Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Marketing
on Mar 3rd, 2014 | 0 comments
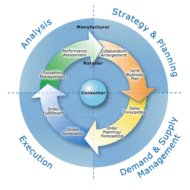
Product Forecasting – An Analogy What is Product Forecasting: It is the science of predicting the degree of success a new product will enjoy in the marketplace. Forecasting is said to be the first and foremost step in the planning process. One of the requirements for effective long-term planning by managers is to assess the changes in technology and environmental conditions that could affect the firm. This is termed as environmental scanning which facilitates the firm to benchmark its performance as against the top industry standards. Technological forecasting involves anticipating development of new products and processes and the time taken for such kind of innovations to be accepted and absorbed in the market. External Environmental Scanning: Environmental forecasts focus on factors such as population growth, availability of resources, social and political trends that may affect the firm’s future. Business firms become more informative on, The percentage of market share for existing products of the firm Future demand for its product range Decline in sales proportions Consumer feedback about product performance Customer satisfaction Sales team performance level Pitfalls in marketing strategies Need for new product development Unidentified customer needs and so on All predictive activity is subject to error, but technological and environmental forecasting is particularly different because they often involve assessing ideas and relationship that do not exist at the time the analysis is being performed. These forecasts are best suited for predicting performance a year or two in the future. Plan of Future Course of Action: Based on forecasting, the firm decides the future course of action. Sales forecasts help the firm to decide on the volume of production for the next few months and aid in aggregate capacity planning. Labor productivity is a crucial factor in determining the success of a business environment, especially a production environment. Manpower planning is purely based on production forecasts where in, the labor hour productivity is also taken into consideration. Forecasting Techniques: In the absence of empirical data, the forecasts must be based on expert opinions. Techniques like Delphi method can be used for this purpose. A group of experts is asked to assess a particular situation, presented with the judgments of others in the group, and then asked to reevaluate their individual positions based on what they have heard. The process continues until a consensus is arrived or until it is apparent that there will be no consensus. This helps the firm to consolidate its position with respect to specific problem situations. The Delphi method has been successfully used to forecast the nature and timing of technological change. Techniques like Delphi and Brain storming also help in the process of identification of bottlenecks, the current business trend, the firm’s future prospects, range of estimates for the desired breakthroughs etc. Although the pattern of a business cycle or a product cycle for the most part, follows a fairly predictable pattern, the firm cannot overlook probabilities, upon which the firm has to capitalize on. The firm has to become alert and employ some innovations at that point of time, when the market becomes saturated. Or else, the rate of growth declines and the firm has to decide whether to continue with the operations which calls for additional investment or close down the...

Posted by Managementguru in Operations Management, Project Management
on Feb 24th, 2014 | 0 comments
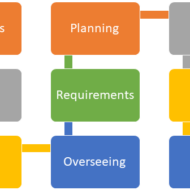
Significance of Operations Management: Business firms need to formulate brilliant operations strategies in order to survive in the market for long. Focus on finance and marketing alone is not sufficient to compete in the global market. The emergence of innovative products and processes from leading companies in different parts of the world is a clear-cut evidence to prove the significance of operations function. Operations management is gaining importance, thanks to public awareness on quality and its applicability in service operations too. Advent of Industrial Revolution: Until the advent of machinery, each and every nation was dependent on agriculture, which was the prime economic activity. After the industrial revolution of the eighteenth century, mechanization in a large scale converted agricultural economy to an industrial economy. Slowly scientific principles were introduced into production activities to make it more systematic and thus “Production Management” evolved. Now service operations have also gained momentum and since the concepts and techniques of production management are applicable to service operations too, it is rightly called as “Operations Management.” Operations management functions at three different levels. Strategic levelTactical levelOperational level Strategic level: At the strategic level, the operations manager must have a long term vision, as to shape up the company’s success in the light of strategic decisions taken, with the approval of the top management. His area of concern would be, New product developmentNew process developmentProduct re-designProcess re-designProcess layoutProduct layoutFacility locationAggregate capacity planningPlanning co-ordination with finance and marketing departments Tactical level: At the tactical level, the operations manager is concerned about the planning and scheduling operations of the desired output. His area of concern would be: Designing a suitable inventory systemPlan for the work force and train them effectivelyQuality control systemMaintenance andReliability assurance system. Operational level: At the operational level, the job of the operations manager is to accomplish the “set targets”, by performing various coordinating and controlling functions. His area of concern would be: Ordering materials at the right timeScheduling productionScheduling workers as per production requirementControlling quality of goods and services producedFollow up of various schedules for proper implementationMaintaining and updating equipment and system reliabilityOn the job skill development of workers, etc. These functions are by no means exhaustive, but only indicative. The process of planning and control operations is not done in water tight compartments, but are interactive and integrative feeding on one another and also aligned in line with the overall corporate objectives. The strategies are evolved for the purpose of efficient utilization of the available resources as well as to predict the changes in the external business environment that calls for suitable action to limit their impact on the goals of the organization, in terms of cost, quality and...




