Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Entrepreneurship, Financial Management, Project Management, Startups
on Jul 19th, 2014 | 0 comments

What is a Startup Cost? Non-recurring costs associated with setting up a business, such as accountant’s fees, legal fees, registration charges, as well as advertising, promotional activities, and employee training. Also called startup expenses, preliminary expenses, or pre-opening expenses. Let me clarify that this discussion pertains to small and medium size enterprise startup costs and not about capital budgeting. Any project that an entrepreneur wishes to undertake has four factors to be considered. Men Material Machine Money Finance is the lifeblood of any business and to be successful, one must, inject sufficient capital into it. Many businesses fail because of under-capitalization. Seed Money Requirements To determine how much seed money you need to start, you must estimate the costs of doing business at least for the first year. Expenses may be categorized as ‘one-time costs’ such as the fee for incorporating your business or the price of a sign for your building. Some will be ‘ongoing costs’, such as the cost of utilities, inventory, insurance, etc. There is a pressing need for you to bring enough working capital to run the day-to-day business affairs. Without a projected fund flow statement and proposal, no bank or financial institution shall offer you long term loans to run the business. First of all, you need to write the business plan and ask yourself the following questions. Ask yourself these 20 questions to make sure you’re thinking about the right key business decisions: Why am I starting a business? What kind of business do I want? Who is my ideal customer? What products or services will my business provide? Am I prepared to spend the time and money needed to get my business started? What differentiates my business idea and the products or services I will provide from others in the market? Where will my business be located? How many employees will I need? What types of suppliers do I need? How much money do I need to get started? Will I need to get a loan? How soon will it take before my products or services are available? How long do I have until I start making a profit? Who is my competition? How will I price my product compared to my competition? How will I set up the legal structure of my business? What taxes do I need to pay? What kind of insurance do I need? How will I manage my business? How will I advertise my business? Courtesy – http://www.sba.gov/ See ‘Short Term Financing’ to know more about financing your business. The term finance sanctioned in the form of ‘Term Loan’ is required for Land and site development Building and civil works Plant and Machinery Installation expenses and Miscellaneous fixed assets which comprise vehicles, furniture and fixtures, office equipment, workshop and laboratory equipment, distribution of power and water supply etc. Expenditure on infrastructure facilities like water supply, power connection, roads, transportation etc., has to be particularly considered if the units are located in economically backward areas. Startup...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Training & Development
on Mar 22nd, 2014 | 0 comments
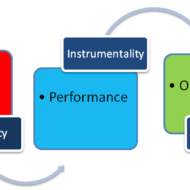
How to create an effective and Sustainable Model for Training and Development? The term “change” is synonymous with competitiveness in modern world and thus corporate firms are in a position to evolve unique, sustainable and strategic training model for employees that will facilitate the following: On one hand the training process motivates the suitable employees to perform well and makes them perceive their role properly in order to accomplish the enterprise objectives. On the other hand the organisation keeps itself abreast by constantly updating and understanding the training needs through Assessment of the external environment and Expectations of the employees in terms of rewards whether intrinsic or extrinsic. Porter and Lawler Model: The Expectancy Motivation Model of Porter and Lawler serves as an inspiration for effective training. The stress is on The value placed on performance outcome by the individual. The degree to which the individual believes that his efforts will lead to attainment of these rewards. Psychological aspect of this model: Almost all individuals are motivated by money ( by the way, Who doesn’t want money!). But money alone does not serve the purpose of motivation. Job satisfaction is a relative term in that different people find different things or elements motivating them in their work environment leading to job satisfaction. It might be Challenge Good inter personal relationship Pay Perks Culture Excellent leader Pressure Stress and the like… Assessment of training need: The training needs must be assessed by the respective organisations considering the following aspects: To transform the individual from the capacity of learner to executor Instil in him confidence to do the job well Relate his job to rewards so that he will try to excel Give your employees scope for career advancement Incorporate technical and technological innovations as part of your training process Physical, emotional and social elements in the internal as well as the external environment must be taken into consideration while training the workforce. Physical– relates to the physical fitness needed to perform the technical skills Psychological– relates to keeping the morale of the employees high at all points and maintaining an amiable work atmosphere Social– relates to the friendly relationship that should exist between the trainer and the trainees and among the trainees. Usefulness of the model: This model lends its support to the training and development process through three steps or stages. Diagnosis stage- Need analysis Formulation stage- Programme planning Evaluation Diagnosis stage: The interplay of ability and role perception Training brings out EFFICIENT as well as DEFICIENT performers. That is one good thing and also making the employee understand the role he is about to play as part of the organisation. Training through learning is one aspect which imparts knowledge and training is considered to be effective if one’s behaviour is modified as per the expectations and demands of the job. Role perception can be misunderstood by some individuals when they might try to exercise undue authority or overlook their duties and responsibilities. Confinement of authority Superior-Subordinate appraisal procedures Clear HR policy formulations are needed to avoid confusion and chaos in role playing. Formulation stage: The effected change through learning is expected to be retained by the employees throughout the career span in the organisation followed by constant grooming. The stress is on the value of the activity to be learnt Giving feedback on the progress of employees towards final training objectives Relate the learning activity to increasing, meaningful materials already studied outside the training programme. Evaluation stage: Training evaluation is particularly necessary when the organisation wants to encourage the competitive spirit amongst the trainers and evaluation is considered as a challenge by itself. If the training provided eliminates obstacles...

Posted by Managementguru in Economics, Financial Management, Principles of Management
on Mar 15th, 2014 | 0 comments
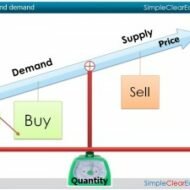
Demand vs. Supply- Parameter deciding market equilibrium The success of economic freedom of a country is naturally reflected in the form of human prosperity. Countries like India are evidencing a consistent increase in their annual GDP rates which obviously must have reduced the population percentage living below poverty line; yet this has not been accomplished and the question is, is it really something to do with the economic model or is it the bureaucracy and inefficiency the root cause for the strain in the economy? Flow of Economic Activity: This discussion aims at shedding some light on the flow of economic activity in a free market economy. The elemental players or contributors in a free enterprise market economy are individuals and firms. Individuals who own or control resources (in the form of labor, capital or natural resources), sell these resources to firms and obtain money. These resources which serve as necessary inputs in the production process add value to firms. The money received by individuals is called factor payment which is utilized to fulfill their consumption demands of goods and services. Two distinct areas of interaction exist between the individuals and firms. One is the product market where the products are bought and sold and the other being a market for production factors, where the inputs such as labor, capital and natural resources are traded. What is the activity in a product market? Fundamentally business is all about demand vs. supply. The consumers’ demand has to be met with by the manufacturers. Profit is the primary motive of any firm and the priority of a firm lies in responding to the demands of the consumer market by supplying goods and services to the potential and prospective buyers. Input costs and production technology are the determinants of supply conditions. People’s preferences and earnings decide the elasticity of market demand. The price of the product and quantity sold is a result of the interaction between demand and supply. In a product market money flows from consumers to firms and goods and services flow from firms to consumers. What happens in a factor market? The reverse of those conditions in the product market are seen in a factor market. Here the individual becomes the supplier of production factors and hence the money flows from firms to individuals and factors of production from individuals to firms. Prices and profits control the flow of money and resources through the factor market and flow of money and goods through the product market. What is a Free Market Enterprise? Added advantage of a free market enterprise is that, the effortlessness with which one can enter and exit the market. The activity flow proves advantageous to each person involved .Firms make profits, individuals are satisfied of their consumption demand for goods and services, resource owners are compensated for their services. If an individual is not able to benefit by trading in these markets, he or she is not required to do so or free to leave the market which ensures that nobody is made worse off by voluntary trade in these markets. Essentially countries have to go in for suitable economic restructuring that promotes equality and even distribution of wealth. Wall Street protest in US is a clear-cut indication of strained market economy which is a result of people’s fury against the prevailing economic...

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting
on Feb 21st, 2014 | 0 comments
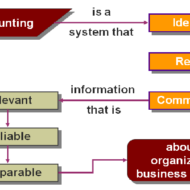
Functions of Accounting: a. Recording: Accounting records business transactions in terms of money. It is essentially concerned with ensuring that all business transactions of financial nature are properly recorded. Recording is done in journal, which is further subdivided into subsidiary books from the point of view of convenience. b. Classifying: Accounting also facilitates classification of all business transactions recorded in journal. Items of similar nature are classified under appropriate heads. The work of classification is done in a book called the ledger. c. Summarizing: Accounting summarizes the classified information. It is done in a manner, which is useful to the internal and external users. Internal users interested in these informations are the persons who manage the business. External users of information are the investors, creditors, tax authorities, labor unions, trade associations, shareholders, etc. d. Interpreting: It implies analyzing and interpreting the financial data embodied in final accounts. Interpretation of the data helps the management, outsiders and shareholders in decision making. Limitations of Accounting: Accounting information is expressed in terms of money. Non monetary events or transactions, however important, are completely omitted. Fixed assets are recorded in the accounting records at the original cost, that is, the actual amount spent on them plus all incidental charges. In this way the effect of inflation (or deflation) is not taken into consideration. The direct result of this practice is that balance sheet does not represent the true financial position of the business. Accounting information is sometimes based on estimates; estimates are often inaccurate. Accounting information cannot be used as the only test of managerial performance on the basis of more profits. Profit for a period of one year can readily be manipulated by omitting such costs as advertisement, research and development, depreciation and so on. Accounting information is not neutral or unbiased. Accountants calculate income as excess of revenues over expenses. But they consider only selected revenues and expenses. They do not, for example, include, cost of such items as water or air pollution, employee’s injuries, etc. Accounting Made Easy Accounting like any other discipline has to follow certain principles, which in certain cases are contradictory. For example current assets (e.g., stock of goods) are valued on the basis of cost or market price whichever is less following the principle of conservatism. Accordingly the current assets may be valued on cost basis in some year and at market price in another year. In this manner, the rule of consistency is not followed...








