Posted by Managementguru in Management Accounting
on Mar 24th, 2015 | 0 comments
What are the advantages and limitations of ratio analysis? Advantages: It is an important and useful tool to determine the efficiency with which working capital is being managed in a business organization. It is a ‘health test‘ for a business firm in that it can gauge whether the firm is financially healthy or not. It aids the management of business concern in evaluating its financial position and performance efficiency. It clearly shows the trend of changes in the market position (upward, downward or static), as it covers a number of previous accounting (financial) periods. The progress or downfall of a firm is clearly indicated by this analysis. It assists in preparing financial estimates for the future (financial forecasting). It facilitates the task of managerial control to a great extent. It helps the credit suppliers and investors in deciding upon a business firm as a potential investment outlet or desirable debtor. Ideal or Standard ratios can be established which can be used as reference points of comparison for a firm’s progress over a period of time. It communicates important information with relation to financial strength, earning capacity, debt (borrowing) capacity, liquidity position, capacity to meet fixed commitments, solvency, capital gearing, working capital management, future prospects etc. of a business concern. This analysis is also useful for bench marking purpose- to compare the working result and efficiency of performance of a business enterprise with that of other firms engaged in the same industry (inter-firm comparison). It helps the management to discharge their basic functions of planning, coordinating, controlling etc. It serves as an instrument for testing management efficiency too. It acts as a useful tool for deciding on certain policy matters. Limitations: Accounting ratios calculated based on ratio analysis will be correct only if the accounting data on which they are based are correct. It is only an analysis of past financial data. In certain cases ratio analysis might prove to be misleading with regard to profits. Continuous fluctuation in price levels ( or, purchasing power of money) seriously affect the validity or comparison of accounting ratios calculated for different accounting periods and make such comparisons very difficult. Comparisons become difficult also on account of difference in the definition of several financial (accounting) terms like gross profit, operating profit, net profit etc. There is lot of diversity in practice as regards to the measurement of ratios. Different firms use different accounting methods and the validity of comparison is severely affected by window dressing in the basic financial statements. A single ratio will not be able to convey much information. This analysis only gives part of the total information required for proper decision-making. This should not be taken as a substitute for sound judgement. It should not be overlooked that business problems cannot be solved mechanically through ratio analysis or other types of financial analysis. Follow ManagementGuru Net’s board Accounting – Financial and Management Accounting on...

Posted by Managementguru in Financial Accounting
on Feb 24th, 2015 | 0 comments

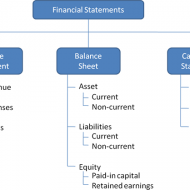
What are known as Final Accounts? Trading, profit & loss account and balance sheet, all these three together, are called as final accounts. Final result of trading is known through Profit and Loss Account. Financial position is reflected by Balance Sheet. These are, usually, prepared at the close of the year hence known as final accounts. They serve the ultimate purpose of keeping accounts. Their purpose is to investigate the consequence of various incomes and expenses during the year and the resulting profit or loss. 1. Trading and Profit and Loss A/c is prepared to find out Profit or Loss. 2. Balance Sheet is prepared to find out financial position of a concern. Trading Account Trading refers buying and selling of goods. Trading A/c shows the result of buying and selling of goods. This account is prepared to find out the difference between the Selling prices and Cost price. Profit and Loss Account Trading account discloses Gross Profit or Gross Loss. Gross Profit is transferred to credit side of Profit and Loss A/c. Gross Loss is transferred to debit side of the Profit Loss Account. Thus Profit and Loss A/c is commenced. This Profit & Loss A/c reveals Net Profit or Net loss at a given time of accounting year. Trading Profit And Loss CMD from knoxbusiness Balance Sheet Trading A/c and Profit & Loss A/c reveals G.P. or G.L and N.P or N.L respectively; besides the Proprietor wants i. To know the total Assets invested in business ii. To know the Position of owner’s equity iii. To know the liabilities of business. Definition of Balance Sheet The Word ‘Balance Sheet’ is defined as “a Statement which sets out the Assets and Liabilities of a business firm and which serves to ascertain the financial position of the same on any particular date.” On the left hand side of this statement, the liabilities and capital are shown. On the right hand side, all the assets are shown. Therefore the two sides of the Balance sheet must always be equal. Capital arrives Assets exceeds the liabilities. BUY “ACCOUNTING CONVENTIONS AND CONCEPTS” OBJECTIVES OF BALANCE SHEET: 1. It shows accurate financial position of a firm. 2. It is a gist of various transactions at a given period. 3. It clearly indicates, whether the firm has sufficient assents to repay its liabilities. 4. The accuracy of final accounts is verified by this statement 5. It shows the profit or Loss arrived through Profit & Loss A/c. PREPARATION OF FINAL ACCOUNTS Preparation of final account is the last stage of the accounting cycle. The basic objective of every firm maintaining the book of accounts is to find out the profit or loss in their business at the end of the year. Every businessman wishes to find out the financial position of his business firm as a whole during the particular period. In order to accomplish the objectives for the firm, it is essential to prepare final accounts which include Trading, Profit and Loss Account and Balance Sheet. It is mandatory that final accounts have to be prepared, every year, in every business. Trading and profit & loss accounts are prepared, after all the accounts have been completely written and trial balance is extracted. Before preparing final accounts, it becomes obligatory to scritinize whether all the expenses and incomes for the year for which accounts are prepared have been duly provided for and included in the accounts. Form of Final Accounts: There is a standard format of final accounts only in the case of a limited company. There is no fixed prescribed format of financial accounts in the case of a proprietary concern and partnership...

Posted by Managementguru in Financial Accounting, Financial Management, Management Accounting
on Apr 3rd, 2014 | 0 comments
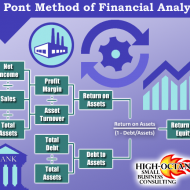
Ratio Calculation From Financial Statement Profit and Loss a/c of Beta Manufacturing Company for the year ended 31st March 2010. Exercise Problem1 Kindly download this link to view the exercise. Given in pdf format. You are required to find out: a) #Gross Profit Ratio b) #Net Profit Ratio c) #Operating Ratio d) Operating #Net Profit to Net Sales Ratio a. GROSS FORFIT RATIO = Gross profit ÷ #Sales × 100 = 50,000 ÷ 1,60,000 × 100 = 31.25 % b. #NET PROFIT RATIO = Net profit ÷ Sales × 100 = 28,000 ÷ 1,60,000 × 100 = 17.5 % c. OPERATING RATIO = #Cost of goods sold + Operating expenses ÷ Sales × 100 Cost of goos sold = Sales – Gross profit = 1,60,000 – 50,000 = Rs. 1,10,000 Operating expenses = 4,000 + 22,800 + 1,200 = Rs. 28,000 Operating ratio = 1,10,000 + 28,000 ÷ 1,60,000 × 100 = 86.25 % d. OPERATING NET PROFIT TO NET SALES RATIO = Operating Profit ÷ Sales × 100 Operating profit = Net profit + Non-Operating expenses – Non operating income = 28,000 + 800 – 4,800 = Rs. 32,000 Operating Net Profit to Net Sales Ratio = 32,000 ÷ 1,60,000 × 100 = 20 % What is a Financial statement? It is an organised collection of data according to logical and consistent #accounting procedure. It combines statements of balance sheet, income and retained earnings. These are prepared for the purpose of presenting a periodical report on the program of investment status and the results achieved i.e., the balance sheet and P& L a/c. Objectives of Financial Statement Analysis: To help in constructing future plans To gauge the earning capacity of the firm To assess the financial position and performance of the company To know the #solvency status of the firm To determine the #progress of the firm As a basis for #taxation and fiscal policy To ensure the legality of #dividends Financial Statement Analysis Tools Comparative Statements Common Size Statements #Trend Analysis #Ratio Analysis Fund Flow Statement Cash Flow Statement Types of Financial Analysis Intra-Firm Comparison Inter-firm Comparison Industry Average or Standard Analysis Horizontal Analysis Vertical Analysis Limitations Lack of Precision Lack of Exactness Incomplete Information Interim Reports Hiding of Real Position or Window Dressing Lack of Comparability Historical...

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Financial Management, Management Accounting, Principles of Management
on Mar 28th, 2014 | 0 comments
ROI – Return on Investment Ratios PROFITABILITY IN RELATION TO INVESTMENTS Return on gross investment or gross capital employed Return on net investment or net capital employed Return on shareholder’s investment or shareholder’s capital employed. Return on equity shareholder investment or equity shareholder capital employed. 1. RETURN ON GROSS CAPITAL EMPLOYED This ratio establishes the relationship between net profit and the gross capital employed. The term gross capital employed refers to the total investment made in business. The conventional approach is to divide Earnings After Tax (EAT) by gross capital employed. Return on gross capital employed = Earnings After Tax (EAT) X 100 / Gross capital employed 2. RETURN ON NET CAPITAL EMPLOYED It is calculated by dividing Earnings Before Interest & Tax (EBIT) by the net capital employed. The term net capital employed in the gross capital in the business minus current liabilities. Thus it represents the long-term funds supplied by creditors and owners of the firm. Return on net capital employed = Earnings Before Interest & Tax (EBIT) X 100 / Net capital employed 3. RETURN ON SHARE CAPITAL EMPLOYED This ratio establishes the relationship between earnings after taxes and the shareholder investment in the business. This ratio reveals how profitability the owners’ funds have been utilized by the firm. It is calculated by dividing Earnings after tax (EAT) by shareholder capital employed. Return on share capital employed = Earnings after tax (EAT) X 100 / Shareholder capital employed 4. RETURN ON EQUITY SHARE CAPITAL EMPLOYED Equity shareholders are entitled to all the profits remaining after the all outside claims including dividends on preference share capital are paid in full. The earnings may be distributed to them or retained in the business. Return on equity share capital investments or capital employed establishes the relationship between earnings after tax and preference dividend and equity shareholder investment or capital employed or net worth. It is calculated by dividing earnings after tax and preference dividend by equity shareholder’s capital employed. Return on equity share capital employed = Earnings after tax (EAT), preference dividends X 100 / Equity share capital employed. The following are some of the important and basic concepts to be understood in management accounting: EARNINGS PER SHARE IT measures the profit available to the equity shareholders on a per share basis. It is computed by dividing earnings available to the equity shareholders by the total number of equity share outstanding. Earnings per share = Earnings after tax – Preferred dividends (if any) / Equity shares outstanding DIVIDEND PER SHARE The dividends paid to the shareholders on a per share basis in dividend per share. Thus dividend per share is the earnings distributed to the ordinary shareholders divided by the number of ordinary shares outstanding. Dividend per share = Earnings paid to the ordinary shareholders / Number of ordinary shares outstanding DIVIDENDS PAY OUT RATIO (PAY OUT RATIO) It measures the relationship between the earnings belonging to the equity shareholders and the dividends paid to them. It shows what percentage shares of the earnings are available for the ordinary shareholders are paid out as dividend to the ordinary shareholders. It can be calculated by dividing the total dividend paid to the equity shareholders by the total earnings available to them or alternatively by dividing dividend per share by earnings per share. Dividend pay our ratio (Pay our ratio) = Total dividend paid to equity share holders / Total earnings available to equity share holders Or Dividend per share / Earnings per share DIVIDEND AND EARNINGS YIELD While the earnings per share and dividend per share are based on the book value per share, the yield is expressed in terms...

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Management Accounting
on Feb 14th, 2014 | 0 comments

Advantages of Management Accounting It helps to increase the efficiency of all functions of management.It helps in target-fixing, decision-making, price-fixing, selection of product-mix and so onForecasting and Budgeting help the concern to plan the future and financial activities.Various tools and techniques provide reliability and authenticity to carry out the business functions.It is useful in controlling wastage and defects.It helps in complete communication between all levels of management.It helps in controlling the cost of production thus increasing the profit percentage.It is proactive-analyses the governmental policies and socio-economic scenario which helps to assess the external environmental impacts on the organization. Limitations of Management Accounting It is concerned with financial and cost accounting. If these records are not reliable, it will affect the effectiveness of management accounting.Decisions taken by the management accountant may or may not be executed by the management..It is very expensive. Only big concerns can adopt this method of accounting.New rules and regulations are to be framed, hence there is a possibility of opposition from the employees.It is only in the developing stage.It provides only data and not decisions.It is a tool to the management and not an alternative of management. These are the advantages and limitations of management accounting. Characteristics of management accounting Following are the characteristic features of management accounting: First and foremost characteristic is that it provides the necessary information to the management. It might be any data- numbers, gross profit, net profit, comaparitive financial statements, profit and loss account etc.,It is purely analytical.The interpretations help the management in timely decision-making.It adopts a selective technique to arrive at the results.Helps to chart-out the future course of action.Also helps to know the present financial condition of the firm and the respective implications on the stake holders. Various tools of management accounting: MARGINAL COSTINGSTANDARD COSTINGBUDGETARY CONTROLRATIO ANALYSISFUND FLOW ANALYSISCASH FLOW ANALYSIS...










