Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Decision Making, Human Resource, Principles of Management, Strategy
on Mar 23rd, 2014 | 0 comments

Strategy implementation is the transformation of chosen strategy into organizational action so as to achieve strategic goals and objectives. The journey towards success is a saga or penance, where your effort and concentration is focused only on achieving the goal. It can be compared to the blinkers of a horse to give direction and avoid distractions. Proper resource planning is the key factor that gives a practical shape to your strategies. The available resources should be put into optimum use. Corporate Resource Planning: Resource planning at the corporate level comprehensively covers the planning for physical resources, human resources, financial and intangible or intellectual resources like patents, copyrights, technology, trademark etc., at the macro level of the firm. These are needed for the corporates to achieve their vision and also give direction to the departments at the functional level. These resources are allocated after giving due consideration to the industry’s cycle position, competitor strength, technological changes in the industry, market share and the type of competition in the industry. Economic Models with Value Additions: For instance, automobile owners have tapped the customer psychology and are concentrating more on producing bug cars that is very appealing to the upper middle class families, since a four wheeler is more comfortable and safe to drive, well within the budget range, ideal for a nuclear family and at the same time serves the purpose of a status symbol. So, these car manufacturers become direct competitors for two wheeler producers. Even if say, 25 to 30 percent of two wheeler population is shifted to four wheeler usage it is a huge success to the car manufacturers. Tata Nano car, a brain child of Ratan Tata is one of its kind. He has capitalized on the middle class Indian frame of mind to go for economic models with value additions. “Nothing is permanent except change”, so in this fast moving business arena all business persons are subjected to the necessity of thinking new, if not big. Corporates concentrate more on their strategic business units which serve as functional units and also a part of an organization, say a factory or a showroom. The resources for each of these business units have to be planned. The human resource department has to play its part in a promising way as human personnel are the critical success factors of an organization that manipulate other resources efficiently. Product and Process Innovations: Product and process innovations are the need of the hour and corporates are spending huge amounts on research and development of new products and processes. It has to be kept in mind that the innovations have to reach the markets quickly in order have an edge over your competitors. Identify your strength Tap the unidentified needs of the consumer Allocate management responsibility for each task Set your priorities by resource rationing Test your key assumptions Whether your product is acceptable in the market Whether the technology is updated All of these help you in forming a strategic platform upon which strategic implementation is done. Rational and realistic assumptions are the basic premises on which your decisions have to be based. Adequate finance, machinery and maintenance, labor force, marketing mix, your product strength, critical success factors of your organization, everything has to be thoroughly analyzed and put into action for successful strategic implementation. Related Videos… Alternative Competitive Advantage Introduction to Strategic...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, International Business, Marketing, Principles of Management
on Mar 11th, 2014 | 0 comments
Key Strategies of Global Marketing Globalization means many things to many people. For some it is a new paradigm – a set of fresh beliefs, working methods and economic, political and socio-cultural realities in which the previous assumptions are no longer valid. For developing countries, it means integration with the world economy. It can be better understood if we look it at this perspective- “the world integrated into one huge market”. It calls for the removal of all trade barriers among countries and a perfect competitive market prevails and the stress can lead to many positive and possible outcomes in terms of QualityQuantityUniquenessForeign exchangeBenefits to the host countryIncreased productivity leading toEconomic growth Well, it does not end there. An MNC (multi national company), by operating in more than one country gains r and d, production, marketing and financial advantages in terms ofcost and labor that other competitors may not enjoy. The global company views the world as one market, minimize the importance of national boundaries, sources, and raise capital and markets wherever it can do the job best. Why do companies go global? One reason could be the rapid shrinking of time and distance across the globe thanks to faster communication, speedier transportation, growing financial flows and rapid technological changes. It is being realized that the domestic markets are no longer adequate and rich. Japanese have flooded the U. S. Market with automobiles and electronic goods because the home market was not big enough to absorb whatever was produced. Companies at the first stage of globalization have only passive dealings with foreign individuals and organizations. By the second stage, companies deal directly with their overseas counterparts, though they might continue to use third parties also. The company might decide to set up an import or export department. Next comes the shedding of domestic capacity and floating an international organization and have a direct hand in exporting, importing, and perhaps producing goods and services abroad. Seldom companies reach this stage, even if they do, they recede later. The company can have a strong foothold in the countries it is organizing its activity only by way of * Superior product quality* Demand* Customer preference for that particular product range that the company offer* A dynamic CEO projecting and boosting company’s image,* Brand image* Availability of skilled labor* Licenses* Access to necessary infrastructure* Feasible financial structure* Viability in the long run* Marketing mix Chennai in India has become a hub for so many corporate as well as global companies since the business climate is very favorable and enterprising. Some of the strategies in globalization would be * Deciding whether to go global* Deciding which markets to enter* Deciding how to enter the market* Learning to handle differences* Adjusting the managing process* Deciding organization structure* Selecting a managerial approach. Developing countries like India have adopted new economic policies that are expected to encourage the international companies setting their foot in India, by which it compels many Indian companies to pursue internationalization vigorously. True globalization marks the beginning of a new economic era of growth and...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Marketing, Principles of Management
on Mar 4th, 2014 | 0 comments

Price Discrimination is nothing but a pricing strategy that charges customers different prices for the same product or service. Price discrimination is adopted by most of the firms in order to group their customers into different segments and fix different prices for each segment for identical products and services. This helps them to increase their revenue as well to cater to the needs of different customer groups. The negative aspect of this exercise is increased administrative costs in segmenting the markets and some people end up paying higher costs. But it has to be remembered that by discriminating prices, firms are able to cut through and exploit all layers of the market, helping them to expand. Elasticity of Demand Price discrimination can be practiced by a firm only which has some control over the price. Backgroung Image Source: Image by Gerd Altmann from Pixabay Obviously a price taker cannot indulge himself in price discrimination. It must be possible to group different markets in terms of price elasticity of demand. Suppose a firm identifies two potential markets, fixes high price for one market and low for another, caution is the key word in that, both the markets should be separable. Otherwise there is the danger of purchasing a product in one market for a lower price and the same being resold in another at a higher price. It might damage the market reputation of the firm as well. Skimming the Profit The process of price discrimination is followed by most of the firms existing in monopolistic and oligopolistic markets, where there is a necessity to exploit potential customers at the earliest in order to skim the profit. Premium customers are targeted first, followed by middle income group and then lower income group. Recent marketing strategies allow middle and lower income group to enjoy all the material comforts and luxuries available for the premium class, by arranging for loans to be settled in equated monthly installments over a period of time. The firms are also engaged in associating themselves with financial institutions and banks, which proves to be a win-win situation for both. Following are some examples cited for your understanding about price discrimination: In legal and medical professions, charging of lower fees to the low income than to high income group.Charging of lower prices abroad than at home for a variety of products and services ranging from books and medicines to movies.Charging of lower prices for elders and children in public transportation and airlines.Charging of lower hotel rates for conventions and meetings.Electronic industry, where the price set initially is high and then it falls down gradually. Firms believe that by offering different prices to different customer groups, can retain the customers and prevent them from switching over to another supplier. Travel agencies offer fanciful package tours with attractive and competent prices that are irresistible. Such is the power of marketing when presented in the right mix targeting the right customers at the right...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Marketing, Principles of Management
on Mar 4th, 2014 | 0 comments
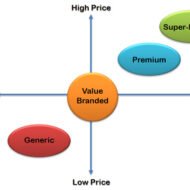
Factors to be Considered for Product Pricing: Price is one of the crucial components of the marketing-mix and plays an important role to bring about product market integration. It is the only factor that generates revenue, the reason why much research is done before fixing the basic price of a product. In a narrow sense, price is the amount of money charged for a product or a service. But in a broader perspective, it is the sum of all values that a customer gain by exchanging money for using a product or enjoying a service; now, what do you mean by values? It may denote customer satisfaction, endurance, efficiency, effectiveness of the purchase etc. Establish the Pricing Objectives: How does a business firm go about fixing the price? The first step would be establishing the pricing objectives based on the factors that govern the price and ascertaining their relevance and importance in the light of prevailing economic conditions. The firm must provide the customers with the value worth the money paid for. Thus determining the product value in monetary terms and formulating pricing policies and strategies accordingly is very important. Price is influenced by both external and internal factors. The internal factors that influence pricing may be, Corporate objectives and marketing objectives of the firm-Obviously a firm would like to survive in the market by maximizing its profit followed by retention of market share. To retain the existing customers and to attract new customers, a firm has to focus on “quality” and “customer service”. If you lose an existing customer, it is equivalent to losing ten new customers, as loyal customers increase your customer listing. Where do you want to stand in the market is another question you have to ask yourself! The desirable market positioning of a firm is also dependent on price fixation mechanisms. The characteristics of a product also influence the pricing, as the nature decides the mode and cost of production. Price elasticity or demand of the product-A hardcore business person will never try to penetrate a new market with his existing product or introduce a new product in existing markets without substantial marketing research, since the demand for the product may very form market to market and only by “test marketing” does a firm can acquire some insight about the nature of demand. Cost of marketing-Without proper canvassing you cannot expect your product to hit the right note. There should be sufficient financial planning that well falls in line with your marketing plan. The external factors that influence pricing may be, Market characteristics-Here, industry analysis is needed, to gauge the trend of the products of similar nature and the stage of the industry in its life cycle-whether it has reached the saturation point. If so, how can you expect to make a mark in an industry that is already falling back? Sometimes, the industry might be thriving, leaving behind certain firms that cannot meet the expectations of the industry. In such cases too, caution is to be exercised to predict your chances of success based on your merits and shortcomings. Bargaining power of the customers-you cannot expect to sell premium products in a market where the potential buyers belong to the middle class category. Even such markets are captured by intelligent marketers who follow the strategy of price skimming. Competitor’s pricing policy-Constant updates about your competitor’s pricing strategy keeps you at bay and also helps you in deciding your game plan. Big corporate firms very rarely come for a compromise in pricing terms, brushing aside their prejudices, if it proves to be win-win situation for both. Government’s regulations on pricing-When you plan to expand...








