Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Financial Accounting
on Aug 24th, 2014 | 0 comments
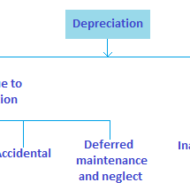
What is meant by Depreciation? It means reduction in the value of a fixed asset used in the business due to #wear and tear and effluxion of time. What is depreciation? Internal and External Causes of depreciation: i. Wear and tear: Caused mainly due to constant use, erosion, rust etc. ii. Efflux of time: Mere passage of time will cause a fall in the value of an asset, even if it is not used. iii. Obsolescence: A new invention or change in fashion or a permanent change in demand may render the asset useless. iv. Depletion: When raw materials or natural resources like mines, quarries and oil wells are extracted continuously, they deplete. v. Accident: An asset may reduce in value because of meeting with an accident, like fire accidents. vi. Fall in the market price. Watch this video on What Is Depreciation – How It Affects Profit And Cash Flow What is the necessity for providing depreciation? According to International Accounting Standard Committee (IASC) “Depreciation is the allocation of the depreciable amount of an asset over its estimated useful life. Depreciation for the accounting period is charged to income either directly or indirectly.” The need for depreciation arises because of the following reasons: To ascertain the true profit of the business for a particular periodTo show the asset at its true value in the balance sheetTo provide funds for replacement of the old asset with a new one Objectives of providing depreciation: To recover the cost incurred on fixed assets over its lifeTo facilitate the purchase of new asset, when the old asset is disposedTo find out the correct profit or loss for the particular periodTo find out correct financial position through balance sheet Factors to be considered while determining the amount of depreciation: I. The total cost of the asset including all freight, insurance and installation charges II. The estimated residual or scrap value at the end of its life III. Estimated number of years of its usefulness It is concerned with charging the cost of fixed assets to operations. But the term depletion refers to the cost allocation for natural resources, whereas the term amortization relates cost allocation for intangible assets. What are the various methods for depreciation? Fixed installment or Straight line or Original cost method.Diminishing Balance Method or Written down value method or Reducing Installment method.Annuity Method.Depreciation fund method or Sinking fund amortization fund method.Insurance policy method.Revaluation method.Sum of the year’s digits method (SYD).Double declining balance method.Depletion method. Related Posts : How to Manage Working Capital?Short Term...

Posted by Managementguru in Economics, Financial Management, International Business, Marketing, Project Management
on Mar 11th, 2014 | 0 comments

What is Trade? Trade is the exchange of commodity and services. International trade represents business transactions taking place at the global level, and it is fundamentally different from domestic trade. Trade at international level demands huge investments, network of franchisees and proficient people to run the show. Many corporate giants are trying to capture Asian markets, especially Indian market, which has become the industrial hub for such economic activities. Economic liberalization has been the focus of many developing countries for the past two decades and this has allowed multinational companies with huge investment potential to enrich the weaker economies. What is International Trade? International trade tries to generate more foreign exchange, which is always good for the economy. Say, if a country has rich resources of petroleum, naturally it will try to sell the surplus to countries not endowed with such natural resources. That is why Middle East nations are prosperous and economically independent. The diversity in productive possibilities in different countries is due to the presence of limited natural resources. When a country gets a head start in a particular product, it can become the high volume, low cost producer. The economies of scale give it a significant advantage over other countries, which find it cheaper to buy from the leading producers than to manufacture the product themselves. Barriers for Effective Trade Every nation must try to specialize in the production and export of those commodities, which are available in plenty and must import such products in the production of which they have a resource deficiency. It should be remembered that there are severe man made barriers in international trade such as, export duties, quotas, exchange restrictions etc.,that hinder the free movement of products. International Trade and Finance Nevertheless, it is not also possible for a country to produce domestically every kind of product. In spite of all these restraining factors, global trade is thriving, thanks to the advanced technological aspects introduced in communication and faster means of transportation. Distance is no more a constraint and the world has become one small global village. Foreign Exchange Issues All domestic transactions, say in a country like India take place in rupees, which is the legal tender in the country. However, in its trade with other countries like USA, Germany, Japan, France and Britain, the payments have to be made in terms of dollars, marks, yens, francs and pound sterling respectively. The mechanism through which payments are effected between two countries having different currency systems is called foreign exchange. It may be also defined as the exchange of money or credit in one country for money or credit in another. Foreign exchange rates can affect relative prices and net exports. A rise in the a nation’s foreign exchange will depress that nation’s net exports and output, while a fall in the foreign exchange rate will increase net exports and output. Because of the significant impact of exchange rates on national economies, countries have entered into agreements on international monetary...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Marketing, Principles of Management
on Mar 4th, 2014 | 0 comments
The Realm of Product Innovation A manufacturer or a service provider, who aspires to be successful in a business market, must indulge himself in research, pertaining to consumer preference as well as the various stages of a product life cycle. This will give him a better chance to make his future decisions concerning the product and also the wisdom to evolve strategies accordingly. Developing a product and introducing it into the market demands certain amount of forethought and prudence. The first step is to study the market, to understand consumer preference as well as to gauge whether your product will be appealing to the customers existing in that market. The prerequisite for this would be market segmentation, that is to statistically estimate the demographic quotient (people belonging to different age groups and ethnic societies) of the sample population and decide on the customers whom you want to target. A product’s success depends mainly on two things: 1) Innovation-lateral thinking, by which you let loose of all your unorthodox methods and stick onto some novel ideas of marketing. 2) Customer-oriented marketing rather than product oriented. This customer oriented concept is advocated by modern marketing consultants and it has proven to be a fantastic proposition. More than the actual product, people like to know more about the values that they obtain out of that product. The secret behind success will be to hit the right note, by propagating more about the value added services that go with the product. Expectations Created by the Product When a product is introduced in a market, say, automobiles for example, since every tom, dick and harry is fond of cars and bikes and they talk a lot about it. It is looked upon by prospective customers with great expectations, which might be due to the great hype created by the manufacturer through advertisements in electronic media, papers and magazines. The product as it hits the market will instantaneously make it big, if it has the right mix of intangible and augmented benefits that make customers happy and they feel that they have bought something worth the money paid for. A luxury car is well received by the market, irrespective of the price tag that is stuck to it, just because of the value added benefits such as, delicacy, great speed, high-performance, safety, insurance and warranty. Product Pre-Launch Analysis Before launching a product, industry analysis is a must, as various similar products might exist and it comes to the question of how different and appealing your product is, for market acceptance. Even minor things can make a big difference, say, for instance, if you are able to float the cheapest car, in terms of price but with great fuel efficiency, the results are obvious. The strategy would be to introduce innovations not only in your product but also in your thinking. Best products emerge as a result of tuning in your wavelength with that of the consumers’. Product Life Cycle A product gets introduced, grows, matures, stabilises and slowly withers off, just like a human being. No man is eternal and so is a product. You may argue that some products are in the limelight for more than their share of lifetime. If you keenly observe, that would have been the result of makeover changes to the product in lieu of the change in people’s liking and analysis of market trend. Some products have a second chance to prove their mettle. They go into hibernation for a while and then re-enter when market conditions seems to be favorable. The perspective from which you look at the life cycle of a product may cast a different idea...






