Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Human Resource, Labor Management, Principles of Management
on Mar 10th, 2014 | 0 comments
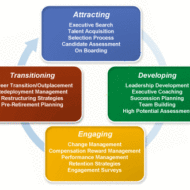
Dimensions of Human Resource Management I would like to brief you on some of the key aspects that mark the paradigm shift in the HR environment towards better management prospects. 1. The Human Resource function has shifted its focus to a much wider canvas that includes Empowerment of EmployeesRestructuring the Organisation and so on. 2. A range of HR sub-systems are involved in Planning The NumbersTypes And Skills Of HrEnsuring Their AvailabilityPlacing In The Right JobPromoting And Nurturing Their Mental HealthHelping Them Develop Special Talent And Skills 3. Human Resource is considered as an “investment” and no more an “expenditure”. Investment in TrainingRe-Training AndContinuous Learning On The Job develops the skills and competences of managers and employees and prove to be an useful investment. 4. The concepts of Learning Organisations AndTeam-Building serves a basis for “Competitive advantage” and “Motivating the employees.” 5. Values that are stressed upon are Co-OperationHarmonisationSynergyTrustBeing Pro-ActiveCollaboration 6. Strategy: VisionMissionObjectivesGoals– How these can be achieved? The techniques that are basically holistic in nature can solve the purpose. Such techniques involve SEWA– Self mastery, Empathy for workers, Worker-directedness and Achievement in performanceABO-Action by Objective Nine Dimensions of an Effective HR Department: What is the reputation of the HR department?What are the criteria (deliverables) that shape HR work?What is the mission or strategy of the capabilities – focused HR department?How is the HR department organised? How does HR facilitate the definition and creation of organisation capabilities?How do we make better HR investment and choices?How do we create HR practices?How does HR go about doing its work? What do HR professionals need to be, know, and do to be effective? Let us make a sincere comparison between the past and the present in terms of HR perspective These techniques produce performers who find their way through any set of given problems, manage themselves and lead the team to a stae of self- realisation. Old model vs New model 1. Job was the basic unit/ Team is the basic unit 2. Relations with environment there handled by the individuals/ Densely networked with environment 3. Information flow was vertical/ now it is vertical, horizontal and holistic 4. Many layers of management / Organisations have become flat 5. Emphasis on structures/ Emphasis on process and literally virtual organisations have evolved 6. Career path upward and linear/ career path lateral and flexible 7. Standardised evaluation and reward system/ Customised evaluation and reward system 8. Ethnocentric/ International 9. Single strong culture/ Multicultural and diversity of viewpoints and...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Labor Management, Organisational behaviour
on Mar 7th, 2014 | 0 comments

People Management and Trade Unions Need for Trade Unions Why do employees join trade unions is an important question. Most of the workers are members of any one of the trade unions. One of the major objectives of trade unionism is to promote industrial democracy. This objective is achieved when trade union is an organization of the workers, for the workers and by the workers”. In practice this rarely happens and instead unions become an oligarchy. Union leaders by and large, show authoritative behavior with less participation, openness and transparency. Decision-making is centralized, elections are often postponed and positions are filled repeatedly by nominations. Rank and file is pampered with promises and seldom gets near to decision-making process. Positions get worse when unions are guided by outside leaders and regulated by the policies of political parties. Ideology of Trade Unions Absence of democratic leadership reduces the effectiveness of trade unions and prevents the development of trade union leadership from among the workers within the industries. In due course, trade unions become obsessed with political ideology or personal interest ousting the welfare of the workers. Before we move on to the functions of trade unions, let us understand the reasons for the existence of such organizations. To get a common platform to air ones views, aims, ideas and feelings and obtain recognition and status among fellow workers. Make use of the principle of unity for the purpose of securing good working conditions, higher economic compensations, better career prospects and welfare needs. Security of employment and protection against calamity of accident, death and social security after retirement. Restrict management action which is against the interest of the workers. Functions of a Trade Union The internal functions of a labor union includes better wage claim, to ensure better working conditions, reasonable work etc.,The external functions include conducting night school, games, sports and other recreational activities. These two functions may be grouped as economic and social functions. Many unions try to capture political power through election, so that they can influence upon the programmes and policies of government in favor of labor. This function is known as political function. Under the legal functions, the interpretation of law takes the major share. A jist of the main purpose of trade organizations: To improve the standard of living and working condition of the workers. To protect the security of workers’ employment. To ensure better health, reasonable working hours and welfare measures. To improve the political status. To raise the vocational status. To bring better participation in the management. To inculcate the feeling of self respect and confidence among worker force. To bring industrial peace and harmony. As long as unionism is considered as an anathema by the management, there will be lack of harmony and mutual trust between the management and labor force. Management must not consider labor unions as a legal obligation as it does not develop faith and goodwill. Instead the union has to be viewed as a partner in trade to live with and work with. Union must also recognize that work is worship and the survival and success of organization depends on the very survival and success of the workforce. Once the team spirit is built up no unreasonable demands will be raised and union leaders must view strikes and lock outs as last resorts to put pressure on management. The Trade Unions Act, 1926– An act to provide for the registration of Trade Unions and in certain respects to define the law relating to registered Trade...




