Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Financial Accounting, Management Accounting
on Oct 24th, 2016 | 0 comments

Types of accounting information may be classified into four categories: Operating informationFinancial accounting informationManagement accounting information andCost accounting information 1. Operating Information: This is the kind of information which is required to conduct the day-to-day activities. Examples of operating information are: Amount of wages paid and payable to employeesInformation about the stock of finished goods available for sale andEach one’s cost and selling priceInformation about amounts owed to and owing by the business enterpriseInformation about stock of raw materials, spare parts and accessories and so on. By far, the largest quantity of accounting information provides the raw data (input) for financial accounting, management accounting and cost accounting. Spend Wisely 2. Financial Accounting: Financial accounting information is meant both for owners and managers and also for the use of individuals and agencies external to the business. This accounting is concerned with the recording of transactions for a business enterprise and the periodic preparation of various reports from such records. The records may be for general purpose or for a special purpose. Focus on the Long Term 3. Management Accounting: Management accounting makes use of both historical and estimated data in assisting management in daily operations and in planning for future operations. It deals with specific problems that is faced by enterprise managers at various organizational levels. The management accountant is often concerned with finding alternative courses of action and then helping to select the best one. For e.g. The accountant may help the finance manager in preparing plans for future financing or may help the sales manager in deciding the selling price to be fixed on a new product by providing suitable data. Generally management accounting information is used in three important management functions: ControlCo-ordination andPlanning 4. Marginal costing This is an important technique of management accounting which provides multi dimensional information that helps in decision making. Specialised Accounting Fields A number of specialized fields in accounting also have evolved besides financial accounting. Management accounting and cost accounting are the result of rapid technological advances and enhanced economic growth. The most important among them are explained below: 1. Tax Accounting: Tax accounting is all about the filing of tax returns and the consideration of the tax implications of proposed business transactions or alternative courses of action. Accountants specializing in this branch of accounting are familiar with the tax laws affecting their employer or clients and are up to date on administrative regulations and court decisions on tax cases. 2. International Accounting: This accounting is concerned with the special issues associated with the international trade of multinational business organizations or MNC’s. Accountants specializing in this area must be familiar with the influences that custom, law and taxation of various countries bring to bear on international operations and accounting principles. 3. Social Responsibility Accounting: This branch is the newest field of accounting and is the most difficult to describe. Social responsibility accounting is so called because it not only measures the economic effects of business decisions but also their social effects, which have previously been considered to be immeasurable. Social accounting is also known as social accounting and auditing, social and environmental accounting, corporate social reporting, corporate social responsibility reporting, non-financial reporting or accounting. Benefits of Social Accounting 4. Inflation Accounting: Inflation accounting is a term describing a range of accounting models designed to correct problems arising from historical cost accounting in the presence of highinflation and hyperinflation. Inflation accounting is used in countries experiencing high inflation or hyperinflation. 5. Human Resources Accounting: Human resource accounting is the process of identifying and reporting investments made in the human resources of an organization that are presently unaccounted for in the conventional accounting practices. It is an extension of standard accounting principles. This system of accounting...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Marketing, Operations Management, Technology
on Jun 18th, 2014 | 0 comments
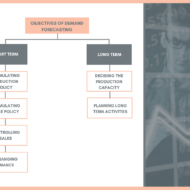
Objectives of Forecasting The objective of this post is to impart some light on the uses and importance of forecasting and to get you acquainted with various forecasting techniques. What is Forecasting? Forecasting is a technique that uses historical data as inputs to make informed estimates that are predictive in determining the direction of future trends. And also to know how these techniques are used in an organization’s decision making process. Nature of Forecast A forecast is an estimate of an event which will happen in future – be it, demand of a product, rainfall at a particular place, population of a country, or growth of a technology.It is estimated based on the past data related to a particular event and hence it is not a deterministic quantity.In any industrial enterprise, forecasting is the first level decision activity before consolidating other decision problems like, materials planning, scheduling, type of production system.Forecasting provides a basis for co-ordination of plans for activities in various units of a company.All the functional managers in any organization will base their decision on the forecast value. So, it provides vital information for that organization. Classification of Forecasts Technology forecastsEconomic forecastsDemand forecasts 1. Technology Forecast Technology is a combination of hardware and software. Hardware is any physical product while software is the know-how, technique or procedure. Technology forecast deals with certain characteristics like level of technical performance, rate of technological advances. It is a prediction of the future characteristics of useful machines, products, process, procedures or techniques. TIFAC – Technology Information Forecasting and Assessment Council is an autonomous organization set up in 1988 under the Department of Science & Technology. In 1993, TIFAC embarked upon the major task of formulating a Technology Vision for the country in various emerging technology areas. 2. Economic Forecast Government agencies and other organizations involve in collecting data and prediction of estimate on the general business environment. Economic forecast This involves the application of statistical models utilizing variables sometimes called indicators. Some of the most well-known economic indicators include inflation and interest rates, GDP growth/decline, retail sales and unemployment rates. This is used to predict future tax revenues, level of business growth, level of employment, level of inflation etc. Also, these will be useful to business circles to plan their future activities based on the level of business growth. 3. Demand Forecast This gives the expected level of demand for goods or services. This is the basic input for business planning and control. Hence, the decisions for all the functions of any corporate house are influenced by demand forecast. Factors Affecting Demand Forecast Business cycleRandom variationCustomer’s planProduct’s life cycleCompetitor’s efforts and pricesCustomer’s confidence and attitudeQualityCredit policyDesign of goods or servicesReputation for serviceSales...

Posted by Managementguru in Financial Management, Principles of Management
on Feb 28th, 2014 | 0 comments
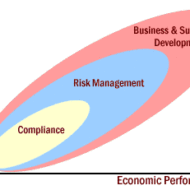
There is no Business Success Without Risk What is the Risk of Taking a Chance in a Business Activity? Business is often viewed as a game or a gamble in which success is always at risk. Think about it, risk is present in every sphere and aspect of our lives and even when you are not running a business. So why the fuss? A thorough knowledge and research of the business activity you are about to perform will give you the needed confidence to go about it. A true business man is an entrepreneur who treats risk as an opportunity rather than a challenge. Business organizations are started with a single purpose, to make profit and then more profit. Only when the organizations grow, there comes the awareness and necessity to think about stakeholders’ interest and working towards a social cause. Initial stages definitely pose threats for the very survival of the organization. Risk is an inherent part of a business as you are not sure about the outcome of your business activity. What are the Chances or Probability? We talk more about probability and chance outcomes when you deal with a particular product. Retail segment is one area where the risk of duplication is high and people have to be cautious and careful in order to protect their copyrights and symbols from being replicated. Mild inflations can benefit the market but recessions put you in doldrums especially if you are dependent on a wholesaler or a manufacturer. Risk can aspect itself in the following ways: Economically- Attrition and effects of global economy Legally- Labor laws and enactments Socially- Expectations from the public in general Government rules and regulations- Government policies and export duties Stakeholder expectations- Wealth maximization and assured profits Environmental – Need to comply with changing standards like waste affluent treatment plants Political scenario- Effects due to changing governments Risk and Uncertainty Risk and uncertainty go hand in hand and you need a risk management template or a model for your reference to solve or manage risks. The first and foremost step would be to identify the risks in your sphere of business activity. Risk documentation or creating a risk profile is an inevitable move for a new organization. This prepares the organization mentally to face challenges in a structured manner and reduces disorientation. It is very important to keep in mind the organisation’s objectives while documenting the risk profile to keep your focus unaltered. Risks evolve continuously and it is the responsibility of the top management to be in line with the market economy to manage the adverse conditions that come in the way. How to Manage Risks? Risk management is an ongoing and continuous process and it cannot be looked upon as a distinct area to be managed by a set of individuals. In a small and upcoming organization the responsibility lies on the shoulders of each and every individual to self assess, evaluate and manage risks and find the right kind of solution that will not be detrimental to the core objectives of the organization. Bigger organizations can afford to have expert opinion by commissioning PROFESSIONALS to identify, assess and manage risks. An overall and broad perspective of risk is what has been analysed here. There are numerous possibilities of risks, whether big or small in magnitude, affecting an organization. A thorough study of the field you are about to venture into, the pros and cons of the business activity, time of launch are few things that will help you to analyse what the market niche warrants for and act accordingly. In further segments, let us look into the factors of risk, identifying and...

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting
on Feb 21st, 2014 | 0 comments
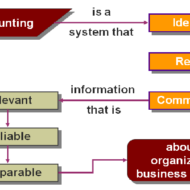
Functions of Accounting: a. Recording: Accounting records business transactions in terms of money. It is essentially concerned with ensuring that all business transactions of financial nature are properly recorded. Recording is done in journal, which is further subdivided into subsidiary books from the point of view of convenience. b. Classifying: Accounting also facilitates classification of all business transactions recorded in journal. Items of similar nature are classified under appropriate heads. The work of classification is done in a book called the ledger. c. Summarizing: Accounting summarizes the classified information. It is done in a manner, which is useful to the internal and external users. Internal users interested in these informations are the persons who manage the business. External users of information are the investors, creditors, tax authorities, labor unions, trade associations, shareholders, etc. d. Interpreting: It implies analyzing and interpreting the financial data embodied in final accounts. Interpretation of the data helps the management, outsiders and shareholders in decision making. Limitations of Accounting: Accounting information is expressed in terms of money. Non monetary events or transactions, however important, are completely omitted. Fixed assets are recorded in the accounting records at the original cost, that is, the actual amount spent on them plus all incidental charges. In this way the effect of inflation (or deflation) is not taken into consideration. The direct result of this practice is that balance sheet does not represent the true financial position of the business. Accounting information is sometimes based on estimates; estimates are often inaccurate. Accounting information cannot be used as the only test of managerial performance on the basis of more profits. Profit for a period of one year can readily be manipulated by omitting such costs as advertisement, research and development, depreciation and so on. Accounting information is not neutral or unbiased. Accountants calculate income as excess of revenues over expenses. But they consider only selected revenues and expenses. They do not, for example, include, cost of such items as water or air pollution, employee’s injuries, etc. Accounting Made Easy Accounting like any other discipline has to follow certain principles, which in certain cases are contradictory. For example current assets (e.g., stock of goods) are valued on the basis of cost or market price whichever is less following the principle of conservatism. Accordingly the current assets may be valued on cost basis in some year and at market price in another year. In this manner, the rule of consistency is not followed...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Economics, International Business, Principles of Management
on Feb 16th, 2014 | 0 comments

The factors that affect the economic environment of business are listed below. Macro Environment The management of a firm is influenced and affected by many factors that exist in the external environment, also called as macro environment. These are beyond the scope of business control and affect the functioning of a business enterprise. Factors of External Environment that Affect Business These factors may present themselves in the form of opportunities or threats and it is the responsibility of a manager to identify the changes in the external environment, be it, social, economic, political, legal, technological, demographic or ecological and devise action plans accordingly, to suit the changing demands and needs of the macro environment. Buying Power of People The most important and prime factor that affects a firm’s operations and its basic survival is the economic factor. Economy of a country is prosperous only when it is self sufficient and withstands the pressure of inflation or recession. Businesses can flourish only if there is a regular demand for the products manufactured. Economic Factors that Affect Demand The buying power of people and their willingness to pay are also important economic factors that affect demand. In developing countries, people concentrate on “saving” rather than spending, where the economy is showing steady growth. For instance in India, people invest their money in gold and land,both being considered as solid appreciating disposable income,assets. Why do we turn to nonprofits, NGOs and governments to solve society’s biggest problems? Michael Porter admits he’s biased, as a business school professor, but he wants you to hear his case for letting business try to solve massive problems like climate change and access to water. Why? Because when business solves a problem, it makes a profit — which lets that solution grow. Watch the Video Disposable Income The ability of people to buy, largely depends on their employment, income tax and price of the product. The disposable income of people in developing countries is very meager and it further decreases if the rate of tax increases. Ability to Buy This also affects his or her ability to buy. If his concentration is on “saving”, again his ability to purchase is restricted. Even if the individual has the purchasing power, there is no assurance that he or she will buy, it all depends on their willingness to buy. The purchasing power parity of developing countries is very low when compared to developed countries. Role of Technology In recent times, technology also has played an enormous role in bringing an array of new products into the market, and has improved man’s preference for better products. For a business firm, it is very difficult to predict people’s preference as well as changes in their preferences. It needs a great deal of market research and regular updations. If the prices are in decreasing trend, people will not buy the product immediately; they will wait for some more time to derive maximum benefit or value out of their purchase. So, people’s perception about the market economy, social influences and changing preferences definitely affect the willingness to buy. Competitive Market Managing the competition proves to be a tougher task for each and every individual business firm. In today’s modern high flying business environment, people always expect value added services for the products purchased. Business organisations are in a position to compete for customer’s interest as well as income. Firms think of price reductions, aggressive promotional efforts, attractive offers, differentiated product offerings and customer service as competitive tools to have a sustainable and distinctive advantage over others. Offering new product designs, attractive packing, extended credit facilities, free door delivery and fast and competent repair services...










