Posted by Managementguru in Economics, Financial Management, International Business, Marketing, Project Management
on Mar 11th, 2014 | 0 comments

What is Trade? Trade is the exchange of commodity and services. International trade represents business transactions taking place at the global level, and it is fundamentally different from domestic trade. Trade at international level demands huge investments, network of franchisees and proficient people to run the show. Many corporate giants are trying to capture Asian markets, especially Indian market, which has become the industrial hub for such economic activities. Economic liberalization has been the focus of many developing countries for the past two decades and this has allowed multinational companies with huge investment potential to enrich the weaker economies. What is International Trade? International trade tries to generate more foreign exchange, which is always good for the economy. Say, if a country has rich resources of petroleum, naturally it will try to sell the surplus to countries not endowed with such natural resources. That is why Middle East nations are prosperous and economically independent. The diversity in productive possibilities in different countries is due to the presence of limited natural resources. When a country gets a head start in a particular product, it can become the high volume, low cost producer. The economies of scale give it a significant advantage over other countries, which find it cheaper to buy from the leading producers than to manufacture the product themselves. Barriers for Effective Trade Every nation must try to specialize in the production and export of those commodities, which are available in plenty and must import such products in the production of which they have a resource deficiency. It should be remembered that there are severe man made barriers in international trade such as, export duties, quotas, exchange restrictions etc.,that hinder the free movement of products. International Trade and Finance Nevertheless, it is not also possible for a country to produce domestically every kind of product. In spite of all these restraining factors, global trade is thriving, thanks to the advanced technological aspects introduced in communication and faster means of transportation. Distance is no more a constraint and the world has become one small global village. Foreign Exchange Issues All domestic transactions, say in a country like India take place in rupees, which is the legal tender in the country. However, in its trade with other countries like USA, Germany, Japan, France and Britain, the payments have to be made in terms of dollars, marks, yens, francs and pound sterling respectively. The mechanism through which payments are effected between two countries having different currency systems is called foreign exchange. It may be also defined as the exchange of money or credit in one country for money or credit in another. Foreign exchange rates can affect relative prices and net exports. A rise in the a nation’s foreign exchange will depress that nation’s net exports and output, while a fall in the foreign exchange rate will increase net exports and output. Because of the significant impact of exchange rates on national economies, countries have entered into agreements on international monetary...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Entrepreneurship, Human Resource, Leadership, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 9th, 2014 | 0 comments
Profile of a successful leader Adaptive Capabilities: Leaders need to radically change their mindset so as to stand the test of time; but the core leadership attributes like vision or creativity, intelligence, commitment, and a healthy dose of luck still continue to define the pre-requisites of success. Integrity of Character is most important when talking about successful leadership. The philosophical undercurrent is that “Be Good, Do Good” and you will be good. The motive must be devoid of mistakes though there is room for mistakes in judgment. Leaders must have a clear vision and be able to communicate this vision to others so that it becomes a shared vision and everybody willingly contributes in fulfilling the vision. Six ‘C’s or six criteria that determine a leader’s credibility Conviction Character Care Courage Composure Competence Cross-Functional Expertise – Acquisition of knowledge should make a leader humble and flexible and gaining knowledge must be seen as a life long experience rather than collection of voluminous data or skills. A leader will try to apply his broad functional knowledge and expertise in the right places and the results will be definitely magnificent. A leader must look into the possible options rather than to plan, the possible rather than the perfect, involvement instead of obedience. Change is the only entity that remains unchanged and it is inevitable for the leaders to consider change as the core element of growth. With accelerated pace of change in the economic, political and socio-cultural environment, leaders not only need to acquire new knowledge and skills but they also need to unlearn many of the things that have out-grown their purposes. Leaders should follow the CODE OF PRIDE to motivate the workforce. P– PROVIDE FOR A POSITIVE WORKING ENVIRONMENT R– RECOGNISE EVERYONE’S EFFORTS I– INVOLVE EVERYONE D– DEVELOP SKILLS AND POTENTIAL E– EVALUATE AND MEASURE CONTINUOUSLY In large corporate organizations, the leader must be willing to share power and control so that leadership is encouraged at various levels. Successful leaders are those who are self-motivated by setting their own standards and compete with themselves. Innovation is the need of the hour What do you mean by innovation? Creating something new or modifying the old one. Here the term innovation implies the change in the “THOUGHT PROCESS” of leaders who are able to turn a crisis into an opportunity. Also called as “THINKING OUT OF THE BOX” where a leader finds new application for old ideas which cannot be discarded or dis-regarded. “You must learn from your past mistakes but not Lea(r)n on your past successes”. High achievers take moderate risks calculating the circumstances and they rely on their own abilities unlike low achievers who invariably like to minimize risks or take wild and irrational risks. Running a corporate business has become more like an experiment since we cannot control or predict the future. It is highly unstable and unpredictable. So leaders have to cope up with this non-linear force acting in the external environment building up pressure. Leaving things as they are can be just as predictable as changing everything, you lose or win both ways. Now let us look at some of the definitions of Leadership 1. “Leadership is generally defined as influencing people so that they will strive willingly towards the achievement of group goals.”- Koontz and O’Donnell 2. “Leadership is the lifting of man’s visions to higher heights, the raising of man’s performance to higher standards, the building of man’s personality beyond its normal limitations.”- Peter F.Drucker 3. “Leadership is the ability to secure desirable actions from a group of followers voluntarily without the use of correction.”- Alford and Beatty 4. “Leadership refers to the quality of the behavior of individuals where by they guide people on their activities in organized efforts.”- Chester I.Bernard Behavioral Commitments of a Leader: Challenging the process Challenging the status quo and act as radical change agents Inspiring others by being pioneers, instigators, navigators and learners Showing risk-taking ability,...

Posted by Managementguru in Human Resource, Labor Management, Training & Development
on Mar 9th, 2014 | 0 comments
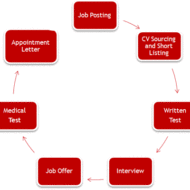
HR Selection Process and Techniques Following the process of recruitment is selection, where the management has to select the right employees at the right time. The intention is to choose appropriate candidates for the unfilled spots and to avoid commitments to those whom the management thinks will not work well. The best qualified individuals from the pool find their place whose qualifications match the job specifications. What is the Selection Process in Human Resource Management? Selection process depends upon the · Size of the company · Nature of the business · Kind and Number of persons to be employed · Government regulations to be followed etc. The process includes 1. Collection of data about the candidate’s qualification 2. Experience 3. Physical and mental ability 4. Nature and Behavior 5. Aptitude and the like Steps in Scientific Selection Process: A. Job Analysis: This is the basic step for finding the right candidate and each organization should lay down job analysis, job description and job specification with clarity in order to lure the right candidates for selection. B. Recruitment: Process of searching for prospective employees and stimulating them to apply for jobs in the organization. C. Application Form: This is also known as the application blank. This facilitates collecting detailed information from the prospective employees regarding their age, gender, family details, qualification, skills, experience, achievements etc. This is widely used to screen employees at the preliminary level. D. Written Examinations: are conducted to gauge the · Mathematical ability · Aptitude · Reasoning · Knowledge in various disciplines · General Knowledge and · English language abilities of the candidates. E. Preliminary Interview: This is suitable to eliminate the undesirable and unsuitable candidates and also to gather personal information from the candidates on a one to one basis. F. Group Discussion: Group discussions help the management to pick out bright candidates from among the group members and also the ability of each individual to adjust to the group. Each group is expected to analyze, interpret and find alternate solutions and select the best solution for a particular case study or subject matter. G. Tests: To further assess the skills of the employees the management conducts different kinds of tests. H. Final Interview: This is the most essential step in the process of selection. The interviewer matches the information obtained about the candidate through the application with that of his own observation and questioning. · Informal · Formal · Planned · Patterned · Non-Directive · Depth · Stress · Group and · Panel interviews are some of the types of interviews conducted in accordance with the job requirement. Also See: Interview Preparation Tips I. Medical Examination: Certain jobs require certain physical qualities like clear vision, perfect hearing, unusual stamina, tolerance of hard working conditions, clear tone etc. J. Reference Checks: The personnel department will engage in checking reference if the candidate passes all the tests and found suitable for the job. What kind of Companies the Employees are Attracted to – Here is an interesting infographic on “How to Attract the Perfect Employee”...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Principles of Management
on Mar 3rd, 2014 | 0 comments
Centralization and De-Centralization Concepts CENTRALIZATION: The term “centralization” has several meanings: Centralization of Performance: Say, if the operations of a company is restricted to a single geographical location, it characterizes centralization of performance. Departmental Centralization: Specialized activities are carried out by a single department, say, maintenance of a whole plant, staff recruitment by HR department etc., Centralization as an aspect of management: This implies restricted delegation and exclusivity of decision-making by the top management. According to Allen, “Centralization is the systematic and consistent reservation of authority at central point in an organization.” According to Weihrich and Koontz, “Centralization (as an aspect of management) is the tendency to restrict delegation of decision-making. What are the special circumstances that force the managers to reserve authority and centralize decision making powers? 1. To facilitate personal leadership 2. To provide for integration 3. To handle emergencies 4. To utilize resources effectively and instantaneously. DECENTRALISATION: It is the tendency to disperse decision making authority in a structured and organized manner. It can be viewed as a philosophy rather than a principle where-in “discretion” plays a major role in deciding which decisions to push down into the organization structure and which to hold near the top. Capital expenditure, Investment analysis and major policy decisions have to be dealt with, by the top management. It is the systematic effort to delegate to the lowest levels of authority except that which can be exercised at central points. TYPES OF DECENTRALIZATION: Three approaches to the concept are: 1. PROFIT CENTRES 2. COST EXPENSE CENTRES 3. INVESTMENT CENTRES Profit Centre: Here the organization is split into divisions on a “product basis” and is given full authority to handle its own scheduled operations, right from placing orders to negotiating the sale of its finished products. Cost Expense Centre: Whenever it is easy to determine the cost of operations, cost centres are established. Cost centres run on “budgets” which acts as a control tool to run the units within the specified budgetary limits. Investment Centre: Useful in the case of big multi-product enterprises where product performance is measured by decentralizing the investment aspect. Each strategic business unit is responsible for the acquisition, use and disposition of fixed resources. Advantages of Decentralization: Managers and executives are relieved form excessive work pressure Even low level employees are involved in decision making thus bringing the decision making process closer to the scene of action. It facilitates product-diversification Creates an opportunity for learning Ensures effective control When a big organization is divided into relatively smaller units, it becomes flexible and also effects close control. Disadvantages of Decentralization: · Conflict arises between people belonging to different levels of the organization · Rising cost · Lack of co-ordination between production and marketing departments · No defined leadership Contingency Factors in Decentralizing: 1. Organizational goals 2. Organizational size 3. Geographical dispersion 4. Technical complexity of tasks 5. Time frame of discussions and decisions 6. Subordinates’ take on issues 7. Planning and control procedures 8. Environmental factors 9. Knowledge and experience of managers Effective Decentralization can be accomplished by · Establishing appropriate centralization · Developing efficient managers · Proper provision for communication and co-ordination · Establishing adequate controls Top management must be willing to delegate authority towards decision making; Middle management must be willing to accept responsibility that is being delegated. Only then effective decentralization is...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Training & Development
on Mar 1st, 2014 | 0 comments

Performance Appraisal Performance Appraisal is considered to be the most significant and indispensable tool for an organization. It is a measure of the employees’ performance levels in terms of the specific job’s requirement. It is a process employed for the purpose of placement, selection for promotions, providing financial rewards and other actions which require differential treatment among the members of a group. Purpose of Performance Appraisal Douglas McGregor says “Formal appraisal plans are designed to meet three needs, one of the organization’s and the other two of the individual namely, Performance appraisal methods facilitate systematic judgments to decide on the salary increases, transfers, demotions or terminations. They serve as a yard stick for an employee as to where he stands in the performance rating queue in the eyes of management and how he needs to adapt or improve himself regarding behavior, attitude, skills or job knowledge. They are used as a means to train and counsel each and every employee by the respective superiors. Performance appraisal can also be termed as Merit rating Behavioral assessment Employee evaluation Personnel review Progress report Staff assessment Service rating. According to Levinson, it definitely provides adequate feedback to each individual for his performance and also serves as a means for changing behavior. Prime Objectives of Performance Appraisal: Helps to maintain man power inventory of an organization which includes quantity and quality, to identify the training needs and aspirations of the work force. To determine increments and provide a reliable index in promotions and transfers to positions of greater responsibility. To improve individual as well as group development by determining the performance standard and motivating the employees to perform well. Providing support to employees who are not able to focus and to bring them back into the groove. The Process of Evaluation: Establishment of performance standards. Communicating the same to employees. Aquiring information through personal observation and statistical reports from the respective departments. Appraising and judging the future potential growth and advancement. Identifying the deviation between the actual and standard performance levels. Discussion with the employee for subsequent improvement or corrective action. Appraisal Summary: 1. Personnel Background covering the following details are collected Age Family background Marital status Children Education Specialization and degrees Office held Work history Social accomplishments Honors and awards Professional or trade organization membership Publications Special limitations Family problems Hobbies and recreational activities 2. Nature of Work: Job performance and personal qualification Technical performance Level of motivation in current position Intelligence as reflected on the job Emotional stability Leadership skills 3. Overall Performance Rating: Recommended action Knowledge Skill Attitude Methods of Performance Appraisal: Traditional methods: These rely upon evaluating an individual’s creativity, intelligence, drive, dependability, leadership potential, initiative and organizing capability which are more of personal in nature. Modern methods: These include ranking method, graphic rating scales, forced choice description method, critical incident and 360 degree evaluation methods. The 360 degree appraisal method is employed in big corporate companies where the individual’s overall performance is appraised by his colleagues, boss, customers, suppliers and stake holders. Management by objectives, management by exception , self appraisal and human asset accounting are other methods used for appraisal. Problems that may arise during performance appraisal: Halo Effect: It is a tendency to let the assessment of an individual’s any one trait to influence the evaluation of that person on other specific traits. The Central Tendency problem: It assigns average rating to all the employees in order to avoid commitment. Similarity error: This occurs when the evaluator evaluates other persons based on ‘self perception’, that is if he perceives himself to be adventurous or daring he may evaluate others looking for that same trait which he possesses. How to make appraisal successful? The superior must be well trained and a composed person to judge without...










