Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Training & Development
on Mar 7th, 2014 | 0 comments

Performance Optimization Through Effective Management An organization is a network of people striving to achieve their targets. So it is a wise thing to synchronize their activities in-order to enhance the harmony and build a strong team as well that protects the network from crumbling by means of mutual trust and behavior. It is imperative for the management to define the structure and hierarchy as well as the techniques that help the organization to efficiently function. Here are some means to make your organization to function efficiently and you’re your team stand apart from the crowd. Training of Subordinates: The better the training of subordinates, the fewer the number of necessary supervisors. Well trained subordinates require not only less of their manager’s time but also less contact with their managers. ‘On the job’ training programmes have found to be more effective in industries which are labor intensive. Coaching and mentoring improve the understanding and efficiency of the workforce and help them to maximize their effort and in turn productivity. Clarity of Delegation of Authority: The most serious symptom of poor organization affecting the span of management is inadequate or unclear authority delegation. If a manager clearly delegates authority to perform a well defined task, a well trained subordinate can get it done with the minimum of manager’s time and attention. But if the subordinate’s task is not clearly defined, either the task will not be performed or it will be a colossal waste of time for the manager to supervise and guide the subordinates’ effort. Clarity of Plans: The character of a subordinates‘ job is defined by the plans to be put into effect. If these plans are well defined, if they are workable, if the authority to undertake them has been delegated, and if the subordinate understands what is expected, little of a supervisor’s time will be required. Such is often the case with a production supervisor, who bears the responsibility of achieving targets within the stipulated time period. If the plans cannot be drawn accurately, subordinates must do much of their own planning where they may lack direction. On the other hand if the superior has setup clear policies to guide decisions and has made sure they are consistent with the operations and goals of the department, work becomes simple and easy for the subordinates to follow. Communication Techniques: If every plan, instruction, order or direction has to be communicated by personal contact and every organization change or staffing problem has to be handled orally, it slows down the managerial activity. The ability to communicate plans and instructions clearly and concisely also tends to increase a manager’s span. At the same time the subordinate’s job is greatly facilitated by superiors who can express themselves well. A manager’s casual easy style may please subordinates, but it reduces the effective span of management and lowers morale as well. Amount of Personal Contact Needed: Many situations cannot be completely handled with written reports, memorandums, policy statements, planning documents and other communication techniques that do not involve personal contact which an executive find it valuable. There are other situations in which the best way of communicating a problem, instructing a subordinate, or “getting a feel” of how people really think is to spend time in personal contact . The high percentage of time spent in meetings and committees might be reduced some what by better training, better policy making and planning, clearer delegation, more thorough staff work, better control system and objectives standard. Studies have revealed that, effective spans were narrower at lower and middle levels of organization but were increased at upper levels and size had little...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Marketing
on Mar 3rd, 2014 | 0 comments
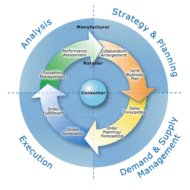
Product Forecasting – An Analogy What is Product Forecasting: It is the science of predicting the degree of success a new product will enjoy in the marketplace. Forecasting is said to be the first and foremost step in the planning process. One of the requirements for effective long-term planning by managers is to assess the changes in technology and environmental conditions that could affect the firm. This is termed as environmental scanning which facilitates the firm to benchmark its performance as against the top industry standards. Technological forecasting involves anticipating development of new products and processes and the time taken for such kind of innovations to be accepted and absorbed in the market. External Environmental Scanning: Environmental forecasts focus on factors such as population growth, availability of resources, social and political trends that may affect the firm’s future. Business firms become more informative on, The percentage of market share for existing products of the firm Future demand for its product range Decline in sales proportions Consumer feedback about product performance Customer satisfaction Sales team performance level Pitfalls in marketing strategies Need for new product development Unidentified customer needs and so on All predictive activity is subject to error, but technological and environmental forecasting is particularly different because they often involve assessing ideas and relationship that do not exist at the time the analysis is being performed. These forecasts are best suited for predicting performance a year or two in the future. Plan of Future Course of Action: Based on forecasting, the firm decides the future course of action. Sales forecasts help the firm to decide on the volume of production for the next few months and aid in aggregate capacity planning. Labor productivity is a crucial factor in determining the success of a business environment, especially a production environment. Manpower planning is purely based on production forecasts where in, the labor hour productivity is also taken into consideration. Forecasting Techniques: In the absence of empirical data, the forecasts must be based on expert opinions. Techniques like Delphi method can be used for this purpose. A group of experts is asked to assess a particular situation, presented with the judgments of others in the group, and then asked to reevaluate their individual positions based on what they have heard. The process continues until a consensus is arrived or until it is apparent that there will be no consensus. This helps the firm to consolidate its position with respect to specific problem situations. The Delphi method has been successfully used to forecast the nature and timing of technological change. Techniques like Delphi and Brain storming also help in the process of identification of bottlenecks, the current business trend, the firm’s future prospects, range of estimates for the desired breakthroughs etc. Although the pattern of a business cycle or a product cycle for the most part, follows a fairly predictable pattern, the firm cannot overlook probabilities, upon which the firm has to capitalize on. The firm has to become alert and employ some innovations at that point of time, when the market becomes saturated. Or else, the rate of growth declines and the firm has to decide whether to continue with the operations which calls for additional investment or close down the...

Posted by Managementguru in Principles of Management, Training & Development
on Feb 22nd, 2014 | 0 comments
Benefits of Training to Employers The employers invest in training because they secure several benefits out of the exercise, which can be summed up as under: Faster learning of new skills Training aids the employers to lessen the learning time of their employees and accomplish higher standards of performance. The employees need not waste time in learning by observing others. If a formal training programme exists in the organization, the qualified instructors will help the new employees to acquire the skills and knowledge to do specific jobs quickly. Increased productivity Training increases the skill of the new employee in while performing a particular job. An increased skill level usually helps in increasing both quantity and quality of output. Training can be of great help even to the existing employees. It helps them to increase their level of performance on their present job assignments and prepares them for future assignments. Standardization of procedures Training can help the standardization of operating procedures, which can be learnt by the employees. Standardization of work procedures makes high levels of performance rule rather than exception. Employees work intelligently and make fewer mistakes when they possess the required know-how and skills. Lesser need for supervision. Trained employees need lesser supervision. Training does not eliminate the need for supervision, but it reduces the need for detailed and constant supervision. A well-trained employee can be self-reliant in his/her work because s/he knows what to do and how to do. Under such situations, close supervision might not be required. Economy of operations Trained personnel will be able to make better and economical use of the materials and the equipment and reduce wastage. Also, the trained employees reduce the rate of accidents and damage to machinery and equipment. Such reductions can contribute to increased cost savings and overall economy of operations. Higher morale The morale of employees is increased if they are given proper training. A good training programme shapes employees’ attitudes towards organizational activities and generates better cooperation and greater loyalty. With the help of training, dissatisfactions, complaints, absenteeism and turnover can also be reduced among the employees. Thus, training helps in building an efficient and co-operative work force. Managerial Development The top management can identify the talent, who can be groomed for handling positions of responsibility in the organizations. Newer talent increases the productivity of the organizations. By providing opportunity for self-development, employees put in their best effort to contribute to the growth of the...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Change management, Marketing, Organisational behaviour, Strategy
on Feb 18th, 2014 | 0 comments

SWOT and Synergy SWOT Analysis On the basis of its resources and behavior, an organization develops certain strengths and weaknesses which when combined lead to synergistic effects. Such effects manifest themselves in the form of organizational competencies. It is necessary for a firm to look for and develop factors that adds to its strength, as strength is considered to be an inherent capacity which an organization can use to gain strategic advantage. Pic Courtesy: Clickfunnels A weakness, on the other hand, is an inherent limitation or constraint which creates a strategic disadvantage for the organization. Financial strength, for example, is a result of availability of financial sources and efficient rotation of funds. A weakness in the operations management area might be a result of inappropriate plant location, obsolete plant layout and technology. It has to be noted that an organization cannot enjoy the privilege of having only strengths and devoid of any weaknesses. Then the performance level would become saturated to the point of monotony and there exists no scope for growth or improvement. Only when presented with challenges, any functional area exhibits synergy, as strengths and weaknesses do not exist in isolation but combine within a functional area, and also across different functional areas. Synergy Synergy is needed at all levels for better productivity. Say, within a functional area like marketing, synergistic effort may occur when the product, pricing, distribution and promotional aspect support each other, resulting in higher level of marketing synergy. The same when happens at an even higher level, leads to operating synergy, say, for example, synergistic efforts between marketing and production department to decide on the production forecast and pricing. Distinctive competence helps a firm to develop strategic advantage that leads to comprehensive growth and development. Limitations of SWOT: A SWOT analysis can over emphasize internal strengths and overlook external threats It can be static and may ignore the changing circumstances It might give undue importance to a single strength or an element of strategy A strength is not necessarily a source of strategic advantage. Amazon.in...








