Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Financial Accounting, Financial Management, Principles of Management
on Apr 10th, 2014 | 0 comments
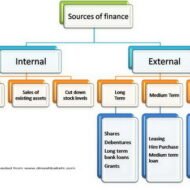
Unsecured and Secured Short Term Sources Unsecured Non-Bank Short Term Sources Commercial Paper: Short-term, unsecured promissory notes, generally issued by large corporations, with maturities of a few days to 270 days. Usually issued in multiples of $100,000 or more. Commercial paper market is composed of the (1) dealer and (2) direct-placement markets. Advantage: Cheaper than a short-term business loan from a commercial bank. Dealers require a line of credit to ensure that the commercial paper is paid off. Private Loans: A short term unsecured loan may be taken from a wealthy shareholder, a major supplier, or other parties interested in assisting the firm through a short term difficulty. Cash Advances for Customers: A customer may pay for all or a portion of future purchases before receiving the goods. This aids the firm to purchase raw materials and produce the final goods. This form of financing is a special arrangement for expensive or custom-made items that would strain the financial resources of the manufacturing company. Secured Short-term Sources: Security (collateral) — Asset (s) is pledged by a borrower to ensure repayment of a loan. If the borrower defaults, the lender may sell the security to pay off the loan. Collateral value depends on: Marketability Life Riskiness Types of Inventory Backed Loans: Field Warehouse Receipt — A receipt for goods segregated and stored on the borrower’s premises (but under the control of an independent warehousing company) that a lender holds as collateral for a loan. Terminal Warehouse Receipt — A receipt for the deposit of goods in a public warehouse that a lender holds as collateral for a loan. Trust Receipt – This loan is secured by specific and easily identified collateral that remains in the control or physical possession of the borrower. A security device acknowledging that the borrower holds specifically identified inventory and proceeds from its sale in trust for the lender. Example: When automobile dealers use this kind of financing for the cars in their showrooms or in stock, it is called floor planning. As implied by the name, this kind of loan requires a considerable degree of trust in the honesty and integrity of the borrower. Once the inventory is sold or the receivable is collected, payment must be remitted to the lender. If there is a default, the loan is said to be secured by bogus collateral. These loans are common when the collateral is easily identified by description or serial number and then each item of collateral has relatively large dollar value. Floating Lien — A general, or blanket, lien against a group of assets, such as inventory or receivables, without the assets being specifically identified Chattel Mortgage — A lien on specifically identified personal property (assets other than real estate) backing a loan. Financial Institutions: Primary sources of secured short term financing are banks and financial institutions, including insurance companies, finance companies, and the financial subsidiaries of major corporations. The best mix of short-term financing depends on: Cost of the financing method Availability of funds Timing Flexibility Degree to which the assets are encumbered It is always better to go for bank loans or loans from established and long standing private institutions because there is a leverage for the debtors to sit for discussions to sort out issued in case of defaults. All banks in India are trying to close accounts labeled under NPA- Non Performing assets either by recovering the money through one time settlement (OTS) or by auctioning the collaterals pledged during the time of loan sanctioning. If you happen to take loans from individuals or third-parties, you cannot enjoy this comfort or breather. Some Finance Quotes and Sayings for You: A...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Financial Accounting, Financial Management, Principles of Management
on Apr 8th, 2014 | 0 comments

Interest Free Sources and Unsecured Interest Bearing Sources A firm obtains its funds from a variety of sources. Some capital is provided by suppliers, creditors, and owners, while other funds arise from earnings retained in business. In this segment, let me explain to you the sources of short-term funds supplied by creditors. Characteristics of short-term financing: Cost of Funds: Some forms of short-term financing may prove to be expensive than that of intermediate and long-term financing while some short-term sources like Accruals and Payables provide funds at no cost to the firm. Rollover Effect: Short-term finance as the name indicates must be repaid within a period of one year – though some sources provide funds that are constantly rolled over. The funds provided by payables, may remain relatively constant because, as some accounts are paid, other accounts are created. Clean-up: This happens when commercial banks or other lenders demand the firm to pay-off its short term obligation at one point in a financial year. Goals of Short-Term Financing: Funds are needed to finance inventories during a production period. Short term funds facilitate flexibility wherein, it meets the fluctuating needs for funds over a given cycle, commonly 1 year. To achieve low-cost financing due to interest free loans. Cash flow from operations may not be sufficient to keep up with growth-related financing needs Interest Free Sources: Accounts Payable Accounts payable are created when the firm purchases raw material, supplies, or goods for resale on credit terms without signing a formal note for the liability. These purchases on “open account” are, for most firms, the single largest source of short-term financing. Payables represent an unsecured form of financing since no specific assets are pledged as collateral for the liability. Even though no formal note is signed, an accounts payable is a legally binding obligation of a firm. Postponing payment beyond the end of the net (credit) period is known as “stretching accounts payable” or “leaning on the trade.” Possible costs of “stretching accounts payable” are Cost of the cash discount (if any) forgone Late payment penalties or interest Deterioration in credit rating Accruals: These are short term liabilities that arise when services are received but payment has not yet been made. The two primary accruals are wages payable and taxes payable. Employees work for a week, 2 weeks or a month before receiving a paycheck. The salaries or wages, plus the taxes paid by the firm on those wages, offer a form of unsecured short-term financing for the firm. The Government provides strict rules and procedures for the payment of withholding and social security taxes, so that the accrual of taxes cannot be readily manipulated. It is however, possible to change the frequency of paydays to increase or decrease the amount of financing through wages accrual. Wages — Benefits accrue via no direct cash costs, but costs can develop by reduced employee morale and efficiency. Taxes — Benefits accrue until the due date, but costs of penalties and interest beyond the due date reduce the benefits. Unsecured Interest Bearing Sources: Self-Liquidating Bank Loans The bank provides funds for a seasonal or cyclic business peak and the money is used to finance an activity that will generate cash to pay off the loan. Borrowed Funds → Finance Inventory → Peak Sales Season → Receivables → Cash → Pay Off the Loan. Three types of unsecured short-term bank loans: Single payment note – A short-term, one-time loan made to a borrower who needs funds for a specific purpose for a short period of time. Line of Credit – An informal arrangement between a bank and its customer specifying the maximum amount of...

Posted by Managementguru in Financial Management, Principles of Management
on Feb 20th, 2014 | 0 comments
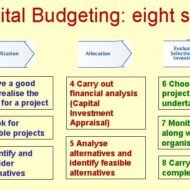
Capital Budgeting- Long Term Resource Planning What is Capital Budgeting? Capital Budgeting refers to the process of planning expenditures that give rise to revenues or returns over a number of years. The process of investment analysis is essential to have a sustainable advantage in the competitive market and to stabilize the profits through resourceful strategic business units. The firm’s management must be on the alert to explore the opportunities present in the market. Obsolete product lines and changes in consumer tastes may present additional problems to a business enterprise affecting the profitability and growth. When a firm decides to venture into projects that demand huge investments, the management has to scrutinize the economic feasibility of such projects. The process of capital investment is also crucial because the projects are for the most part irreversible. Say, for example, if a business firm purchases a special type of machinery, and after installation, if the firm reverses its decision to sell the merchandise due to some technical reasons, it will have only a very small second hand value. Business firms based on the cash flow of the project and the capital recovery period do long-term investment. Why do firms opt for capital budgeting. The reasons may be: To replace worn out equipments that will affect the production efficiency To replace obsolete equipments to install new and more efficient ones To expand production facilities in lieu of increasing demand for the firm’s products and to capture new markets To divest the surplus funds from other business units and to rotate the funds, as idle funds will not generate any revenue To develop new products Research and development Investments made to comply with government regulations, such as projects undertaken to meet government’s health and safety regulations, pollution control and to satisfy other legal requirements. People Involved The proposals for new projects come from the internal environment, such as department heads, executives, employees and of course the management. Experts in product development, marketing research, industrial engineering examine the investment proposals and they may regularly meet with the heads of other divisions in brainstorming sessions to zero in on the proposals. This free course from Udemy is Ideal for people interested in entrepreneurship, fintech, big data, startups, finance, private equity, VCs, & investing. https://www.udemy.com/crowdfund-investing-101-the-basics-of-equity-crowdfunding/ Departments Involved While the firm’s top management makes the final say or decision to undertake or not a major investment project, the process is likely to involve most of the firm’s divisions. Each department has to present its view on the feasibility and viability of the project. The marketing department- on the demand for the new or modified products that the firm plans to sell The production, engineering, personnel and purchasing departments- on the estimation and cost of the investment projects The financing department on- how the required investments funds have to be raised. Thus, the process of expenditure analysis can truly be said to integrate the operation of all the major divisions of the...






