Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Marketing, Operations Management, Principles of Management, Strategy
on Mar 16th, 2014 | 0 comments
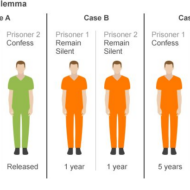
Game theory and strategy What is Game Theory: Set of concepts designed for decision making in situations of competition and conflict under specified rules. The prisoner’s dilemma: The prisoner’s dilemma is a canonical example of a game, analyzed in game theory that explains why two individuals might not cooperate, even if it appears that it is in their best interest to do so; Albert W. Tucker formalized the game with prison sentence payoffs and gave it the “prisoner’s dilemma” name. To solve many practical problems that are encountered in economic, military or other disciplines, one has to deal with situations in which there are two or more conflicting parties striving for the same objective and the outcome of each action of one party depends solely on the opposite parties choice of a course of action. As we all know only one horse can win the race ultimately and the other parties only can prolong the race or see to that they make every possible move to delay the opponent’s success. So, what’s this game theory all about? This is a special mathematical method that was evolved mainly to analyze conflict situations where the number of competitors is finite, each participant has a definite set of actions to choose and there is a conflict of interest between the competitors. So it helped the participants to reach a decision that would put them in the winning post. This theory has spilled its implications on business situations where success is the motto and conflict and competition the order of the day. Only the best among the best survive. Darwin’s theory, “Survival of the fittest” applies not only to biological organisms but also to business organizations which are also abuzz with activity. Chance Moves: Games like chess, checkers are played according to a definite set of rules laid down and these game patterns has inspired business persons to introduce strategies in business, where the concentration is mainly focused on the chance moves that defeats the opponent. Big business corporates mainly concentrate on the strengths and weaknesses of their competitors to have an edge over them. A real game is controlled and regulated by the statutory rules to be followed but a business game involves lot of killer instincts and intuitions combined with rational thinking and logic. Optimal Strategy: The first party always puts himself in the shoes of the other party and tries to perceive how the other party would react in a particular situation. Although the aim is to win, choosing the optimal strategy is what matters. It will at least keep you in bay. Precise solutions can be arrived at if you plan your game fittingly. The anticipation and thrill that is involved in a strategic game is matchless. We witness a lot of firms imitating what the leader of the market does. The risk is borne solely by the firm introducing the change and the firm takes the major share of profit as it is the pioneer and if it loses the next strategic move is planned for. For a company with sound financial position, the chance move is worth giving a try, head or tail doesn’t matter. The stalkers are benefited by the waiting period during which they come to know of the pros and cons of the strategy employed by the leader. Games are played in the true spirit of sportsmanship, but a business faces cut throat competition. There is no space for any courtesy or liberal approach. If you are quick enough to pick the pulse of the people by gauging their preferences, analyzing the market conditions and employing timely strategies you will at...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 2nd, 2014 | 0 comments
Principles of Planning and Forecasting The guidelines of principles of planning are as follows: 1. Principle of primacy of planning: As discussed earlier planning is the prime function of management and precedes all the other functions. 2. Principle of verifiable objectives: The objectives set must be clear, achievable and verifiable in order to attain a feasible management model. 3. Principle of planning premises: The contributing factors in the external environment are government policies, economic factors, market standing, and consumer preferences etc. that decide the success of planning. Planning is done based on these assumptions but nevertheless, all the factors external to the business have to be thoroughly analyzed to ensure concrete planning. 4. Principle of limiting factor: Cost is one of the major limiting factor; production cost has to be factorized to ensure economy of scale and potential resources needed for a business in the likes of men, material and other physical resources have to be taken into consideration. 5. The commitment principle: Planning and decisions whether short term or long term is valid only for a particular period. The long term plan is nothing but the future impact of today’s decisions. Decisions concerning new product development by a company aims at creating an impact for the next 15 years or so while decisions concerning sales target has to be accomplished on a periodic basis- monthly or quarterly. 6. Principle of flexibility: A plan should be flexible and give room for contingencies like losses incurred through unexpected events. 7. Principle of navigational change: Plans while suggested to have built-in flexibility are also subjected to periodical review in the light of environmental fluctuations. A business can not stick to a long term plan devised originally since it is equally important to check on events and expectations periodically. FORECASTING AND PLANNING: Forecasting is a management technique that relies on both past experiences and present assumptions to predict the future. Again this serves as an important premise for the planning process. The conditions of the external environment though out of one’s control, if properly estimated, can lead an organization to produce wonderful results. TYPES OF FORECSATS: Economic forecast: To gauge the general economic scenario and its effect on sales. Technological forecast: To predict what new technologies can be developed, when and how to bring feasibility to the operations involved. Competition forecast: To look into the competitor strength and tactics and know where one stands. Social forecast: To predict the attitude of people and social conditions. Supplier’s forecast: Reveals the response of suppliers. FORECASTING TECHNIQUES: 1. Quantitative time series analysis: Monthly sales data is plotted in a chart and the past data helps in consolidating the sales volume and fluctuations in sales. Sales trend is determined and the assumption is that, the future will reflect the past and present trend and hence can be projected. If there is a lull in sales, reasons for the decline can be known by taking feedback from various quarters like, suppliers, consumers and employees. 2. Derived forecast: The forecast done for a specific purpose may be reused for another purpose. For example a census data can help you to determine the demography of a particular geographical area that might help you to reach your target customers. 3. Casual methods: If the underlying cause for the variable can be determined, the forecast can be arrived mathematically and produce quite accurate results. Social media marketing is very popular now a days and instantly you know how many hits are received for a particular product and the ratio of conversion into sales. 4. Brain storming: People with knowledge and expertise assemble in order to discuss the pros and cons of a particular idea, be it the launch of a new product, product promotion or withdrawal of a product line. 5. Delphi method: In this method, each and very expert is contacted independently and opinions are drawn...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Principles of Management
on Feb 26th, 2014 | 0 comments
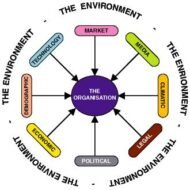
Factors of External Environment of Business What do you mean by Business Environment: The sum total of all things external to firms and industries that affect the functioning of the organization is called Business Environment. Elements of Business Environment 1. ECONOMIC 2. SOCIAL 3. CULTURAL 4. POLITICAL 5. LEGAL 6. TECHNOLOGICAL 7. DEMOGRAPHIC 8. GEOGRAPHICAL 9. ECOLOGICAL 1. Economic Environment This refers to all economic factors that influence and affects the very survival of an organization. Can be classified into · Economic factors affecting demand · Competitive forces Economic factors affecting demand The existence of an organization depends on the demand for its products or services. The customers’ ability to buy and willingness to pay determine the demand factor. The buying power is determined again by · Employment · Income taxes · Saving and · Prices The money acquired by an individual through employment is utilized for paying taxes which is the first priority and then comes saving or spending. In developing countries like India, much importance is attached to the habit of saving in the form of insurance policies or mutual fund deposits or investment on immovable assets. This makes the economy strong and stable even during times of recession, whereas we witness the economy of some developed countries entirely shaken when there is an economic depression. Sub Prime Lending Sub prime lending may prove to be disastrous for a growing or grown nation when the money is lent by the banks to third parties without proper securities or collaterals. While the initiative is intended to increase the growth rate or GDP, the end result may not live up to the expectations when the money is parted to individuals or firms with poor financial credentials. Disposable Income Disposable income also decreases when the tax rate increases and his/her ability to buy is reduced. Equally important is the willingness to by because the fact that an individual has the ability does not mean that he or she will buy. Willingness is affected by the preferences for products and the expectation about future factors like the price fluctuation, increase in one’s own income, general economic trend and so on. Competitive forces Firms have to first survive in order to succeed in the market. To accomplish this they exert competitive force on each other through one or the other following methods. · Price cutting · Promotion-advertising, personal selling · Design, feature and packing · Number and type of customer services offered give a cutting edge to firms competing in the race. 2. Social and Cultural Environment The social environment depends upon the · The class structure · Mobility · Nature of the social organization and · Development of social institutions People always have the unending desire to move from one occupational category to another and this is the main reason for high job turn over in IT industries for various reasons like pay, promotions, job satisfaction etc., This is the same reason which can be attributed to the failure of many good projects that go underway due to lack of continuation of the same initiative with which it was started. The above said process is more prevalent in urban societies than rural where scope of mobility is much the less among farmers, artisans and those engaged in traditional crafts and cottage industries. 3. Political Environment A smart manager has to be on tenter hooks to gauge the trends in political scenario that directly or indirectly affect the functioning of the firm. The political weather is highly unpredictable and may be classified into · Long-term changes · Quick changes · Cyclical changes · Regional changes Now-a-days we see that the economic depression in...

Posted by Managementguru in Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Feb 22nd, 2014 | 0 comments
Organizational change is concerned with making things different and change agent is a person or group of persons who act as catalysts to bring about change. Say, managers and outside expert consultants can be called as change agents. What is Organizational Change? This is how you have to Strategise in order to Win Organizational development refers to the overall development of an organization in terms of improving the ability of that organization in tandem with the needs of the external environment and involves a system oriented approach to change. Recommended: Resourceful Guide on Organizational Development from Maryville University titled ” Organizational Development Guide: Definition, Process & Development Models “ Organizational change: All the elements of a social system like people, formal organization, informal organization, operational environment, communication, decision making and patterns of co-operation are bound to change when there is change in the external environment but this gives rise to a positive pressure which acts like a self-correcting mechanism to modify and set right the bottle-necks or loop-holes in the working system. Causes For Change Work force: The increasing awareness and educational qualification among the workforce is responsible for the attitude change. You can expect loyalty from workers above fifty but not workers who fall under the age category thirty. This is because their loyalty is oriented towards their career and not to the employer. Technology change: Internet, telecommunication systems, computers, robotics, flexible manufacturing operations have created a great impact on the working style of firms and necessitated the work force to be tech-savvy in order to survive in the job market. Economic, social, political, and physical environmental changes: Economic– Business cycles, inflation, recession, stock market crashSocial– Changing life styles and preferences of customers is the keyPhysical– Consumers, suppliers, employees, union, shareholders and the governmentPolitical– Political decisions affecting the market, pressure, legal hassles:- all these affect the working of a firm. Changes in competition: Global economy has brought big players from countries like USA, Japan, Germany and the like to compete in the same market and successful organizational are those who have adapted to competitive environment. When we talk about organizational change, we emphasize on “PLANNED CHANGE OR DELIBERATE CHANGE” in order to suit ourselves to the changing environment. Otherwise, according to Darwin’s theory of “Survival of the fittest” you will fade away in due course of evolution. This Infographic clearly reveals the fact that “It is not the strongest of the species that survive, nor the most intelligent, but the one most responsive to...








