Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Marketing, Operations Management, Technology
on Jun 18th, 2014 | 0 comments
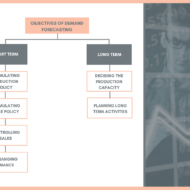
Objectives of Forecasting The objective of this post is to impart some light on the uses and importance of forecasting and to get you acquainted with various forecasting techniques. What is Forecasting? Forecasting is a technique that uses historical data as inputs to make informed estimates that are predictive in determining the direction of future trends. And also to know how these techniques are used in an organization’s decision making process. Nature of Forecast A forecast is an estimate of an event which will happen in future – be it, demand of a product, rainfall at a particular place, population of a country, or growth of a technology.It is estimated based on the past data related to a particular event and hence it is not a deterministic quantity.In any industrial enterprise, forecasting is the first level decision activity before consolidating other decision problems like, materials planning, scheduling, type of production system.Forecasting provides a basis for co-ordination of plans for activities in various units of a company.All the functional managers in any organization will base their decision on the forecast value. So, it provides vital information for that organization. Classification of Forecasts Technology forecastsEconomic forecastsDemand forecasts 1. Technology Forecast Technology is a combination of hardware and software. Hardware is any physical product while software is the know-how, technique or procedure. Technology forecast deals with certain characteristics like level of technical performance, rate of technological advances. It is a prediction of the future characteristics of useful machines, products, process, procedures or techniques. TIFAC – Technology Information Forecasting and Assessment Council is an autonomous organization set up in 1988 under the Department of Science & Technology. In 1993, TIFAC embarked upon the major task of formulating a Technology Vision for the country in various emerging technology areas. 2. Economic Forecast Government agencies and other organizations involve in collecting data and prediction of estimate on the general business environment. Economic forecast This involves the application of statistical models utilizing variables sometimes called indicators. Some of the most well-known economic indicators include inflation and interest rates, GDP growth/decline, retail sales and unemployment rates. This is used to predict future tax revenues, level of business growth, level of employment, level of inflation etc. Also, these will be useful to business circles to plan their future activities based on the level of business growth. 3. Demand Forecast This gives the expected level of demand for goods or services. This is the basic input for business planning and control. Hence, the decisions for all the functions of any corporate house are influenced by demand forecast. Factors Affecting Demand Forecast Business cycleRandom variationCustomer’s planProduct’s life cycleCompetitor’s efforts and pricesCustomer’s confidence and attitudeQualityCredit policyDesign of goods or servicesReputation for serviceSales...

Posted by Managementguru in Economics
on Feb 16th, 2014 | 0 comments

Monetary and Fiscal Policy Countries worldwide are concerned about the following issues while setting up monetary and fiscal policies; namely, the appropriate level of aggregate demand and the best blend of monetary and fiscal mix. Monetary policy focuses on the movement of money within the country, the inflow of foreign exchange and varying interest rates fixed by the Reserve Bank. Fiscal policies are concerned about stabilizing the economy and handle public revenue, expenditure and debts. The pattern of resource allocation and distribution of income affect the drafting of fiscal policies. Monetary policy is very well restricted by the government’s decision on public expenditure and taxation. The tactical combination of both will help determine the composition of GDP. The purpose of monetary policy: The purpose of monetary policy is to ensure availability of credit to the productive sectors of the economy and also regulation of money supply. Econometric models, which use statistical techniques to assess the impact of monetary policy changes on the macro economy, usually find that changes in money supply have a major impact on production in the short term, with greater impact on the proportion of nominal GDP in terms of wage and price inertia as time progresses. Annual budgets are always a nightmare for the common people as tax imposed on commodities has a say on their disposable income. For example, if the price of crude oil is on the rise, the government can do nothing but to increase the fuel prices. Inflation leads to an increase in interest rates charged by banks nationalized or private, affecting small-and medium-scale business firms. Some terminologies related to monetary policy: Let us get ourselves familiar with some of the terminologies in connection with monetary policy. This may help you to understand the subject in a better way. Repo rate: Rate at which RBI lends to other banks against securities Reverse Repo Rate: Rate at which RBI borrows from other banks Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR): Amount of money to be set aside by the banks with RBI against their deposits Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR): Percentage of bank funds to be maintained in government securities Capital Adequacy Ratio: Capacity of banks to work within the time line and risks. Bank Rate: Minimum interest rate at which the Central Bank offers commercial loans to other banks Inflation: Steady rise in prices of commodities Money Supply: Sum total of money circulating in the economy Money flow, policy variables and liquidity conditions have a direct bearing on savings, investment, consumption, inflation, employment and GDP.The ability of a country to improve its standard of living over time depends almost entirely on its ability to improve technology and capital used by the workforce. In short, the budget deficit should be reduced, which guarantees the rate of national savings and increased purchasing power parity (PPP). Main objectives of monetary policy: There have been changes in the objectives of monetary policy from time to time and vary from country to country. Sometimes the monetary policy adopted by a country may have different objectives, which are contradictory. In such cases, the country may have to compromise by setting the priorities. Some of the main objectives of monetary policy: • Price stability • Exchange rate stability • Full employment • High rate of economic growth • Equitable distribution of income Main objectives of Fiscal Policy: Post the Great Depression of the 1930s, it was well realized that governments should actively participate in economic activities to achieve economic growth and equity, through sound fiscal policies. The purpose of fiscal policy lies in: • Achieving full employment • The maintenance of stability • Increasing the rate of capital formation • Development of a model of...




