Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Principles of Management
on Feb 25th, 2014 | 0 comments

Evolution of Management Theory -II MANAGEMENT PROCESS SCHOOL Henri Fayol (1841-1925) Henri Fayol has propagated 14 principles on management which are very popular. 1. Division of labor: He insists on a high degree of specialization in order to improve efficiency. Both managerial and technical works are amenable to specialization which leads to better work with the same efforts. 2. Authority and Responsibility: Authority can be classified into Official and Personal authority, the former needed by a manager to extract work from the subordinates and the latter emanating from the manager’s own intelligence, integrity, experience, personality, knowledge and skills. Responsibility comes along with authority; one who has the authority should also be able to take up responsibility. 3. Discipline: Obedience, diligence, correct attitude and outward mark of respect is the essence of discipline which exists as an unwritten agreement between the management and its employees 4. Unity of Command: A subordinate must receive orders and instructions from one superior only. 5. Unity of Direction: Activities of similar nature should be grouped under one superior so that the efforts could be streamlined towards the common goal. 6. Sub-ordination of individual’s interest to the Common Goal: The personal interests of an individual (like money, recognition etc.) should not be placed before the goal of the organization, which is maximizing production. 7. Remuneration: Fair and equitable remuneration should be provided to employees to ensure better production and satisfaction. 8. Centralization: The concentration and dispersal of authority must be balanced in an organization 9. Scalar Chain: The authority chain from top to bottom should be followed at all times for the purpose of effective communication. 10. Order: Human and material resources should be co-ordinated so as to be in the required place at the required time. 11. Equity: Fairplay, justice and friendliness is what the employees expect of the organization. 12. Stability of Tenure of Personnel: Too much of Job turn over and rotation affect the work in progress and destruct the stability of the work units 13. Initiative: Subordinates must be encouraged to participate in the decision making process to show their initiative. 14. Espirit De Corps: “In union there is strength and so is team work.” Team spirit and a sense of unity and togetherness should be fostered and administered in an organization. Join Over 290+ Other Entrepreneurs Who Are Using This Course. Become An Outsourcing Master In 30 Minutes James D.Mooney and Allen C.Reilay The Line and the Staff Principle: According to this principle, the line authorities get things done while it recognizes the role of staff authority who are experts in providing guidance and advice. The emphasis is on, · Hierarchial structure · Clear decision · Delegation of Authority and Responsibility · Specialization of Tasks · Co-ordination of activities and · Utilization of staff experts A short course designed to help managers select the right person to join their team! Staff Recruitment THE HUMAN RELATIONS SCHOOL The human behaviorists believed in COLLABORATIVE management which is possible when managers are capable of harmonizing the efforts of individuals at all levels of the organization. This concept draws heavily from psychology and social psychology. · Motivation · Leadership · Communication · Training · Participative management · Group dynamics are assigned importance The important contributors are Elton Mayo, Roethlisberger, Mary Parker Follet, Chester I Bernard, Abraham Maslow and Douglas McGregar. THE EMPIRICAL SCHOOL Case study analogy is the best way to understand management is the idea behind this school of thought. The mistakes of managers are converted into rich experiences over a period of time and the findings are transferred to the practitioners in the management profession. The contributors are, · American Management Association · Harvard Business School · Ernest Dale. However, critics feel that this may not be suitable when it...

Posted by Managementguru in Economics
on Feb 17th, 2014 | 0 comments
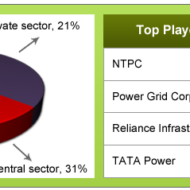
Significance of Privatization Privatization that has gathered momentum since around the 1980’s has become the hallmark of the new wave of economic reforms sweeping across the world. It refers to the transfer of ownership or management of an enterprise from the hands of the public sector to private sector. It also means the withdrawal of the state from an industry or sector, partially or fully. Privatization marks a change from dogmatism to pragmatism and amounts to a reversal of policy. It is evident that the economic growth rate has multiplied ever since privatization has come into existence. What is Privatization? 1. The transfer of ownership of property or businesses from a government to a privately owned entity. 2. The transition from a publicly traded and owned company to a company which is privately owned and no longer trades publicly on a stock exchange. Performance of Public Sector: The performance of state owned enterprises in many countries have, by and large been far from satisfactory. This may be attributed to the prevalence of bureaucracy and red tapism in most of the public sector administration. They have often put large burdens on public budgets and external debt. Economic inefficiencies in the production activities with high costs of production, inability to innovate and costly delays in delivery of the goods produced are some of the shortcomings of the public sector. There is also ineffectiveness in the provision of goods and services such as failure to meet intended objectives, diversion of benefits to elite groups, and political interference in the management of enterprises. The relationship between the management and the labor unions is strained owing to the expansion of bureaucracy. Why Privatization? These problems have led many governments to undertake programmes of public sector reform. One Such reform is privatization of publicly managed activities to discard the inefficiencies and improve the economic growth rate. For privatization to succeed: Privatization cannot be sustained unless the political leadership is committed to and unless it reflects a shift in the preferences of the public arising out of dissatisfaction with the performance of other alternatives. Now-a-days, private sector enterprises have started dominating even core industries like petroleum, power and communication under the leadership of visionaries who may be the heads of the states or owners of such private organizations. Public services to be provided by the private sector must be specific or have a measurable outcome. Consumers should be able to link the benefits they receive from a service to the costs they pay for it. Since they will then shop more wisely for different services. Privately provided services should be less susceptible to fraud than government services if they are to be effective. Equity is an important consideration. Privatizing the state owned enterprises reduces corruption and the benefit goes to the society. The process encourages entrepreneurship and leads to intense development of capital market. Governments usually want to sell the least profitable enterprises, those that the private sector is not willing to buy at a price acceptable to the Government. The Government may even fear that if it gives a free rein to the private sector management, its power might be at stakes. All said and done most of the governments view privatization as an important strategy of economic...




