Posted by Managementguru in Human Resource, Motivation, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Training & Development
on Mar 18th, 2014 | 0 comments
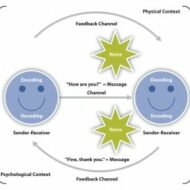
Promoting Effective Communication in the Work Place A purpose or an idea to be conveyed is needed for communication to happen. The question is how well or how successful you are in transmitting the message (mind you! without transforming it) to the receiver in the proposed meaning, whatever the channel might be! Communication must serve the following functions… Effective Control Motivational expression Information Fundamentally communication helps in controlling the behavior of the members of an organization in several ways. Either formal or informal, it controls the activities of the employees by prescribing certain procedures of communication to be followed when there is a grievance or a difficulty regarding his/her job, the work situation etc. Communication provides Vital Information: Communication also motivates people by clarifying what needs to be done, how to be done and how they are performing and what can be done to improve their performance. Most important function is that communication provides vital information that is crucial for members at all spans or levels to make effective decisions. The feelings of members are also articulated as grapevine in an organization, and in a way it serves as an outlet for their emotional expression. Grapevines: Grapevines are always not harmful, they might even give you information about the pulse of people working for you and if you are really sharp, “you can work it out to your advantage. Communication is always referred to as “oxygen”, we can feel only when it breaks down. Communication plays an important role in managerial and organizational effectiveness. Nevertheless, on the other side it can be the root cause of all the problems in your organization. This excellent infographic on Business Etiquette and Body Language Blunders clearly indicates how body language and gestures influence communication to a greater level. Source: www.thewebsitegroup.uk Effective Communication: In general, effective communication is the prerequisite for any healthy organization and the attainment of its standard objectives. Most of us are in fact aware of how our vocabulary has been modified to reflect political correctness. For instance we have replaced certain words like handicapped, blind and elderly by physically challenged, visually impaired and senior. One must be sensitive to others feelings. Words are the primary means by which people communicate; so due importance must be given for politically correct words both in the society at a larger level and in firms at the micro level. Increasingly, I find people like being addressed by their designation capacities. Even people might get offended if you call them by their first names as it is regarded to be disrespectful. But I think it is always better to address a person giving due respect to his position if you are reporting to him. That way there is no scope for conflicts and strained relationships. Western countries are more modern in their outlook and have a broader perspective on human interactions than the east. Gestures: Words mean different things to different people. In organizations, people of different background work together, so they have their own language of expressing their opinions and ideas. So it calls for a uniformity of language that is well understood and appreciated by all. Gestures also play their part in communicating ideas. So self controlled expressions, proper behavior are also necessary that completes a communication process. Ultimately proper communication leads to… Satisfied employees Effective feedback Organisational efficiency Freedom for suggesting ideas Enhanced interpersonal relationships Closely knit organisational network Encouraging trust and openness. Communication is an on-going process and the purpose is “not to dictate but to make the employees understand the big picture” as to how the process imparts success and viability to the...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 3rd, 2014 | 0 comments
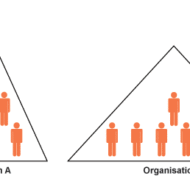
Levels of Organization An organization is a network consisting of people interacting to accomplish the enterprise objectives. The inter relationship is always complex as groups tend to develop conflicts and difference of opinion among themselves and in between. Hence the structure of an organization should be designed to clarify who is to do what task and who is responsible for what results and to furnish decision-making devoid of uncertainty. Organization implies to Recognizing and classifying the required activities Grouping of activities in order to achieve the objectives Appointing a manager and assigning him with the necessary authority to lead each group The provision for co-ordination vertically and horizontally “Organization is the establishment of authority and relationships with provision for coordination between them, both vertically and horizontally in the enterprise structure,” According to Koontz. FORMAL ORGANISATION It implies a formalized intentional structure of roles or positions. Formal organization must be flexible. The formal structure is laid down by the top management The levels are designed on the basis of specialization Purely task oriented and not people oriented Rules are very stringent and everyone is expected to follow them without fail INFORMAL ORGANISATION A network of personal and social relations arising spontaneously as people associate with one another and not restricted by the formal rules or structure. One important aspect of organizing is the establishment of department. Department designates a distinct area, division, or branch of an organization over which a manager has authority for the performance of specified activities. Spontaneous in nature More people oriented Based on religion, culture, common problems faced by the workforce etc., Membership is voluntary and the same person can be a member of many groups. ORGANISATION LEVELS AND SPAN OF MANAGEMENT Why there is a need to organize? To co-ordinate the activities of the people involved in the organization’s functions for which there needs to be certain levels established to facilitate the co-operation effective. There are two types of spans, 1. Wide span 2. Narrow span Pic Courtesy: LumenLearning WIDE SPAN: Wide span of management has fewer organizational levels with more number of sub-ordinates reporting to a superior. Though it proves advantageous for the superior as delegation becomes part of the process and hence work is shared, care must be taken in selecting the right people for completion of tasks and clear policies must be made to avoid confusion. There is this tendency of overloaded superiors to become decision bottlenecks and there exists the danger of superior’s loss of control too. This kind of management needs exceptionally qualified managers to lead the respective groups. NARROW SPAN: Narrow span of management involves many organizational levels with fewer number of employees reporting to a superior. This facilitates close supervision, close control and fast communication between superiors and subordinates. On the contrary, superiors tend to get too involved in subordinates’ work and this kind of management incurs higher costs due to many levels in the organization and there is excessive distance between the lowest and top most levels. FACTORS DETERMINING AN EFFECTIVE SPAN: 1. Training of Subordinates: Well trained subordinates save much time and energy of the superiors and training has to be a continuous process as the technological policies and procedures are subjected to change periodically. 2. Clarity of Delegation of Authority: Clarity implies direction and guidance from the manager’s end to the subordinate. A manager has the responsibility of clearly explaining the task and the methods involved to complete the task in a suitable manner to his subordinates. In cases of machine handling, “On the Job Training” becomes inevitable. If not, the work will not be completed as per the schedule due to lack of clarity. 3. Clarity of Plans: In a production environment, the workers have to be...

Posted by Managementguru in Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Feb 22nd, 2014 | 0 comments
Organizational change is concerned with making things different and change agent is a person or group of persons who act as catalysts to bring about change. Say, managers and outside expert consultants can be called as change agents. What is Organizational Change? This is how you have to Strategise in order to Win Organizational development refers to the overall development of an organization in terms of improving the ability of that organization in tandem with the needs of the external environment and involves a system oriented approach to change. Recommended: Resourceful Guide on Organizational Development from Maryville University titled ” Organizational Development Guide: Definition, Process & Development Models “ Organizational change: All the elements of a social system like people, formal organization, informal organization, operational environment, communication, decision making and patterns of co-operation are bound to change when there is change in the external environment but this gives rise to a positive pressure which acts like a self-correcting mechanism to modify and set right the bottle-necks or loop-holes in the working system. Causes For Change Work force: The increasing awareness and educational qualification among the workforce is responsible for the attitude change. You can expect loyalty from workers above fifty but not workers who fall under the age category thirty. This is because their loyalty is oriented towards their career and not to the employer. Technology change: Internet, telecommunication systems, computers, robotics, flexible manufacturing operations have created a great impact on the working style of firms and necessitated the work force to be tech-savvy in order to survive in the job market. Economic, social, political, and physical environmental changes: Economic– Business cycles, inflation, recession, stock market crashSocial– Changing life styles and preferences of customers is the keyPhysical– Consumers, suppliers, employees, union, shareholders and the governmentPolitical– Political decisions affecting the market, pressure, legal hassles:- all these affect the working of a firm. Changes in competition: Global economy has brought big players from countries like USA, Japan, Germany and the like to compete in the same market and successful organizational are those who have adapted to competitive environment. When we talk about organizational change, we emphasize on “PLANNED CHANGE OR DELIBERATE CHANGE” in order to suit ourselves to the changing environment. Otherwise, according to Darwin’s theory of “Survival of the fittest” you will fade away in due course of evolution. This Infographic clearly reveals the fact that “It is not the strongest of the species that survive, nor the most intelligent, but the one most responsive to...






