Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Human Resource, Labor Management, Principles of Management
on Mar 10th, 2014 | 0 comments
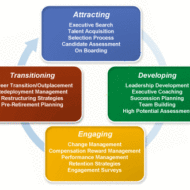
Dimensions of Human Resource Management I would like to brief you on some of the key aspects that mark the paradigm shift in the HR environment towards better management prospects. 1. The Human Resource function has shifted its focus to a much wider canvas that includes Empowerment of EmployeesRestructuring the Organisation and so on. 2. A range of HR sub-systems are involved in Planning The NumbersTypes And Skills Of HrEnsuring Their AvailabilityPlacing In The Right JobPromoting And Nurturing Their Mental HealthHelping Them Develop Special Talent And Skills 3. Human Resource is considered as an “investment” and no more an “expenditure”. Investment in TrainingRe-Training AndContinuous Learning On The Job develops the skills and competences of managers and employees and prove to be an useful investment. 4. The concepts of Learning Organisations AndTeam-Building serves a basis for “Competitive advantage” and “Motivating the employees.” 5. Values that are stressed upon are Co-OperationHarmonisationSynergyTrustBeing Pro-ActiveCollaboration 6. Strategy: VisionMissionObjectivesGoals– How these can be achieved? The techniques that are basically holistic in nature can solve the purpose. Such techniques involve SEWA– Self mastery, Empathy for workers, Worker-directedness and Achievement in performanceABO-Action by Objective Nine Dimensions of an Effective HR Department: What is the reputation of the HR department?What are the criteria (deliverables) that shape HR work?What is the mission or strategy of the capabilities – focused HR department?How is the HR department organised? How does HR facilitate the definition and creation of organisation capabilities?How do we make better HR investment and choices?How do we create HR practices?How does HR go about doing its work? What do HR professionals need to be, know, and do to be effective? Let us make a sincere comparison between the past and the present in terms of HR perspective These techniques produce performers who find their way through any set of given problems, manage themselves and lead the team to a stae of self- realisation. Old model vs New model 1. Job was the basic unit/ Team is the basic unit 2. Relations with environment there handled by the individuals/ Densely networked with environment 3. Information flow was vertical/ now it is vertical, horizontal and holistic 4. Many layers of management / Organisations have become flat 5. Emphasis on structures/ Emphasis on process and literally virtual organisations have evolved 6. Career path upward and linear/ career path lateral and flexible 7. Standardised evaluation and reward system/ Customised evaluation and reward system 8. Ethnocentric/ International 9. Single strong culture/ Multicultural and diversity of viewpoints and...

Posted by Managementguru in Human Resource, Labor Management, Training & Development
on Mar 9th, 2014 | 0 comments
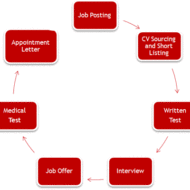
HR Selection Process and Techniques Following the process of recruitment is selection, where the management has to select the right employees at the right time. The intention is to choose appropriate candidates for the unfilled spots and to avoid commitments to those whom the management thinks will not work well. The best qualified individuals from the pool find their place whose qualifications match the job specifications. What is the Selection Process in Human Resource Management? Selection process depends upon the · Size of the company · Nature of the business · Kind and Number of persons to be employed · Government regulations to be followed etc. The process includes 1. Collection of data about the candidate’s qualification 2. Experience 3. Physical and mental ability 4. Nature and Behavior 5. Aptitude and the like Steps in Scientific Selection Process: A. Job Analysis: This is the basic step for finding the right candidate and each organization should lay down job analysis, job description and job specification with clarity in order to lure the right candidates for selection. B. Recruitment: Process of searching for prospective employees and stimulating them to apply for jobs in the organization. C. Application Form: This is also known as the application blank. This facilitates collecting detailed information from the prospective employees regarding their age, gender, family details, qualification, skills, experience, achievements etc. This is widely used to screen employees at the preliminary level. D. Written Examinations: are conducted to gauge the · Mathematical ability · Aptitude · Reasoning · Knowledge in various disciplines · General Knowledge and · English language abilities of the candidates. E. Preliminary Interview: This is suitable to eliminate the undesirable and unsuitable candidates and also to gather personal information from the candidates on a one to one basis. F. Group Discussion: Group discussions help the management to pick out bright candidates from among the group members and also the ability of each individual to adjust to the group. Each group is expected to analyze, interpret and find alternate solutions and select the best solution for a particular case study or subject matter. G. Tests: To further assess the skills of the employees the management conducts different kinds of tests. H. Final Interview: This is the most essential step in the process of selection. The interviewer matches the information obtained about the candidate through the application with that of his own observation and questioning. · Informal · Formal · Planned · Patterned · Non-Directive · Depth · Stress · Group and · Panel interviews are some of the types of interviews conducted in accordance with the job requirement. Also See: Interview Preparation Tips I. Medical Examination: Certain jobs require certain physical qualities like clear vision, perfect hearing, unusual stamina, tolerance of hard working conditions, clear tone etc. J. Reference Checks: The personnel department will engage in checking reference if the candidate passes all the tests and found suitable for the job. What kind of Companies the Employees are Attracted to – Here is an interesting infographic on “How to Attract the Perfect Employee”...

Posted by Managementguru in Human Resource, Training & Development
on Feb 28th, 2014 | 0 comments
Definitions of Human Resource Management: 1. “A series of integrated decisions that govern employer-employee relations. Their quality contributes to the ability of organisations and employees to achieve their objectives.” (Milkovich & Boudreau, 1997). 2. “Concerned with the people dimension to management. Since every organisation comprises people, acquiring their services, developing their skills, motivating them to higher levels of performance and ensuring that they continue at the same level of commitment to the organisation are essential to achieving organisational goal. This is true, regardless of the type of organisation: viz. government, business, education, health, recreation, or social action.” (Decenzo & Robbins, 1989). 3.”The planning, organising directing and controlling of the procurement, development, compensation, integration, and maintenance of human resource to the end those individual, organisational, and social objectives are accomplished.” (Flippo, 1984). 4. “The organisation function that focuses on the effective management, direction, and utilisation of people; both the people who manage produce and market and sell the products and services of an organisation and those who support organisational activities. It deals with the human element in the organisation, people as individuals and groups, their recruitment, selection, assignment, motivation, empowerment, compensation, utilisation, services, training, development, promotion, termination and retirement.”(Tracey,1994 ) Knowledge Workers Human resource management is therefore understood as the all significant art and science of managing people in an organisation. Increasing research output in behavioral sciences, new trends in managing ‘knowledge workers’ and advances in training methodology and practices have led to substantial expansion of the scope of human resource management function in recent years. HRM is not just an arena of personnel administration anymore but rather a central and pervasive general management function involving specialised staff as assistants to main line managers. Managing employee relationships is the role of the Human Resource department Human Resource Management is a process of valuing and developing people at work, this includes: Recruitment and selection Employee communication and engagement (participation) to increase employee retention Training and development Leadership WHAT IS YOUR GREATEST WEAKNESS Labour turnover & staff retention Labour turnover refers to the proportion of a workforce that leave during a period of time (usually one year) Labour turnover = number of staff leaving during the period x 100 average number of staff Staff retention refers to the ability of a firm to keep its workers. The disadvantages of having a large proportion of staff leaving each year include: The cost of recruiting replacement workers The cost of training the new workers Loss of productivity whilst replacements are found Loss of experienced workers Negative impact on reputation WHAT IS YOUR GREATEST STRENGTH Methods to control turnover: 1. Financial methods of motivation Bonuses Profit share Fringe benefits 2. Non financial methods of motivation Employee engagement and empowerment Training and development Promotion opportunities 3. Improved Human Resource Management procedures Four Fundamental Principles of HRM: Human Resource is the organisation’s most important asset; Personnel policies should be directed towards achievement of ENTERPRISE goals and strategic plans; Corporate culture exerts a major influence on achievement of excellence and must therefore be strengthened with consideration of employee welfare. Whilst integration of corporate resources is an important aim of HRM, it must also be recognised that all organisations are ‘pluralist societies’ in which people have differing interests and concerns, which they defend and at the same time function collectively as a cohesive group. →Evolution of...






