Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Change management, Entrepreneurship, Human Resource
on Apr 16th, 2014 | 0 comments

Entrepreneurs are the mechanism by which our economy turns demand into supply. They create new ventures that provide new, improved products and services. Here we list some of the principal qualities of entrepreneurs and how those qualities help in shaping up our economy. Productivity Accelerators: Entrepreneurship raises productivity through technical and other forms of innovation. Entrepreneurs as risk bearers find resources and fill market gaps that would be missed by larger, more bureaucratic organizations. They allow a country to extract every last bit of marginal capacity out of whatever resources exist within the society. Brilliant Tips on Productivity by some Popular Entrepreneurs: Focus on one thing at a time: It may seem like a no-brainer, but multitasking can actually cut back on your productivity. Instead of juggling multiple projects at once, schedule out blocks of time — or even entire days — during which you only focus on one task or one project. Steph Auteri, @stephauteri, Word Nerd Pro Outsource, outsource, outsource: Everything may be a priority, but you are not equally brilliant at everything. Eliminate the unnecessary tasks and outsource your weaknesses so your time and focus is directed to where you’ll make the biggest impact for the business. Kelly Azevedo, @krazevedo, She’s Got Systems Define roles and divide work: Make sure everyone on the team has distinct roles defined, and divide work accordingly. Everyone on a proactive team will want to do everything, and clearly defined roles make it clear who should do what. David Gardner, @david_gardner, ColorJar Job Creators: It is a powerful tool of job creation –Entrepreneurship as a whole contributes to social wealth by creating new markets, new industries, new technology, new institutional forms, new jobs and net increases in real productivity. The jobs constructed through their activities in turn lead to equitable distribution of income which leads to higher standards of living for the population. Entrepreneurship facilitates the transfer of technology. Entrepreneurs play a strategic role in commercializing new inventions and products. They play a critical role in the restructuring and transformation of economy. Their behavior breathes vitality into the life of large corporations and governmental enterprises. Market Competitiveness: They make the markets more competitive and thereby reduce both static and dynamic market inefficiencies. Micro-preneurs working in the informal sector circumvent established government authority when governments and their programmes inhibit economic development. They stimulate redistribution of wealth, income and political power within societies in ways that are economically positive and without being politically disruptive. Social Welfare: They improve social welfare of a country harnessing dormant, previously overlooked talent. They create new markets and help in expansion into international markets. The unique feature of entrepreneurship – that it is a low cost strategy of economic development, job creation and technical innovations. Technology Innovation: Technology entrepreneurship is also important for sustainable development as Nobel Prize Laureate prof. Dan Schechtman puts it: “Technological entrepreneurship is a key to the well-being of the world”. India has been the first among the few developing countries to have assigned a significant and categorical state role to small scale industries from the first Five Year Plan itself, and the small scale sector has emerged as a dynamic and vibrant sector of the economy during the eighties. If the country develops pucca infrastructure and removes the hurdles in the operative environment politically and legally, no doubt the Indian economy will be scaling to greater heights. Surplus manpower (educated and un-educated), which has been a great liability can become an asset once those with potential are selectively groomed for self-employment and enterprise formation, leading to further job...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Leadership, Principles of Management
on Mar 5th, 2014 | 0 comments
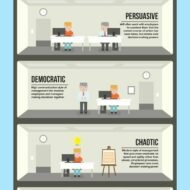
Management styles vary by company, level of management, and even from person to person. Let us see the different management styles practised in different parts of the world for your better understanding. Managerial practices in Asian countries The managerial practices in Asian countries like Japan, China and India are quite different from that of economically advanced countries in the west. Industrial nations are in a position to adopt managerial approaches that suits their mode of operations and nature of labor force. In Asian countries, a paternalistic or participative leadership style is followed while directive style of leadership pattern suits the west. Basically, this difference arises due to the cultural background of people influenced by their tradition. Japanese management East Asian countries like Japan have a set of cultural norms that cannot be overlooked or sacrificed for the sake of business. Their cultural instincts are very strong and they believe in life long employment. Japanese management practice lays emphasis on seniority and shows great concern for each and every employee. The objectives are set by the lower level employees and it is passed on to the top level management for approval. These proposals are scrutinized by the supervisors who tactfully suggest the necessary changes, instead of simply accepting or rejecting the proposed objectives. This creates a sense of belonging and the employees identify themselves with the goals of the company. Participative Style You cannot assure that a participative style of decision making always proves beneficial. Sometimes, managers have to show their individualism by taking tough decisions, when the situation warrants for such an action. Here the leader also becomes the firm decision maker. This is quite common in the west, where the leaders identify themselves with the profession rather than the company. Such solo decision making sometimes result in sub-optimal decisions. We are not going to compare and contrast between the various management approaches and which is better. The discussion aims at throwing light on different approaches and styles of management and how it affects the productivity of an organization. https://click.linksynergy.com/deeplink?id=omtjfcspUOE&mid=39197&murl=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.udemy.com%2Fcourse%2Fleadership-and-lean-management-masterclass%2F Collective Decision Making Japanese management relies on collective decision making (consensus), where the decision making might take time, but it is implemented quickly. The Japanese management is highlighted in this discussion to demonstrate the effectiveness of their approach which is followed by many western nations to ensure success. The novelty is in the fact that they treat people as human beings and not just another factor in production. The communication flows from bottom to top and back. Care is taken to define the problem with clarity before going for a decision. In the west, managers are criticized to come to conclusions even before defining the problem. https://click.linksynergy.com/deeplink?id=omtjfcspUOE&mid=39197&murl=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.udemy.com%2Fcourse%2Fnew-manager%2F Bureaucracy Bureaucracy still prevails in most of the Asian countries hindering the progress of business communities. What started as an amazing administrative legacy has now turned authoritarian. Even if the employee knows what the manager says is incorrect; he has to obey the instructions, just because it is issued by his superior. The people are expected to follow the instructions provided and not to question or suggest. Collective Responsibility Collective responsibility and accountability, an informal organizational structure, common organizational culture and competitive spirit makes participative management approach distinct and successful. When the leader acts as a facilitator and not a dictator, naturally the employees will try to give their best shot. Collective responsibility might sometimes lead to ambiguity of decision responsibility. But individual responsibility and accountability vouches for clear and specific decision responsibility. Quality control circle Quality control circle is another feature that distinguishes Japanese management from others. Workshops are organized in a periodic fashion to arrive at solutions for problem situations, be it worker welfare, bottlenecks or interpersonal skills. The focus is on group performance and peers help one another in enhancing the performance and...

Posted by Managementguru in Economics, Entrepreneurship, Human Resource
on Mar 1st, 2014 | 0 comments
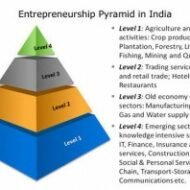
Entrepreneurship in Developing Economies Entrepreneurial development is a complex process of change. It has been recognized as an important ingredient of economic development. The development of entrepreneurial activity depends upon the closely interlinked economic, social, cultural, religious and psychological variables. Developing countries of late have adopted a deliberate policy of promoting and encouraging small enterprises as a strategy, for the overall development of their countries. Practical Problems Faced by Developing Countries The numerous problems confronted by developing countries such as, a high rate of population growth, a relatively low rate of economic growth, a low level of capital income with nearly fifty percent of the population subsisting below the poverty line and mounting increase in the figures of educated unemployed-all these check the growth of entrepreneurial activities. Countries have to plan realistically, mobilize and harness resources, have control over factors of growth and development and give direction to the development process. Naturally then, the national and economic goals will be focused towards: Production and productivity to be increased in the primary, secondary and tertiary sectors Maximum harnessing and utilization of material and human resources Solving problems of unemployment Having a check on population growth Equitable distribution of wealth and income To increase the purchasing power parity To increase the gross national product To increase the real per capita income Improving the quality of life Industrial Development The larger scope and potential to achieve these goals lie in the development of the industrial sector of the national economy, and the only alternative to raise the level of living is development of industries. Here, we are not merely concerned with certain quantum of growth and development in the industrial field. Theoretically, the desired quantum of industrial development could be supported by a few large investments and capital intensive units run by a small number of big entrepreneurs. But what is envisaged is to have the same quantum of industrial development with a wider spread consisting of large number of small entrepreneurs all over the country. This would result in development of small scale and tiny sector industries all over the country and would generate employment opportunities to the educated unemployed, skilled people and other potential entrepreneurs from various segments of the society. Scenario of Asian Countries Most of the Asian countries like India and China are encouraging and promoting entrepreneurial development leading to industrial and economic development. India is now a hot spot for automobiles and its accessories. Being a cost-effective core market for auto components sourcing for global auto makers, the automotive sector is a potential sector for entrepreneurs. Entrepreneurs are risk bearers, find resources and fill market gaps that would be missed by larger, more bureaucratic organizations. Entrepreneurs improve the social welfare of a country by harnessing dormant, previously overlooked talent. Surplus manpower which is considered a great liability can be converted into assets once those with potential are selectively groomed for self-employment and enterprise formation, leading to further job...






