Posted by Managementguru in Human Resource, Labor Management, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Training & Development
on Mar 18th, 2014 | 0 comments

Evolution and Growth of Human Resource Management It is very interesting to trace out the evolution and growth of Human Resource Management. People – The Principal Resource The principal resource of any organization is people and managing people is the most important and challenging aspect of an organization. What we call human resource management today, dates back to 1800 b.c.,which is evident from the inscriptions of Babylonian code of Hammurabi and Kautilya’s Arthasashtra, which explains in detail the importance of selection, incentives, performance evaluation, quality of a manager and wage rates. So,we understand that the concept of managing people has existed even in the previous eras through ancient literature and philosophy. India, China and Greece have been the origin points of human resource management concepts. Evolution of Human Resource Management Industrial Revolution Till, 1930’s, there was no such department called “personnel management” that was considered necessary to cater to the needs and welfare of the labor society. The factory manager was acting as a link between the workers and the management, and most of the time he had to comply with the rules of the management to satisfy them, even if it were against the welfare of the workers. Also proper attention was not given to areas like, worker safety, security and living conditions. Industrial revolution saw mass exodus of workers to urban areas in search of jobs. Need for Employment Department Application of science and technology in production made the rich owners even richer; the poor workers were not paid adequately and their life became miserable. Since the owners lost direct contact with the employees, managers came into the picture to take over control of production and administration. Machines ruled the industry and importance of labor got reduced. This condition existed for sometime until the advent of new and improved management concepts by people like F.W.Taylor who is considered to be the father of scientific management and B.F.Goodrich who was instrumental in forming the “employment department” which can be considered the fore runner of present human resource department. Introduction of Scientific Management Scientific methods were introduced to make the workers perform the job with ease and perfection. It also saved enormous time and reduced the monotony of work. job-designs, job-specification, training and development and human relations were given due importance and the owners slowly started realizing the importance of labor. Through 1940’s to 1970’s behavioral approach was applied to professional management, the major architects being Abraham Maslow, Herzberg and Douglas McGregor. This approach suggested managers to modify their leadership styles to suit the type of followers and motivate the workers. Consequences of World War I and II World War I and II also had profound influence on Human resource development. The concepts of role playing, improved training methods, supervision and group discussions came into the fray. The advent of labor unions also established a clear pathway for the workers to claim their rights, ably supported by the labor laws enacted by various governments. International labor organization was formed in 1919 which created sensation in the worker community all over the world. All said and done, empowerment of workers has been achieved only in developed nations where “job security” is no more a great concern because job opportunities are more. But in unorganized and small sectors, employers continue to exploit workers because “supply” is more than “demand”. The responsibility to develop and empower the employees solely lies on the shoulders of human resource department. It should try to address the problems of workers to the management and amicably settle issues relating to wages, welfare, safety and security. → Objectives and Functions of...

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting
on Feb 21st, 2014 | 0 comments
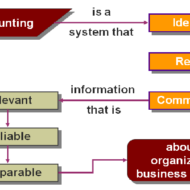
Functions of Accounting: a. Recording: Accounting records business transactions in terms of money. It is essentially concerned with ensuring that all business transactions of financial nature are properly recorded. Recording is done in journal, which is further subdivided into subsidiary books from the point of view of convenience. b. Classifying: Accounting also facilitates classification of all business transactions recorded in journal. Items of similar nature are classified under appropriate heads. The work of classification is done in a book called the ledger. c. Summarizing: Accounting summarizes the classified information. It is done in a manner, which is useful to the internal and external users. Internal users interested in these informations are the persons who manage the business. External users of information are the investors, creditors, tax authorities, labor unions, trade associations, shareholders, etc. d. Interpreting: It implies analyzing and interpreting the financial data embodied in final accounts. Interpretation of the data helps the management, outsiders and shareholders in decision making. Limitations of Accounting: Accounting information is expressed in terms of money. Non monetary events or transactions, however important, are completely omitted. Fixed assets are recorded in the accounting records at the original cost, that is, the actual amount spent on them plus all incidental charges. In this way the effect of inflation (or deflation) is not taken into consideration. The direct result of this practice is that balance sheet does not represent the true financial position of the business. Accounting information is sometimes based on estimates; estimates are often inaccurate. Accounting information cannot be used as the only test of managerial performance on the basis of more profits. Profit for a period of one year can readily be manipulated by omitting such costs as advertisement, research and development, depreciation and so on. Accounting information is not neutral or unbiased. Accountants calculate income as excess of revenues over expenses. But they consider only selected revenues and expenses. They do not, for example, include, cost of such items as water or air pollution, employee’s injuries, etc. Accounting Made Easy Accounting like any other discipline has to follow certain principles, which in certain cases are contradictory. For example current assets (e.g., stock of goods) are valued on the basis of cost or market price whichever is less following the principle of conservatism. Accordingly the current assets may be valued on cost basis in some year and at market price in another year. In this manner, the rule of consistency is not followed...




