Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Operations Management
on Feb 18th, 2015 | 0 comments
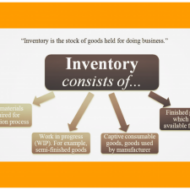
Inventory Control Learning Objective: To know the meaning, types and functions of inventories Meaning of Inventory: The word inventory refers to any kind of resource having economic value and is maintained to fulfil the present and future needs of an organization. Fred Hansman has defined Inventory as “An idle resource of any kind provided such a resource has economic value”. Such resources may be classified into three categories: A. Physical resources such as raw materials, semi-finished goods, finished goods, spare parts, lubricants etc. B. Human resources such as unused labor (man power) and C. Finance resources such as working capital etc. Inventory of resources is held to provide desirable service to customers and to achieve sales turnover target. At the same time holding big inventory severely affects the cash flow and working capital of an organization if the production vs demand cycle is not stream-lined. Because inventory often represents more than 25% of total assets and therefore it becomes very essential to maintain an optimal level of inventory in each resource so that the total inventory cost is near its minimum. Functions of Inventory: Inventory serves several important functions that add flexibility to the operations of a firm. Provides stock of goods to meet the anticipated demand of customers. In the case of consumer goods with a seasonal demand, the establishment of inventories in distribution and production warehouses also ensures that production can run continuously at full capacity despite swings in seasonal demand. De-Coupling function: The down time in one manufacturing stage should not affect the whole manufacturing process and this vital purpose is solved by holding inventory which acts as a buffer between successful stages of production. Quantity Discounts: Many suppliers offer QD’s for large orders of inventory. Procurement warehouses can result from a company’s desire to get volume discounts from a supplier or more favorable conditions from a carrier. Price speculation – Inventory also helps to hedge against inflation and price changes. Inventories of procurement and distribution warehouses are increased if the price of a good is expected to rise. In such a situation, the purchasing company aims to amass the good at the current low price. The supplier may speculate that supply shortages will drive the prices higher, and he uses the warehouse to store the good. Shortages can occur regularly due to irregular supply of raw materials, weather, quality problems or improper deliveries. Inventory shall act as “safety stock’ – extra goods on hand which reduce the risk of stock-outs. Helps to permit operations to continue smoothly with the use of “work in process” inventory. This is because it takes time to make goods and because a pipeline inventory is stocked through-out the process. JUST IN TIME MANUFACTURING CONCEPT Types of Inventory: Inventory can be classified according to the basis of type of material maintained in the firms and also on the basis of the functions they tend to perform in an organization. On the basis of type of material, the firms maintain four types of inventories: Raw material inventory Work in process inventory Maintenance/operating supply (MRO) inventory and Finished goods inventory Raw material inventory is the one which has been purchased and yet to be processed. The work in process material has undergone some change but is not completed. Work in process exists because of the time it takes for a product to be made which is called the “CYCLE TIME.” MRO inventory is devoted to maintenance/repair/operating supplies. They exist because the need and timing for maintenance and repair of some equipment are unknown. Products completed and waiting for shipment are called finished goods inventory. Finished goods may be inventoried because customer demand for...

Posted by Managementguru in Operations Management, Project Management
on Feb 24th, 2014 | 0 comments

Materials Handling Minimize Movement and Maximize Productivity Manufacturing organizations handle many types of materials in their production environment. Raw materials, materials-in-progress, finished goods, accessories, components, packaging materials, maintenance and repair supplies, scrap and many more must be handled in an efficient manner to make the operations cost-effective and to avoid wastage. The principle behind material handling process is said to be “no handling”, which is not practicable in reality. So it would be appropriate to say, that the objective of materials handling would be, to reduce the number of handlings as well as reducing the distances through which the materials are handled. Why efficient materials handling is inevitable in a manufacturing set-up? The movement of materials from the receiving area to the shipping area through the production line does not add value to the product but only to the cost. Further, plant layout and materials handling are complementary to each other. A production facility must incorporate a good plant layout that enhances the efficiency of movement of materials with ease and should deliver maximum productivity. Principles for Efficient Materials Handling There are certain principles that serve as a guide for efficient materials handling. These provide a framework for selecting specific materials handling equipments that form the core of the production system. Eliminate handling-If not, reduce the distance travelled by the materials Keep moving-If not, reduce the time spent at crucial points Simple patterns of material flow is appreciated-If not, reduce back tracking, cross overs, congestion Carry pay loads Carry full loads Use reliable and inexpensive source of power Materials handling should be considered in the light of movement of men, machines, tools and information. It also depends on the type of product manufactured, quantity, value and size of the organization. Cost effectiveness can be achieved if the firm is able to reduce the manufacturing cycle time through faster movement of materials and thus work-in-progress inventory costs can also be controlled and reduced. Design of the plant layout that facilitates sequential flow of materials through the production facility, improved working conditions, safety in the movement of materials, contribution to better quality by avoiding damage to the materials due to inefficient handling and workers being appraised about the importance of smooth materials handling result in higher productivity at lower manufacturing cost. Interested in being served food by Robots! Factors to considered while deciding on material handling equipments: Adaptability, flexibility, load capacity, power, speed, nature of supervision required, space requirements, ease of maintenance, environment friendliness and cost are some of the factors to be taken into consideration while deciding on the type of material handling equipments. Also the capabilities of manpower to operate the equipment and safety of personnel cannot be overlooked. It is important to select and design, materials handling system that are expensive to purchase and operate. For instance, if overhead cranes are to be used, the structure of the building should be strong enough to support the installation. Spacious aisles are mandatory if the loads are heavy and transported across the shop floors. Equipments used: Elevators, hoists, industrial trucks like fork-lift trucks, pallet trucks, pipelines, automatic transfer devices, automated guided vehicles, and industrial robots are some of the handling equipments that have found their ideal place in this process. Materials handling activity should be evaluated like any other activity to gauge its effectiveness. The focus should be on the manufacturing cycle efficiency, equipment utilization, percentage of time lost, total number of moves and material handling costs as percentage of manufacturing...




