Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Operations Management
on Feb 18th, 2015 | 0 comments
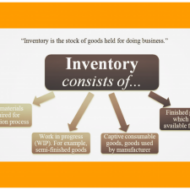
Inventory Control Learning Objective: To know the meaning, types and functions of inventories Meaning of Inventory: The word inventory refers to any kind of resource having economic value and is maintained to fulfil the present and future needs of an organization. Fred Hansman has defined Inventory as “An idle resource of any kind provided such a resource has economic value”. Such resources may be classified into three categories: A. Physical resources such as raw materials, semi-finished goods, finished goods, spare parts, lubricants etc. B. Human resources such as unused labor (man power) and C. Finance resources such as working capital etc. Inventory of resources is held to provide desirable service to customers and to achieve sales turnover target. At the same time holding big inventory severely affects the cash flow and working capital of an organization if the production vs demand cycle is not stream-lined. Because inventory often represents more than 25% of total assets and therefore it becomes very essential to maintain an optimal level of inventory in each resource so that the total inventory cost is near its minimum. Functions of Inventory: Inventory serves several important functions that add flexibility to the operations of a firm. Provides stock of goods to meet the anticipated demand of customers. In the case of consumer goods with a seasonal demand, the establishment of inventories in distribution and production warehouses also ensures that production can run continuously at full capacity despite swings in seasonal demand. De-Coupling function: The down time in one manufacturing stage should not affect the whole manufacturing process and this vital purpose is solved by holding inventory which acts as a buffer between successful stages of production. Quantity Discounts: Many suppliers offer QD’s for large orders of inventory. Procurement warehouses can result from a company’s desire to get volume discounts from a supplier or more favorable conditions from a carrier. Price speculation – Inventory also helps to hedge against inflation and price changes. Inventories of procurement and distribution warehouses are increased if the price of a good is expected to rise. In such a situation, the purchasing company aims to amass the good at the current low price. The supplier may speculate that supply shortages will drive the prices higher, and he uses the warehouse to store the good. Shortages can occur regularly due to irregular supply of raw materials, weather, quality problems or improper deliveries. Inventory shall act as “safety stock’ – extra goods on hand which reduce the risk of stock-outs. Helps to permit operations to continue smoothly with the use of “work in process” inventory. This is because it takes time to make goods and because a pipeline inventory is stocked through-out the process. JUST IN TIME MANUFACTURING CONCEPT Types of Inventory: Inventory can be classified according to the basis of type of material maintained in the firms and also on the basis of the functions they tend to perform in an organization. On the basis of type of material, the firms maintain four types of inventories: Raw material inventory Work in process inventory Maintenance/operating supply (MRO) inventory and Finished goods inventory Raw material inventory is the one which has been purchased and yet to be processed. The work in process material has undergone some change but is not completed. Work in process exists because of the time it takes for a product to be made which is called the “CYCLE TIME.” MRO inventory is devoted to maintenance/repair/operating supplies. They exist because the need and timing for maintenance and repair of some equipment are unknown. Products completed and waiting for shipment are called finished goods inventory. Finished goods may be inventoried because customer demand for...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Marketing, Principles of Management, Strategy
on Mar 16th, 2014 | 0 comments

Strategies to Tide Over Competition Distinctive Competence: is nothing but a set of unique capabilities that certain firms possess allowing them to make inroads into preferred markets and to gain advantage over the competition. Human brain is the greatest think tank and it evolves new methodologies of business management from time to time in order to sustain as well as win the race. Planning is the key factor that decides the rise or downfall of a business empire. “Where we are?” and “Where we want to be in the next few years?” is how every business leader’s basic thought process must be, without which he cannot proceed further in the competitive corporate environment. If we call planning as the basement of a building, then it should be very precise, clear cut and robust so that the business empire built on this basement will never collapse and it will also serve as a role-model for everyone who aspires to set his foot in the corporate business world. At the corporate level, strategic planning helps to establish the Purpose Mission and Objective for the firm as a whole and “outlines the overall plan to attain them.” Strategy is nothing but a unique set of action plan that will distinguish you from your competitors and make you have an edge over them. Likewise strategic planning is nothing but thinking out of the box to” CREATE YOUR OWN NICHE MARKET” in the business environment. STRATEGIC COMPETENCE takes you to the top of the ladder; but to withhold your position you need to formulate innovative ideas to tide over the challenges in the market. Strategic planning facilitates this process by giving you time frame to complete your short term objectives and long term goals. Infographic Courtesy: The 4 key sources to seek insights for marketing planning Planning for SBU’s: Business level planning is done for the enterprise’s STRATEGIC BUSINESS UNITS or SBU’S. These are individual” cash cows” that makes your business noteworthy and also brings in constant revenue to run your other units successfully even in periods of recession or if a particular product is not that successful as you might have expected it to be. I shall compare a business plan to a travel plan. Both involve planning, resources, capital, marketing and so on. . . Both have starting points but a business plan and its objectives never end and you can never come back to the starting point in a business as that of a travel, because you only expand and grow to greater heights in a business provided your plan is pucca. And also the strategy seeks the integration and control of marketing, finance, production and human resources at the functional level. Strategic Plans at different functional levels: Strategic plans at different levels must be integrated to ensure that they work in tandem and reinforce each other, thereby contributing to the corporate level strategy adopted for the entire corporate group. I would call strategic planning as” INTELLIGENCE DESIGN CHOICE ACTIVITY “adopted by a corporate and it has become an inevitable feature in the directory of the business world....

Posted by Managementguru in Economics, International Business
on Feb 16th, 2014 | 0 comments

Economic Growth Strategies A Purview on Economic Growth Strategies for Developing Countries A developing country is one where the per capita income is low relative to that of fully developed countries. In human terms developing countries typically have major population percentage with poor health, low levels of literacy, inadequate dwellings and meager diets. The key to development rests on four fundamental factors namely human resources, natural resources, capital formation and technology. Human resources: A lot of poor countries are forever running hard just to stay in place. Even as a developing nation’s GDP rises, so does its population. So it becomes a mammoth task for such nations to overcome poverty with birth rates so high. Equitable distribution of wealth cannot happen in an economy unless and until it becomes self sufficient. One strategy will be to curb the population, even if such actions run against prevailing religious norms. Strategies for Developement Economic planners in developing countries lay great emphasis on the following strategies of development with regard to human capital: Control disease and improve health and nutrition Improve education, reduce illiteracy and train workers Above all, do not underestimate the importance of human resources. Literate people are knowledgeable and resourceful; their analytical skills help them to weigh the pros and cons of specific social situations that affect their standards of living. Asian countries like India and China with exploding population figures are in a situation to invest their human capital for productive purposes. Pinning Your Way to Profit With Pinterest Natural Resources: Some developing nations with meager endowments of natural resources such as land and minerals have to divide the available resources among the dense population. Perhaps the most valuable of all the resources would be arable land, as most of the people in developing countries employ themselves in farming, which is the primary economic activity. Hence the productive use of land with appropriate conservation, fertilizers and tillage will go- far in increasing a poor nation’s output. More over land ownership patterns are a key to providing farmers with strong incentives to invest in capital land’s yield. When farmers own land, they are more willing to make improvements, such as irrigation systems and undertake appropriate conservation practices. The governments have to think in these lines if their economy is based on agricultural activity: Farmers should be appraised about modern farming techniques and provided with farming equipments and fertilizers at subsidized rates. Note:-nothing should be given as free as freebies make them lethargic and unmotivated. Much of cultivable lands are being destroyed for commercial purposes which have to be checked. Power generation and supply should be copious and uninterrupted as farming, solely is dependent on availability and usage of ground water. Pumping of water is done through jet pumps and electric motors. Budding population can make a marked difference in the field of farming, as it is impossible for a nation to generate white collar jobs for everyone and it definitely elevates the capacity of youth from being mere employees to that of owners. Organic farming has found a place for itself in international market and human capital of developing nations can be employed in research and development of new strains that will facilitate to capture the global market. Capital formation: Rates of productive capital formation are low in developing countries because of deprived income; little can be saved for the future. The financing of growth in poor countries has always been an unstable link in the productive mechanism. Countries should definitely have a balanced and cautious approach when they plan to finance ambitious development programmes as they will be forced to borrow heavily from other developed countries or the World Bank. Technological change and innovations: This is...






