Posted by Managementguru in Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Strategy, Training & Development
on Mar 31st, 2014 | 0 comments
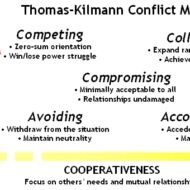
Conflict is a Part of Organizational Life Managers need to be alert to the presence of conflicts. Their focus should be oriented towards the goals to be accomplished. If there is a conflict, they should aim to resolve it smoothly by not over-reacting to the situation. They should take the help of persons who can best settle the issue, be ready to bargain and not issue orders. Their concentration should be on the problem and not on persons. True to the saying – Am I not destroying my enemies when I make friends of them?- President Abraham Lincoln Conflicts are Functional and Healthy: Conflicts in organisations are generally considered to be dysfunctional. On the contrary, many top executives of big companies view conflicts, as a means, to sufficiently analyse a problem and postpone decision making until all critical aspects of an issue are evaluated properly. Conflicts may occur within the individual, between individuals, between the individual and the group or between groups. There are many potential sources of conflict in today’s corporate organisations. The complex inter personal relationships and high degree of interdependence causes friction. Difference of Opinion: When many people must work together, conflict is inevitable, as it is human nature to clash and complain. Conflict is the personal divergence of interests between groups or individuals. The need to share scarce resources, difference in goals between organisational units, difference in values, attitudes and perception, ambiguously defined work responsibilities are some of the major sources of conflict. Functional Conflicts: Functional conflicts support the goals of a group, improve its performance and are constructive in nature. Dysfunctional conflicts hinder the performance of a group and are destructive in nature. It has not been precisely defined, as to what criterion demarcates functional from the dysfunctional. It is only the group’s performance and the delivered result or outcome that determines the nature of the conflict. Conflicts, irrespective of their type can bring these benefits to the firm: Bring hidden issues to the surface. Encourage creativity and innovation. Improves communication and make changes more acceptable. Increases group cohesion. Strategies to Resolve Conflicts: So, what kind of strategy do you think best suits in resolving conflicts? Avoiding or smoothing conflicts may be a temporary measure, only to bounce back in full force. Forcing might create undesirable consequences. The only option left is to confront the situation, face-to-face meeting of the conflicting parties for the purpose of identifying the problem and resolving it through an open discussion. Make Structural Changes to Lessen Conflicts: By making structural changes, conflicts can be managed. The objectives of a group are modified and then integrated to suit the purpose. Also changes in the structure of the organization, that is, clarification of authority-responsibility relationship, improving the working atmosphere, ambience and work locations help in resolving conflicts. Proper Communication: Lack of proper communication, ego clashes between the people in line and staff positions, a superior’s autocratic leadership style, differing educational backgrounds, lack of co-ordination between inter-departments are all rich sources of conflict. These can be resolved with the right kind of attitudinal approach and an open mind from the management’s...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 3rd, 2014 | 0 comments
Group Dynamics Any effective group has three core activities: 1. Accomplishing its goals 2. Maintaining itself internally 3. Developing and changing in ways that improves its effectiveness. Let us now try to understand the various dimensions of an effective group that facilitate the above mentioned three core elements to function properly which provide a sense of direction to the productive group. a) Group goals: Must be clearly understood. Be relevant to the needs of the group members. Highlight the positive inter dependence of members. Evoke from every member a high level of commitment to their accomplishment. b) Communication: Must communicate their ideas and feelings accurately and clearly. Effective two way communication is mandatory for interaction c) Participation and Leadership: All should participate and all should be listened to. Share responsibilities that eases the burden. Increases the cohesiveness of the group. d) Appropriate decision making procedure: Balance between time and member resources. Flexible decision making to suit the needs of the situation. e) Power and Influence: · Should be equal · Based on expertise, ability and access to information and not on authority · Coalitions must be formed between group members on the basis of mutual influence and interdependence. f) Conflicts: · Are to be encouraged as they promote involvement in the group’s work, improve quality and creativity in decision making. · Minority opinions should be accepted and used g) Group Cohesion: · Needs to be high · Level of acceptance, support, and trust among the members decide how cohesive the group is h) Problem Solving: · Problems should be resolved with minimal energy and permanently · Existence of problems must be found out quickly and solutions should improve the effectiveness of group behavior i) Inter-personal effectiveness: · Needs to be high · It is a measure of how all the consequences of your behavior match your intention. ⇓ Picture Courtesy: 6 WAYS TO DEVELOP A WINNING TEAM CULTURE Group Cohesiveness: This is defined as the average resultant force acting on members to remain in a group. The characteristics or criteria that determine group cohesiveness are as follows: 1. Degree of dependency on the group: The greater the number of individual needs are satisfied, the greater the cohesiveness. 2. Size: If the size of the group interaction is low, it results in low cohesiveness. If the size of the group is small, the members tend to have free and more interaction, leading to high level of cohesiveness and vice versa. 3. Homogeneity: Where the interests and background of the group is similar, you find greater cohesiveness. 4. Outside pressure: Outside pressure minimizes internal conflicts leading to high cohesiveness. You find people responding with greater cohesiveness during times of natural disaster and calamities. 5. Competition: Competition between the members of the same group or intra group competition reduces cohesiveness but competition members of different groups or inter-group competition increases cohesiveness. Group Cohesiveness can be encouraged by the following ways: · Make the group smaller · Encourage agreement with group goals · Increase the time members spend together · Stimulate competition with other groups · Give rewards to groups rather than to a single member · Physically, isolate the group. ...




