Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, International Business, Marketing, Principles of Management
on Mar 11th, 2014 | 0 comments
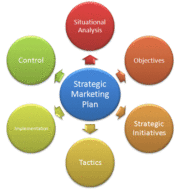
Key Strategies of Global Marketing Globalization means many things to many people. For some it is a new paradigm – a set of fresh beliefs, working methods and economic, political and socio-cultural realities in which the previous assumptions are no longer valid. For developing countries, it means integration with the world economy. It can be better understood if we look it at this perspective- “the world integrated into one huge market”. It calls for the removal of all trade barriers among countries and a perfect competitive market prevails and the stress can lead to many positive and possible outcomes in terms of QualityQuantityUniquenessForeign exchangeBenefits to the host countryIncreased productivity leading toEconomic growth Well, it does not end there. An MNC (multi national company), by operating in more than one country gains r and d, production, marketing and financial advantages in terms ofcost and labor that other competitors may not enjoy. The global company views the world as one market, minimize the importance of national boundaries, sources, and raise capital and markets wherever it can do the job best. Why do companies go global? One reason could be the rapid shrinking of time and distance across the globe thanks to faster communication, speedier transportation, growing financial flows and rapid technological changes. It is being realized that the domestic markets are no longer adequate and rich. Japanese have flooded the U. S. Market with automobiles and electronic goods because the home market was not big enough to absorb whatever was produced. Companies at the first stage of globalization have only passive dealings with foreign individuals and organizations. By the second stage, companies deal directly with their overseas counterparts, though they might continue to use third parties also. The company might decide to set up an import or export department. Next comes the shedding of domestic capacity and floating an international organization and have a direct hand in exporting, importing, and perhaps producing goods and services abroad. Seldom companies reach this stage, even if they do, they recede later. The company can have a strong foothold in the countries it is organizing its activity only by way of * Superior product quality* Demand* Customer preference for that particular product range that the company offer* A dynamic CEO projecting and boosting company’s image,* Brand image* Availability of skilled labor* Licenses* Access to necessary infrastructure* Feasible financial structure* Viability in the long run* Marketing mix Chennai in India has become a hub for so many corporate as well as global companies since the business climate is very favorable and enterprising. Some of the strategies in globalization would be * Deciding whether to go global* Deciding which markets to enter* Deciding how to enter the market* Learning to handle differences* Adjusting the managing process* Deciding organization structure* Selecting a managerial approach. Developing countries like India have adopted new economic policies that are expected to encourage the international companies setting their foot in India, by which it compels many Indian companies to pursue internationalization vigorously. True globalization marks the beginning of a new economic era of growth and...

Posted by Managementguru in Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 1st, 2014 | 0 comments
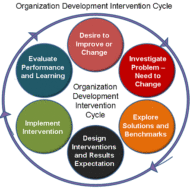
Organizational Development Training and development is an important aspect of human resource development. However the traditional methods and approach of T&D has its own limitations in that the focus is on individual development and behavior modification. This has seldom produced organizational development and hence in 1960’s an integrated approach called the ‘OD’ or organizational development was developed. Meaning and definition of organizational development (o.d.) “A process used to enhance both the effectiveness of an organization and the well being of its members through planned interventions.” OD is the systematic application of behavioral science knowledge for the purpose of improving productivity, efficiency, effectiveness and overall health of the total organization. The applied interventions attempt to modify the beliefs, assumptions, values, attitudes and standards of both the individuals and groups thereby transforming the organizational culture for the betterment of system as a whole. FEATURES OF ORGANIZATIONAL DEVELOPMENT: HUMANISM: The focus is on the employees, their attitude and inter-personal relationships. An organization is a network of people whose emotions, outlook and cohesiveness are more important than monetary and other physical aspects because it is they who take the organization to the next higher level. This is made possible by open communication, free and frank discussions of problems with employees by the managers, inter-personal trust and above all, sense of belongingness, comradeship and team spirit. PROBLEM-SOLVING NATURE: The purpose of an OD intervention is to solve a problem. The employees themselves are given the opportunity to identify the problem by Survey Feedback and find a suitable solution through analysis. This is a cyclic process and also called as “Action Research”. SYSTEMS APPROACH: OD is concerned with not the structure or persons per se, but with the interplay of structure and persons. LEARNING THROUGH PARTICIPATION: The participants of the learning process are none other than the employees. They unlearn old things and learn new things by identifying, analyzing and finding the right solution to the bottlenecks. TOP MANAGEMENT SUPPORT AND INVOLVEMENT: OD intervention is successful only when top management involvement is full-fledged and ensures participation from all levels of managers and all departments in such an exercise. MULTIPLE INTERVENTIONS: Intervention takes place at various levels, individual as well as group and the purpose is molding desirable work culture and leadership styles suitable for the organization. ROLE OF CONSULTANT: Employing an external consultant will be more appropriate as he is less susceptible to influences and more objective. He acts as the change agent facilitating co-ordination and stimulation. CONTINGENCY PLANS: Alternate plans are also devised if in case the original plan fails; the idea is one that of trial and error, hence the need for contingency plans and approach to OD problem. RENSIS LIKERT’S OD FRAMEWORK: Rensis Likert’s 4 system OD framework aims at moving towards truly participative system. Care and caution must be adhered to steer the system gradually from where the organization now works. He also introduced diagnostic analysis to find what causes the current problem. His three part diagnostic analysis includes: A. OUTPUT CAUSES: Low productivity, absenteeism, declining profit B. INTERVENING CAUSES: Organization structure, control, policy and leadership C. ROOT CAUSES: Attitude, motivation level, empowerment and organization culture Tips for Organization Development OD CULTURE: “The OD paradigm values human and organizational growth, collaborative and participative processes and a spirit of enquiry.” Brown and Covey have made some attempts to identify OD values from the following: Norms and Values: Respect for people: People are the most important of all resources. So giving due respect and importance to people induces the creativity and innovation in them. Trust and Support: Trust, openness and supportive climate improve organization culture and empowerment. Power Equalization: This emphasizes hierarchical authority, control and centralization. Confrontation: Do not...




