Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Entrepreneurship, Marketing, Startups, Strategy
on Dec 21st, 2017 | 0 comments
Let’s Learn the Nuances of Business Strategy How Do You Define Business Strategy? Business strategy is nothing but a series of decisions that are made by the management of a company in order to obtain or maintain a competitive advantage over a period of time. It shows the overall direction of a company. It is also future focused and contains long-term sustainable goals. For startups, creating business plans can be night marish and hectic, hence this short guide which throws some light on “How to use Powerpoint as an effective tool to showcase your bsuiness plan” to investors in a simple yet appealing manner. A great business strategy will encompass the following characteristics: A clear direction of where the company is going and concrete plans necessary to execute the decisions An unmistakable understanding of the company’s core competencies Will solve the marketplace demands and address real customer needs Will contribute to sustainable competitive advantage Will be properly documented but gives room for future change in accordance with the environment THE THREE BEST GENERIC BUSINESS STRATEGIES 1. COST LEADERSHIP This strategy is followed by market giants like Wal-Mart, McDonald’s, IKEA to name a few wherein, the companies focus on building a large market share by slashing the prices – mush lower than their competitors. Typically, such customers will be less loyal and more price-sensitive. The real challenge is to succeed at offering the lowest price, but still maintain profitability and a high return on investment. The company has to necessarily run a tight ship by controlling its operational costs to improve efficiency. 2. PRODUCT DIFFERENTIATION This strategy requires the company to develop products that are “better than” or “more unique than” its competitors. The main focus is to differentiate itself from its rivals. The differentiation could be in the form of higher-end quality materials, excellent customer service, unique company image or branding, or other customer oriented values. Typically, companies going for this strategy can charge premium pricing since their customers tend to be more loyal and less price-sensitive. 3. MARKET SEGMENTATION This strategy simply focuses on a niche or sub-market to sell your products or services to. This is best suited when you are competing in an overly saturated market. For example the gift basket industry is highly competitive and over saturated. If you choose to enter the field, you might have to choose a product differentiation strategy combined with appropriate market segmentation strategy. Hence you might focus on selling high end products to the wedding market. A Wonderful Infographic from Americanexpress.com that clearly explains what needs to be done to experience an explosive business growth… WHAT TO DO WHEN BUSINESS IS SLOW Write a business plan If you have never written one now is the time to grab a chair and fabricate a really crafty business plan with your mission, vision, values and marketing strategy included. Rebrand Work on your logo, test new colors, change your site layout, breathe some fresh life into your branding strategy. SEND A THANK YOU NOTE TO YOUR CLIENTS FIND NEW VENDORS Read a book Discover guerilla marketing tactics and best keep business secrets by reading Cold Pitch Create a list of prospects using leading networks like LinkedIn and reach out via email Create a lead magnet A lead magnet is an opt-in gift that you offer visitors, whether online or offline to encourage them to be part of your tribe and purchase your product or services. Let’s understand what makes a company innovative? 48% – coming up with new ideas for products and services 33% – listening to customers 33% – continuing to improve current product 33% – offering a unique product 28% –...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Decision Making, Entrepreneurship, Marketing
on Sep 21st, 2014 | 0 comments
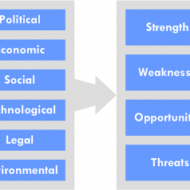
Business Viability Checklist for Entrepreneurs Hey Folks, here is a checklist for business viability or feasibility analysis, the fore-most step before starting a venture. Whether you are a dare devil driver yearning to embrace entrepreneurship as a result of your eternal frustration of saying” Yes-Boss” 24/7, or a first generation entrepreneur , this checklist will be of immense help in that it will reduce the elements of uncertainty and risk. Unlock massive growth using the business development channel. Learn pitching, BD strategy, cold emailing, & deal closing. Bestselling **** Many businesses look at profit within quotes as ultimate viability. Even if the business is not currently profitable or undergoing a growth surge, or just going through a bad patch – there is an anticipation of being profitable at some future date. This hope of future profit warrants continued investment. We can also consider the social and environmental aspects of an organization adding value, if it satisfies any social costs. You need to know what is viability? Viability is defined as the ability to survive or persist. In a business sense, that ability to survive is ultimately linked to financial performance and position. A business is viable where either: it is returning a profit that is sufficient to provide a return to the business owner while also meeting its commitments to business creditors it has sufficient cash resources to sustain itself through a period when it is not returning a profit. ASK YOURSELF THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS BEFORE STARTING-UP THE OPEARTIONS: Why are some companies PROFITABLE and some not? Why do some companies CONTINUE TO EXIST and some not? What does success and survival mean? How ESSENTIAL is profit? How can a company survive when it is not making a profit? How can a company NOSE-DIVE when it is making a large profit? How VITAL is growth? Can a company become NON-VIABLE simply because it fails to maintain its year-on-year growth? How imperative is CORPORATE IMAGE? Are these factors relevant to business viability? The following post from franchisesunder10k.net provides great insight on easy online businesses to start in 2018. https://franchisesunder10k.net/these-are-the-easy-online-business-opportunities-you-ve-been-looking-for Fundamentals of a Feasibility Plan • Provide key information needed by investors and bankers • Reasons for its chance of success/failure • Supporting Documents • Explanation of the principal concept underlying your venture and what sets it apart from other businesses. Infographic Courtesy : Entrepreneur.com SOME OF THE REASONS WHY NEW VENTURES FAIL • Lack of Objective Evaluation • No Real Insight into the Market • Inadequate Understanding of Technical Requirements • Poor Finance Understanding • Lack of Unique Selling Proposition • Ignorance of Legal Issues Let us now look at some of the important dimensions of business viability: Market viability Technical viability Business Model viability Management model viability Economic and Financial Model viability Market Viability: Utilize Porter’s 5 Competitive Forces Model to understand market viability and industry position. Technical Viability: You do not have to incorporate specific financial information in the technical portion of your feasibility study, but all data in this component must support your financial figures represented elsewhere. Basic things that most businesses need to include in their technical feasibility study include: Materials Labor Transportation or Shipping Physical Location Technology Business Model Viability: P.E.S.T. Analysis A PEST analysis is a business measurement tool. PEST is an acronym for Political, Economic, Social and Technological factors, which are used to assess the market for a business or organizational unit. Management Model Viability: Decision making process Training and Cross-training Management Capability to effectively lead the organization in a sustainable growth mode Management Systems and processes, and General Leadership Capabilities are scrutinized. Economic and Financial Mode Viability: Capital Structure Cash Management Profitability and Liquidity are dealt with when...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Marketing, Principles of Management
on Mar 4th, 2014 | 0 comments

Trends in Consumer Marketing FMCG’s: Consumer marketing is defined as creating and selling products, goods and services to individual buyers, as opposed to trying to appeal to businesses. You would have often heard about this – Fast moving consumer goods. These are nothing but products that are destined for use by ultimate customers or households that cannot be done with, as their usage is on a day to day basis. It might make some sense if I cite some examples – toothpaste, soaps, shaving creams, talcs, body lotions; these are meant for personal consumption and the demand for such products is direct and needs less of relationship marketing. Brand Focus: The number of customers in the consumer market is relatively large and the product purchase is influenced by even emotional factors. The focus is on the brand name and some people ardently follow a particular brand for ages, and this might be attributed to the effect that has been created by mass media advertising, or it might be due to the fact that they might identify themselves in some or the other with the product. It becomes a personal companion over a period of time. Impulse Buying: The decision making process is informal and often simple. Sometimes, it is influenced by the budget equations and feasibility. Impulse buying is also common in consumer market. At times, the consumers go adventurous and like to try their hands on new products. Branding is an important feature that retains the customer base for business firms and that’s why market analysts are attaching so much of significance to advertisements and sales promotions, to make their product a household name. Distribution Network: The firms must have a pucca distribution network linking different parts of the territories, where they want to expand their market. Say, for instance, a soft drink can be made popular by branding, but if there is no sufficient supply in the market, how do you expect customers to support your product? Equally important is providing the customers with a product size that best suits their budget. Consumer Marketing Infographic: Researchomatic.com Market Segmentation: Market segmentation recognizes the existence of distinct market groups, each with a distinct set of needs. Through segmentation, the firm directs its product and promotional efforts towards those markets that will benefit most from or will get the greatest enjoyment from its merchandise. Over the years, segmentation has become a popular strategic technique as the market is ever flushed with competitors. Influence of Price: A number of sellers are seen in this kind of consumer market and it is only the market that decides the price and not the participants. The marketers have nothing to lose if they sell at the market price, but if they plan to sell at slightly higher price levels than that of the market, it will prove detrimental to their objective. https://www.businessmodelscholar.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/3.pdf They are only price takers and not price makers. But they have the leverage to freely enter and exit the market. If the consumers foresee a fall in the general price levels of a product, they wait for some more time to take full advantage of the situation and decide to postpone the purchase. If the market shows an increasing price trend, it is the other way round, either they buy in bulk or go for substitutes.Say, if the price levels of coffee is on the rise, people opt for tea. Demand for consumer goods is price elastic. Consumers don’t care for much technical specifications; they only care for the quality backed up by a strong brand name. Post by Free MBA...






