existing markets. Expansion through integration: A company attempts to widen the scope of its business activities in such a manner that it results in serving the same set of customers. The alternative technology dimension of the business definition undergoes a radical change. Firms try to move up or down in the value chain to meet the demands of the customers by integrating adjacent activities. Expansion through co-operation: It may include mergers, takeovers, joint ventures and strategic alliances. Two firms try to combine their resources, capabilities and core competencies to pursue mutual interests to develop, manufacture or distribute goods and services. Expansion through internationalization: International strategies are formulated in the wake of globalization where most of the developing countries have liberalized their economic policies facilitating foreign direct investments, generating foreign exchange. Many multinational and transnational companies are setting up their operations in developing countries to factorise the economies of scale and to enjoy the advantages of cheap labor and availability of resources. Stability Strategy: Many firms go for stability strategies that are devoid of any risks. They are quite contented with the modest profit gained from the present business activity and try to maintain the same level of performance, until and unless there is a pressure from the market in the form of competition. Only few firms have that adventurous attitude to take risks in order to have a sustainable competitive...

Posted by Managementguru in Change management, Economics, International Business, Principles of Management
on Mar 15th, 2014 | 0 comments
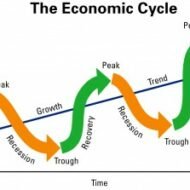
Factors That Influence Global Economy The industrial and business environment of developing countries has been subjected to a sea of changes owing to the economic reforms and policies in the light of globalization, privatization and liberalization. A long term economic vision is necessary for these countries to establish themselves in the global market which facilitates the process of becoming self sufficient in due course of time. Let me present you with a synopsis of how this change can happen and how countries are adapting themselves in lieu of the global economic boom. Multi Brand Retail Markets: Many multinational companies have acquired and are trying to acquire a major part of equity in multibrand retail markets of the host country and sometimes they opt for Joint ventures to factorize the economy of scale which also proves to be a win-win situation for both the parties. Developing countries have altered their economic views on foreign direct investment and are very liberal in their attitude in providing with the necessary licenses. The entry of multinational companies and their potential investment has even altered core sectors like power, oil and telecommunications. Moreover, the benefit of cheap labor, economic subsidies for the start of operations in economically backward regions lures foreign investors. Rush of Entrepreneurship: There is a rush of entrepreneurship in the developing countries, in the form of setting up of small scale industries, cottage industries for which liberal subsidies are provided by the governments to encourage the act of entrepreneurialism. Also people want to go for diversification, mergers and acquisitions in the wake of global competition. Capital Markets’ Role: Capital markets have gained new buoyancy. The rapid growth of stock market and its influence over the international economic scenario have made foreign brokers to keenly follow the market changes for potential investment. The one striking feature of the economy of developing countries is that, it is a self made economy and withstands the pressures of the business cycle, such as recession and inflation, unlike foreign markets that have failed to stabilize their markets owing to what is called sub prime lending, a plan that has failed to achieve the desired economic growth. Instead of making the capital market alive with fresh infusions of funds, it has left many banks and financial institutions bankrupt. Banking Sector: Banking sector has scaled to greater heights and has come under a competitive environment. Deregulation of interest rates to attract potential investors, new technology, products and aggressive marketing usher in new competition; disinvestment of government equity in nationalized banks have made banks to operate as commercial institutions and their services get marketed as branded consumer products. Financial services have emerged as a new business and funding options are aplenty increasing the chances of raising capital. This has evolved as a separate and major source of business fetching revenue to the service providers. Private Sector: Private sector is gaining importance in countries like India, where they have entered all the core industries like oil, mining, telecommunications, road building, railways, ports, civil aviation etc. This serves as a revenue source for the government and this kind of economic restructuring has brought a wave of enthusiasm amongst the potential investors. Imports have become an entrepreneurial activity and are out of the government domain and this has been facilitated by relaxation of licensing hassles. These are some of the recent trends in the developing countries that have captured the interest of multinational...




