Posted by Managementguru in Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Strategy, Training & Development
on Mar 31st, 2014 | 0 comments
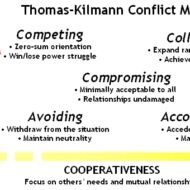
Conflict is a Part of Organizational Life Managers need to be alert to the presence of conflicts. Their focus should be oriented towards the goals to be accomplished. If there is a conflict, they should aim to resolve it smoothly by not over-reacting to the situation. They should take the help of persons who can best settle the issue, be ready to bargain and not issue orders. Their concentration should be on the problem and not on persons. True to the saying – Am I not destroying my enemies when I make friends of them?- President Abraham Lincoln Conflicts are Functional and Healthy: Conflicts in organisations are generally considered to be dysfunctional. On the contrary, many top executives of big companies view conflicts, as a means, to sufficiently analyse a problem and postpone decision making until all critical aspects of an issue are evaluated properly. Conflicts may occur within the individual, between individuals, between the individual and the group or between groups. There are many potential sources of conflict in today’s corporate organisations. The complex inter personal relationships and high degree of interdependence causes friction. Difference of Opinion: When many people must work together, conflict is inevitable, as it is human nature to clash and complain. Conflict is the personal divergence of interests between groups or individuals. The need to share scarce resources, difference in goals between organisational units, difference in values, attitudes and perception, ambiguously defined work responsibilities are some of the major sources of conflict. Functional Conflicts: Functional conflicts support the goals of a group, improve its performance and are constructive in nature. Dysfunctional conflicts hinder the performance of a group and are destructive in nature. It has not been precisely defined, as to what criterion demarcates functional from the dysfunctional. It is only the group’s performance and the delivered result or outcome that determines the nature of the conflict. Conflicts, irrespective of their type can bring these benefits to the firm: Bring hidden issues to the surface. Encourage creativity and innovation. Improves communication and make changes more acceptable. Increases group cohesion. Strategies to Resolve Conflicts: So, what kind of strategy do you think best suits in resolving conflicts? Avoiding or smoothing conflicts may be a temporary measure, only to bounce back in full force. Forcing might create undesirable consequences. The only option left is to confront the situation, face-to-face meeting of the conflicting parties for the purpose of identifying the problem and resolving it through an open discussion. Make Structural Changes to Lessen Conflicts: By making structural changes, conflicts can be managed. The objectives of a group are modified and then integrated to suit the purpose. Also changes in the structure of the organization, that is, clarification of authority-responsibility relationship, improving the working atmosphere, ambience and work locations help in resolving conflicts. Proper Communication: Lack of proper communication, ego clashes between the people in line and staff positions, a superior’s autocratic leadership style, differing educational backgrounds, lack of co-ordination between inter-departments are all rich sources of conflict. These can be resolved with the right kind of attitudinal approach and an open mind from the management’s...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Training & Development
on Mar 22nd, 2014 | 0 comments
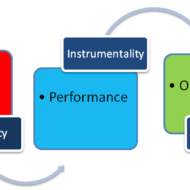
How to create an effective and Sustainable Model for Training and Development? The term “change” is synonymous with competitiveness in modern world and thus corporate firms are in a position to evolve unique, sustainable and strategic training model for employees that will facilitate the following: On one hand the training process motivates the suitable employees to perform well and makes them perceive their role properly in order to accomplish the enterprise objectives. On the other hand the organisation keeps itself abreast by constantly updating and understanding the training needs through Assessment of the external environment and Expectations of the employees in terms of rewards whether intrinsic or extrinsic. Porter and Lawler Model: The Expectancy Motivation Model of Porter and Lawler serves as an inspiration for effective training. The stress is on The value placed on performance outcome by the individual. The degree to which the individual believes that his efforts will lead to attainment of these rewards. Psychological aspect of this model: Almost all individuals are motivated by money ( by the way, Who doesn’t want money!). But money alone does not serve the purpose of motivation. Job satisfaction is a relative term in that different people find different things or elements motivating them in their work environment leading to job satisfaction. It might be Challenge Good inter personal relationship Pay Perks Culture Excellent leader Pressure Stress and the like… Assessment of training need: The training needs must be assessed by the respective organisations considering the following aspects: To transform the individual from the capacity of learner to executor Instil in him confidence to do the job well Relate his job to rewards so that he will try to excel Give your employees scope for career advancement Incorporate technical and technological innovations as part of your training process Physical, emotional and social elements in the internal as well as the external environment must be taken into consideration while training the workforce. Physical– relates to the physical fitness needed to perform the technical skills Psychological– relates to keeping the morale of the employees high at all points and maintaining an amiable work atmosphere Social– relates to the friendly relationship that should exist between the trainer and the trainees and among the trainees. Usefulness of the model: This model lends its support to the training and development process through three steps or stages. Diagnosis stage- Need analysis Formulation stage- Programme planning Evaluation Diagnosis stage: The interplay of ability and role perception Training brings out EFFICIENT as well as DEFICIENT performers. That is one good thing and also making the employee understand the role he is about to play as part of the organisation. Training through learning is one aspect which imparts knowledge and training is considered to be effective if one’s behaviour is modified as per the expectations and demands of the job. Role perception can be misunderstood by some individuals when they might try to exercise undue authority or overlook their duties and responsibilities. Confinement of authority Superior-Subordinate appraisal procedures Clear HR policy formulations are needed to avoid confusion and chaos in role playing. Formulation stage: The effected change through learning is expected to be retained by the employees throughout the career span in the organisation followed by constant grooming. The stress is on the value of the activity to be learnt Giving feedback on the progress of employees towards final training objectives Relate the learning activity to increasing, meaningful materials already studied outside the training programme. Evaluation stage: Training evaluation is particularly necessary when the organisation wants to encourage the competitive spirit amongst the trainers and evaluation is considered as a challenge by itself. If the training provided eliminates obstacles...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Marketing, Operations Management, Principles of Management, Strategy
on Mar 16th, 2014 | 0 comments
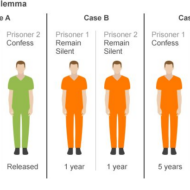
Game theory and strategy What is Game Theory: Set of concepts designed for decision making in situations of competition and conflict under specified rules. The prisoner’s dilemma: The prisoner’s dilemma is a canonical example of a game, analyzed in game theory that explains why two individuals might not cooperate, even if it appears that it is in their best interest to do so; Albert W. Tucker formalized the game with prison sentence payoffs and gave it the “prisoner’s dilemma” name. To solve many practical problems that are encountered in economic, military or other disciplines, one has to deal with situations in which there are two or more conflicting parties striving for the same objective and the outcome of each action of one party depends solely on the opposite parties choice of a course of action. As we all know only one horse can win the race ultimately and the other parties only can prolong the race or see to that they make every possible move to delay the opponent’s success. So, what’s this game theory all about? This is a special mathematical method that was evolved mainly to analyze conflict situations where the number of competitors is finite, each participant has a definite set of actions to choose and there is a conflict of interest between the competitors. So it helped the participants to reach a decision that would put them in the winning post. This theory has spilled its implications on business situations where success is the motto and conflict and competition the order of the day. Only the best among the best survive. Darwin’s theory, “Survival of the fittest” applies not only to biological organisms but also to business organizations which are also abuzz with activity. Chance Moves: Games like chess, checkers are played according to a definite set of rules laid down and these game patterns has inspired business persons to introduce strategies in business, where the concentration is mainly focused on the chance moves that defeats the opponent. Big business corporates mainly concentrate on the strengths and weaknesses of their competitors to have an edge over them. A real game is controlled and regulated by the statutory rules to be followed but a business game involves lot of killer instincts and intuitions combined with rational thinking and logic. Optimal Strategy: The first party always puts himself in the shoes of the other party and tries to perceive how the other party would react in a particular situation. Although the aim is to win, choosing the optimal strategy is what matters. It will at least keep you in bay. Precise solutions can be arrived at if you plan your game fittingly. The anticipation and thrill that is involved in a strategic game is matchless. We witness a lot of firms imitating what the leader of the market does. The risk is borne solely by the firm introducing the change and the firm takes the major share of profit as it is the pioneer and if it loses the next strategic move is planned for. For a company with sound financial position, the chance move is worth giving a try, head or tail doesn’t matter. The stalkers are benefited by the waiting period during which they come to know of the pros and cons of the strategy employed by the leader. Games are played in the true spirit of sportsmanship, but a business faces cut throat competition. There is no space for any courtesy or liberal approach. If you are quick enough to pick the pulse of the people by gauging their preferences, analyzing the market conditions and employing timely strategies you will at...

Posted by Managementguru in Economics
on Feb 17th, 2014 | 0 comments
Significance of Privatization Privatization that has gathered momentum since around the 1980’s has become the hallmark of the new wave of economic reforms sweeping across the world. It refers to the transfer of ownership or management of an enterprise from the hands of the public sector to private sector. It also means the withdrawal of the state from an industry or sector, partially or fully. Privatization marks a change from dogmatism to pragmatism and amounts to a reversal of policy. It is evident that the economic growth rate has multiplied ever since privatization has come into existence. What is Privatization? 1. The transfer of ownership of property or businesses from a government to a privately owned entity. 2. The transition from a publicly traded and owned company to a company which is privately owned and no longer trades publicly on a stock exchange. Performance of Public Sector: The performance of state owned enterprises in many countries have, by and large been far from satisfactory. This may be attributed to the prevalence of bureaucracy and red tapism in most of the public sector administration. They have often put large burdens on public budgets and external debt. Economic inefficiencies in the production activities with high costs of production, inability to innovate and costly delays in delivery of the goods produced are some of the shortcomings of the public sector. There is also ineffectiveness in the provision of goods and services such as failure to meet intended objectives, diversion of benefits to elite groups, and political interference in the management of enterprises. The relationship between the management and the labor unions is strained owing to the expansion of bureaucracy. Why Privatization? These problems have led many governments to undertake programmes of public sector reform. One Such reform is privatization of publicly managed activities to discard the inefficiencies and improve the economic growth rate. For privatization to succeed: Privatization cannot be sustained unless the political leadership is committed to and unless it reflects a shift in the preferences of the public arising out of dissatisfaction with the performance of other alternatives. Now-a-days, private sector enterprises have started dominating even core industries like petroleum, power and communication under the leadership of visionaries who may be the heads of the states or owners of such private organizations. Public services to be provided by the private sector must be specific or have a measurable outcome. Consumers should be able to link the benefits they receive from a service to the costs they pay for it. Since they will then shop more wisely for different services. Privately provided services should be less susceptible to fraud than government services if they are to be effective. Equity is an important consideration. Privatizing the state owned enterprises reduces corruption and the benefit goes to the society. The process encourages entrepreneurship and leads to intense development of capital market. Governments usually want to sell the least profitable enterprises, those that the private sector is not willing to buy at a price acceptable to the Government. The Government may even fear that if it gives a free rein to the private sector management, its power might be at stakes. All said and done most of the governments view privatization as an important strategy of economic...








