Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Financial Management, Marketing, Strategy
on Jul 15th, 2014 | 0 comments
What is Financial Capability? The availability, usage and management of funds have a bearing on the financial capability of an organization and ability to implement its strategies. A financial manager has to pool, deploy and allocate financial resources taking into consideration the capital or long term investments, working capital or short-term liabilities and repayment capacities. Factors that influence financial capability of an organization: 1. Factors related to source of funds: Capital structure, procurement of capital, controllership, financing pattern, working capital availability, borrowing, capital and credit availability, reserves and surplus, and relationship with lenders, banks and financial institutions. 2. Factors related to usage of funds: Capital investment, fixed asset acquisition, current assets, loans and advances, dividend distribution and relationship with shareholders. 3. Factors related to #management of funds: Financial accounting and budgeting systems, management control system, state of financial health, cash, inflation, return and risk management, cost reduction and control, and tax planning and advantages. Typical Strengths that Support Financial Capability: • Access to financial resources • Amicable relationship with financial institutions • High level of credit worthiness • Efficient capital budgeting system • Low cost of capital as compared to competitors • High level of shareholder’s confidence • Effective management control system • Tax benefits due to various government policies The examples given below show how strengths and weakness affect the financial capability of organizations: • A company faced many problems due to instability in the top management, an unfavorable public image, unfavorable government relations etc., but it had inherent strengths like a huge amount- to the tune of Rs.1000 crores invested in fixed assets which the company used for funding its diversification plans. Here we see one particular strength over-shadowing all other weaknesses which can be rectified in due course of time. • A scooter company had collected nearly Rs.1150 crores as advance for booking of scooters, but within five years, its cash position deteriorated owing to sudden and unforeseen cancellation of bookings and withdrawal of deposits, resulting in a huge interest burden. Had the company had a strong financial backup, it would have survived the trouble. Matching strengths and weaknesses with opportunities and threats requires that a firm should direct its strengths towards exploiting opportunities and blocking threats while minimizing exposure of its weaknesses at the same...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Financial Accounting, Financial Management, Principles of Management
on Apr 10th, 2014 | 0 comments
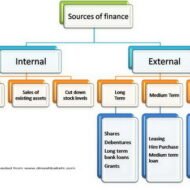
Unsecured and Secured Short Term Sources Unsecured Non-Bank Short Term Sources Commercial Paper: Short-term, unsecured promissory notes, generally issued by large corporations, with maturities of a few days to 270 days. Usually issued in multiples of $100,000 or more. Commercial paper market is composed of the (1) dealer and (2) direct-placement markets. Advantage: Cheaper than a short-term business loan from a commercial bank. Dealers require a line of credit to ensure that the commercial paper is paid off. Private Loans: A short term unsecured loan may be taken from a wealthy shareholder, a major supplier, or other parties interested in assisting the firm through a short term difficulty. Cash Advances for Customers: A customer may pay for all or a portion of future purchases before receiving the goods. This aids the firm to purchase raw materials and produce the final goods. This form of financing is a special arrangement for expensive or custom-made items that would strain the financial resources of the manufacturing company. Secured Short-term Sources: Security (collateral) — Asset (s) is pledged by a borrower to ensure repayment of a loan. If the borrower defaults, the lender may sell the security to pay off the loan. Collateral value depends on: Marketability Life Riskiness Types of Inventory Backed Loans: Field Warehouse Receipt — A receipt for goods segregated and stored on the borrower’s premises (but under the control of an independent warehousing company) that a lender holds as collateral for a loan. Terminal Warehouse Receipt — A receipt for the deposit of goods in a public warehouse that a lender holds as collateral for a loan. Trust Receipt – This loan is secured by specific and easily identified collateral that remains in the control or physical possession of the borrower. A security device acknowledging that the borrower holds specifically identified inventory and proceeds from its sale in trust for the lender. Example: When automobile dealers use this kind of financing for the cars in their showrooms or in stock, it is called floor planning. As implied by the name, this kind of loan requires a considerable degree of trust in the honesty and integrity of the borrower. Once the inventory is sold or the receivable is collected, payment must be remitted to the lender. If there is a default, the loan is said to be secured by bogus collateral. These loans are common when the collateral is easily identified by description or serial number and then each item of collateral has relatively large dollar value. Floating Lien — A general, or blanket, lien against a group of assets, such as inventory or receivables, without the assets being specifically identified Chattel Mortgage — A lien on specifically identified personal property (assets other than real estate) backing a loan. Financial Institutions: Primary sources of secured short term financing are banks and financial institutions, including insurance companies, finance companies, and the financial subsidiaries of major corporations. The best mix of short-term financing depends on: Cost of the financing method Availability of funds Timing Flexibility Degree to which the assets are encumbered It is always better to go for bank loans or loans from established and long standing private institutions because there is a leverage for the debtors to sit for discussions to sort out issued in case of defaults. All banks in India are trying to close accounts labeled under NPA- Non Performing assets either by recovering the money through one time settlement (OTS) or by auctioning the collaterals pledged during the time of loan sanctioning. If you happen to take loans from individuals or third-parties, you cannot enjoy this comfort or breather. Some Finance Quotes and Sayings for You: A...

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Financial Accounting
on Feb 21st, 2014 | 0 comments
Characteristics and Objectives of Accounting What is Accounting: According to American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA), “Accounting is the art of recording, classifying and summarizing in a significant manner and in terms of money transactions and events which are, in part at least, of a financial character and interpreting the results thereof.” American Accounting Association (AAA) has defined accounting as “the process of identifying, measuring and communicating economic information to permit informed judgements and decisions by users of the information.” Characteristics of Accounting: i. Accounting is the art of recording and classifying different business transactions. ii. The business transactions may be completely or partially of financial nature. iii. Generally the business transactions are described in monetary terms. iv. In accounting process, the business transactions are summarized and analyzed so as to arrive at a meaningful interpretation. v. The analysis and interpretations thus obtained are communicated to those who are responsible to take certain decisions to determine the future course of business. The Small Biz Doers’ Guide to Small Biz Accounting Objectives of accounting: a. To record the business transactions in a systematic manner. b. To determine the gross profit and net profit earned by a firm during a specific period. c. To know the financial position of a firm at the close of the financial year by way of preparing the balance sheet d. To facilitate management control. e. To assess the taxable income and the sales tax liability. f. To provide requisite information to different parties, i.e., owners, creditors, employees, management, Government, investors, financial institutions, banks etc. ...






