Posted by Managementguru in Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Strategy, Training & Development
on Mar 31st, 2014 | 0 comments
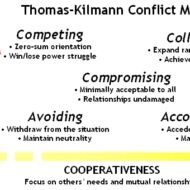
Conflict is a Part of Organizational Life Managers need to be alert to the presence of conflicts. Their focus should be oriented towards the goals to be accomplished. If there is a conflict, they should aim to resolve it smoothly by not over-reacting to the situation. They should take the help of persons who can best settle the issue, be ready to bargain and not issue orders. Their concentration should be on the problem and not on persons. True to the saying – Am I not destroying my enemies when I make friends of them?- President Abraham Lincoln Conflicts are Functional and Healthy: Conflicts in organisations are generally considered to be dysfunctional. On the contrary, many top executives of big companies view conflicts, as a means, to sufficiently analyse a problem and postpone decision making until all critical aspects of an issue are evaluated properly. Conflicts may occur within the individual, between individuals, between the individual and the group or between groups. There are many potential sources of conflict in today’s corporate organisations. The complex inter personal relationships and high degree of interdependence causes friction. Difference of Opinion: When many people must work together, conflict is inevitable, as it is human nature to clash and complain. Conflict is the personal divergence of interests between groups or individuals. The need to share scarce resources, difference in goals between organisational units, difference in values, attitudes and perception, ambiguously defined work responsibilities are some of the major sources of conflict. Functional Conflicts: Functional conflicts support the goals of a group, improve its performance and are constructive in nature. Dysfunctional conflicts hinder the performance of a group and are destructive in nature. It has not been precisely defined, as to what criterion demarcates functional from the dysfunctional. It is only the group’s performance and the delivered result or outcome that determines the nature of the conflict. Conflicts, irrespective of their type can bring these benefits to the firm: Bring hidden issues to the surface. Encourage creativity and innovation. Improves communication and make changes more acceptable. Increases group cohesion. Strategies to Resolve Conflicts: So, what kind of strategy do you think best suits in resolving conflicts? Avoiding or smoothing conflicts may be a temporary measure, only to bounce back in full force. Forcing might create undesirable consequences. The only option left is to confront the situation, face-to-face meeting of the conflicting parties for the purpose of identifying the problem and resolving it through an open discussion. Make Structural Changes to Lessen Conflicts: By making structural changes, conflicts can be managed. The objectives of a group are modified and then integrated to suit the purpose. Also changes in the structure of the organization, that is, clarification of authority-responsibility relationship, improving the working atmosphere, ambience and work locations help in resolving conflicts. Proper Communication: Lack of proper communication, ego clashes between the people in line and staff positions, a superior’s autocratic leadership style, differing educational backgrounds, lack of co-ordination between inter-departments are all rich sources of conflict. These can be resolved with the right kind of attitudinal approach and an open mind from the management’s...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Human Resource, Motivation, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 10th, 2014 | 0 comments

Employee Morale – Role and Effect What is Morale? Morale is a word that conveys different meaning to different people. It might imply the following meanings: 1. Mental Attitude or Mind set from a psychologist’s perspective 2. A feeling of togetherness from an individual’s point of view 3. Group consent in terms of a business environment etc. Morale can be defined as ” an attitude of mind which conditions how well or how badly duties are performed”- W.H.Walley It can also be defined as ” the collective attitudes of workers towards one another, the employer, the management, or their work”-J.C.Denyen Morale is ” the capacity of group of people to pull together persistently and consistently in pursuit of a common purpose”-Dr.Deighton Morale is thus the undercurrent in an organisation that determines the performance levels of the employees as it dictates employees’ enthusiasm, voluntary conformance with regulations and orders and willingness to co-operate with fellow workers to accomplish the enterprise objectives. Poor morale is evident from in-subordination, discouragement and dislike of job, company and associates. Nature of Morale What it is? : Emotional by nature , a state of well- being and an attitude of mind. What it does? : Directly related to quality of work, enthusiasm, motivation, productivity, discipline, co-operation and initiative. Where it resides? : In the minds, attitudes and emotions of employees as individuals and as groups. Whom it affects? : Employees and executives during their interaction and ultimately the customers and the community. What it affects?: Willingness to work and placing the enterprise objective behind self interest. To summarise, the ill effects of Bad Morale would be Reduced productivityIncreased absenteeismAntagonism towards managementToo much of complaints and grievancesIncreased employee turn-overFriction between employeesAlcoholismAccidentsIncreased lethargy In contrary High Morale leads to Willing co-operation towards enterprise objectivesLoyalty to the managementGood behaviour in conformance with the rules and regulationsStrong and coherent groups leading to organisational staminaPrioritising jobs and placing self interest behind organisational objectivesIncreased sense of participationPride in organisation Picture Courtesy: extramadness.com Ways to Improve Employee Morale From the workers’ point of view: Fair compensation and bonusSatisfactory working conditions conforming to safety and securityTreated with dignityEfficient and amiable leadershipScope for expressing their views for improvementAcceptable working hoursEnsuring economic security From the management’s view point Co-operation from the employeesStability of tenureIncreased productivityLow cost per unitLoyalty of the workers Is it possible to measure Employee Morale? Level of productivity: When the morale is low due to different reasons, higher is the chance of absenteeism, accidents and grievances since the employees try to overlook their responsibilities towards the organisation. Therefore it is the responsibility of the management to settle and score issues relating to employees or unions then and there to avoid those issues blowing out of proportion. Morale Surveys These are generally conducted by individual organisations to find out if the employees are satisfied with their job and task and how they feel about it. This is considered to be a fairly important measure to gauge the kind of relationship the employees have with the management. Surveys also indicate whether the channel of communication is open between the superiors and sub-ordinates and serves as an emotional release for the workers to express their real feelings. Types of Morale Surveys: Objective Surveys: Objective type of questions are given to the employees for answering but the flaw is that, the management representative writes the answers and this does not give a chance for the workers to express their feelings. Descriptive Surveys: Here the employees write their answers to queries asked which are more descriptive in nature and reflects the actual feelings of each individual. Projective Surveys: Sometimes psychological tests are conducted to bring out the hidden feelings from tight lipped employees or who fear the management. The management must be aware of the following morale...




