Posted by Managementguru in Decision Making, Human Resource, Principles of Management, Project Management, Training & Development
on Mar 19th, 2014 | 0 comments
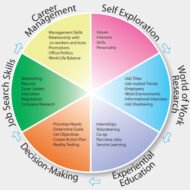
Have you ever thought about how to gain insight into yourself? Well, it is high time, if you really want to make it to the top of your career path and it is supposed to be the best personal strategy. Setting up of long range plans helps you to formulate your career strategies accordingly. To reach the destination, you need to have clear travel plans. Like wise, devising your career plans is inevitable to reach the ultimatum in your work environment. Following is a five step chart to help you create a solid career plan. Self Evaluation What do you enjoy? What are your priorities? Strengths and weaknesses? Name the things you want from a job? Skills Analysis What are your qualifications and experience? What are your key strengths and skills? What are your biggest achievements to date? What are your areas of development/ which area of interest excites you the most? Set your direction The broad industries that really appeal to you. The types of roles that would suit you best. How these options match your personal preferences? Key skills you’ll need to develop. Commit to a time frame Make milestones for the next six, twelve, eighteen months. How will you achieve your training and education goals? How will you gain additional skills and experience needed? How will you expand your network, and by when? Review your career plan Now you know your goals and how to achieve them, monitor your progress at least every six months to stay on track. I reckon that the following tenets infuse some confidence to those who want to achieve: Set your goals highNever settle for lessNever under estimate yourselfYou are born to achieve somethingYou are different from othersYou possess that “in thing” that is going to take you places Career advancement, is something that is not the sole proprietorship of the managerial cadre. It applies to anyone who has the “will” to learn and move forward. One’s attitude towards time, achievement, change, material things, work etc., determines the extent to which he is prepared to pursue his career with a long range plan. managementguru.net Decision Making: Another important aspect of career planning is the tough preposition of decision making. If a qualified and experienced manager is adept in all areas of management, naturally he gets confused as to “which way to go”, when presented with a chance to take up another job, in pursuit of better career prospects such as pay or promotions. People sometimes tend to resist career planning for the fear of making decisions and sometimes due to the fear of failure of achieving goals in the new set up, which might be a big blow to their ego. This dilemma of choosing a goal is commonly noticed in students who want to pursue higher education. Since it involves not only decision making but also determines their capability to be successful in the chosen field of activity. If an individual wants to become a doctor, he or she has to give up to pursue other opportunities, say, to become a lawyer or an engineer. Commitment: Furthermore, career advancement means more involvement and commitment, which makes you a quick learner. And in the process to achieve your goals, you become well versed in the area of specialization, however complex the subject or situation may be. Psychology has its role to play in career planning too. People who are extroverts easily manage to work things up to their advantage, for the simple fact that they socialize well, which is important for a manager to be a good liaison. Time Frame: The planning horizon of your career depends on the time taken to make yourself qualified to suit...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Entrepreneurship, Human Resource, Leadership, Principles of Management, Training & Development
on Mar 18th, 2014 | 0 comments
Executive Development – Options are Wide Open Who is an Executive: A person or group having administrative or managerial authority in an organization. While “executive” and “manager” and “leader” are often used interchangeably, “executive” is commonly used to signify the top 5% to 10% of the organization. Executive Development : aimed at developing the skills and competencies of those that (will) have executive positions in organisation. Capabilities of a Good Manager: A good manager can make an organization grow, survive and shine amidst tough competition, if he is bestowed with corporate competencies such as perseverance, capacity to put in hard work, sense of loyalty and responsibility, all of which may be inherited or acquired qualities. Loyalty stems from internalized morality that may be a result of his value system. Executive success is what the organizations should aim for, and firms should try to figure out the fundamental components that make up the success formula or equation. Road to Self-Development: In less developed countries, employees are more than satisfied if they are provided with a job that offers safety and security. Their thinking is restricted to mere physical and biological comforts and does not go beyond that point, where self development and self-actualization come into the picture. In developed countries, the situation is quite different, where the workers aim for empowerment and look for reasons that motivate them to do a job. Money also has its due role to play, and people whose wages are very meager cannot be expected to aim for empowerment, where their single motive is mere survival. Abraham Maslow’s Point of View: Abraham Maslow puts forward the hierarchical needs theory, arguing that, there are five levels of needs for people in general, right from physiological needs at the bottom of the pyramid and need for self actualization at the top, and safety, security and esteem needs coming in between. He points out that, once a need is satisfied, it ceases to be a motivator. This is so evident in our day to day lives, where wants and needs never cease to exist and once a want is satisfied, human mind wanders to catch hold of another. So, organizations should understand and analyze, what factors best motivate their employees, particularly their managers (who might serve as a source of inspiration to their subordinates).It should be remembered that non-availability of jobs leads to dissatisfaction whereas availability of jobs need not motivate employees. Some factors which have been proven to be real motivators are as following: Recognition Opportunities for self development Additional responsibilities(lateral expansion) Timely rewards(in terms of money and appreciation) Security Inculcating a sense of belongingness Conducive corporate atmosphere Corporate culture Good human relations Economic burden makes people less enthusiastic and anxious in developing countries and this hinders them from delivering to their fullest potential. Also the bureaucratic approach followed by conservative firms, autocratic leadership style and lack of supportive atmosphere make people work like automatons devoid of creativity. Such firms may show good results in terms of productivity initially, but in due course has to pay the price, in terms of absenteeism, high attrition rates and less efficiency. It has been proven that job satisfaction is directly proportional to efficiency. When people find a job tedious and monotonous, they tend to lose interest, which will be evident from their lack lustrous performance. Performance management has its bearing on executive success and by providing with ample scope for career advancement and autonomy; managers prove their mettle even within limited scope of resources. Acceleration of executive change implies the development of the executive mind for performing managerial activities in a better way. Note : A survey of CEOs in Fortune 500 enterprises indicated that executives spend little time with their...

Posted by Managementguru in Change management, Economics, International Business, Principles of Management
on Mar 15th, 2014 | 0 comments
Factors That Influence Global Economy The industrial and business environment of developing countries has been subjected to a sea of changes owing to the economic reforms and policies in the light of globalization, privatization and liberalization. A long term economic vision is necessary for these countries to establish themselves in the global market which facilitates the process of becoming self sufficient in due course of time. Let me present you with a synopsis of how this change can happen and how countries are adapting themselves in lieu of the global economic boom. Multi Brand Retail Markets: Many multinational companies have acquired and are trying to acquire a major part of equity in multibrand retail markets of the host country and sometimes they opt for Joint ventures to factorize the economy of scale which also proves to be a win-win situation for both the parties. Developing countries have altered their economic views on foreign direct investment and are very liberal in their attitude in providing with the necessary licenses. The entry of multinational companies and their potential investment has even altered core sectors like power, oil and telecommunications. Moreover, the benefit of cheap labor, economic subsidies for the start of operations in economically backward regions lures foreign investors. Rush of Entrepreneurship: There is a rush of entrepreneurship in the developing countries, in the form of setting up of small scale industries, cottage industries for which liberal subsidies are provided by the governments to encourage the act of entrepreneurialism. Also people want to go for diversification, mergers and acquisitions in the wake of global competition. Capital Markets’ Role: Capital markets have gained new buoyancy. The rapid growth of stock market and its influence over the international economic scenario have made foreign brokers to keenly follow the market changes for potential investment. The one striking feature of the economy of developing countries is that, it is a self made economy and withstands the pressures of the business cycle, such as recession and inflation, unlike foreign markets that have failed to stabilize their markets owing to what is called sub prime lending, a plan that has failed to achieve the desired economic growth. Instead of making the capital market alive with fresh infusions of funds, it has left many banks and financial institutions bankrupt. Banking Sector: Banking sector has scaled to greater heights and has come under a competitive environment. Deregulation of interest rates to attract potential investors, new technology, products and aggressive marketing usher in new competition; disinvestment of government equity in nationalized banks have made banks to operate as commercial institutions and their services get marketed as branded consumer products. Financial services have emerged as a new business and funding options are aplenty increasing the chances of raising capital. This has evolved as a separate and major source of business fetching revenue to the service providers. Private Sector: Private sector is gaining importance in countries like India, where they have entered all the core industries like oil, mining, telecommunications, road building, railways, ports, civil aviation etc. This serves as a revenue source for the government and this kind of economic restructuring has brought a wave of enthusiasm amongst the potential investors. Imports have become an entrepreneurial activity and are out of the government domain and this has been facilitated by relaxation of licensing hassles. These are some of the recent trends in the developing countries that have captured the interest of multinational...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Entrepreneurship, Human Resource, Leadership, Principles of Management
on Mar 13th, 2014 | 0 comments
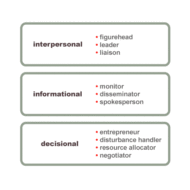
Research on Managerial Roles by Henry Mintzberg and Peter Drucker Henry Mintzberg, the canadian academic observed a few managers and analysed their behaviors and arrived at some conclusions which are listed in the table below. He also identified and attributed ten managerial roles of significance in correlation with the managerial functions. S.NoManagement Functions% of time spent1.Relating to external environment1.82.Planning and setting Objectives19.53.Decision-making6.04.Organising15.05.Leadership and inter-personal role28.46.Communication12.67.Control12.78.Staffing4.1 This table very clearly explains the role of a manager as a leader and the extent of influence he exerts on his sub-ordinates. Proper planning and goal-setting are the key contributors for the successful functioning of a firm. LEADER VS. MANAGER Coming to the managerial roles they can be classified as, 1. Interpersonal roles 2. Informational roles 3. Decisional roles Inter-Personal Roles: Figurehead role– The function is more of a ceremonial nature, like attending the family functions of employees, greeting visitors and a manager performs the symbolic duties of a head of the organization.Leader– He has to plan the HR requirements and motivates the staff to perform well. “Managers are people who do things right; leaders are people who do the right thing.” Remember a manager has to be a leader whereas it is not so in the case of a leader.Liaison– The manager acts as a link between the organization and the external environment to build image and rapport. Informational Roles: Monitor– The manager has to update himself with the current scenario in order to utilize the information for organizing and prompt decision-making.Disseminator– The manager has to communicate and distribute information to his subordinates to effectively accomplish the enterprise objectives.Spokesperson– Efficiently has to communicate the company’s policies to prospective clients and others. Decisional Roles: Entrepreneur– He has to be innovative by adapting to the changes in the environment. He has to be adventurous, persistent and strategic during tough times.Disturbance handler– He has to find appropriate solutions to problemsResource allocator– He has to apportion and allocate resources properly besides delegating authority to the work forceNegotiator– He has to negotiate resources outside and conflicts inside the organization. MANAGERIAL DIMENSIONS Managing: Science or Art? One perspective is Managing, like all other disciplines- whether medicine, music composing or even cricket is an art. It is “know-how.” Still managers can use the organized knowledge about management to perform better. So let us put it this way, Managing as practice is an art; the organized knowledge underlying the practice may be referred to as a science. Let them be complementary to each other and be present in peaceful co-existence. Drucker “ON MANAGERIAL FUNCTIONS ” – A manager has to look after The specific purpose and mission of a firmIncrease productivity by making the employees more productiveConsiderate about social impacts and social responsibilities In his view, the areas a manager has to focus and concentrate are 1. Market standing 2. Innovation 3. Productivity 4. Financial and Physical resources 5. Profitability 6. Manager performance and development 7. Worker performance and attitude 8. Public responsibility He says that business has only two functions- marketing and innovation. While others were concentrating on products and commodities, he concentrated on people and their performance. His “management by objectives- MBO ” became a very popular concept though it faced criticism. MBO according to Drucker is a philosophy that rests on a concept of human action, behaviour and motivation. It sets personal goals (both shortterm and longterm) to be achieved by each individual working for the organization and coverts them into challenges to be accomplished, thus motivating the individuals. The Effective Manager The effective manager is a situational manager who evaluates each approach in the light of circumstances and selects the one that most effectively and efficiently achieve individual...

Posted by Managementguru in Economics, Financial Management, International Business, Marketing, Project Management
on Mar 11th, 2014 | 0 comments

What is Trade? Trade is the exchange of commodity and services. International trade represents business transactions taking place at the global level, and it is fundamentally different from domestic trade. Trade at international level demands huge investments, network of franchisees and proficient people to run the show. Many corporate giants are trying to capture Asian markets, especially Indian market, which has become the industrial hub for such economic activities. Economic liberalization has been the focus of many developing countries for the past two decades and this has allowed multinational companies with huge investment potential to enrich the weaker economies. What is International Trade? International trade tries to generate more foreign exchange, which is always good for the economy. Say, if a country has rich resources of petroleum, naturally it will try to sell the surplus to countries not endowed with such natural resources. That is why Middle East nations are prosperous and economically independent. The diversity in productive possibilities in different countries is due to the presence of limited natural resources. When a country gets a head start in a particular product, it can become the high volume, low cost producer. The economies of scale give it a significant advantage over other countries, which find it cheaper to buy from the leading producers than to manufacture the product themselves. Barriers for Effective Trade Every nation must try to specialize in the production and export of those commodities, which are available in plenty and must import such products in the production of which they have a resource deficiency. It should be remembered that there are severe man made barriers in international trade such as, export duties, quotas, exchange restrictions etc.,that hinder the free movement of products. International Trade and Finance Nevertheless, it is not also possible for a country to produce domestically every kind of product. In spite of all these restraining factors, global trade is thriving, thanks to the advanced technological aspects introduced in communication and faster means of transportation. Distance is no more a constraint and the world has become one small global village. Foreign Exchange Issues All domestic transactions, say in a country like India take place in rupees, which is the legal tender in the country. However, in its trade with other countries like USA, Germany, Japan, France and Britain, the payments have to be made in terms of dollars, marks, yens, francs and pound sterling respectively. The mechanism through which payments are effected between two countries having different currency systems is called foreign exchange. It may be also defined as the exchange of money or credit in one country for money or credit in another. Foreign exchange rates can affect relative prices and net exports. A rise in the a nation’s foreign exchange will depress that nation’s net exports and output, while a fall in the foreign exchange rate will increase net exports and output. Because of the significant impact of exchange rates on national economies, countries have entered into agreements on international monetary...










