Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Training & Development
on Mar 20th, 2014 | 0 comments
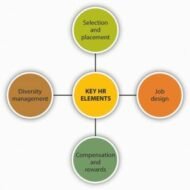
Managing Critical Factors of HR The prerequisite for an organization to excel in all aspects of its business activities is absolute strategic management of its HR functions.Human resource management is an extensive term that covers various aspects of personnel function. This discussion is focused on three main aspects that constitute human resource management. Personnel administration Human resource development Industrial relations Personnel administration: It can be also called as the HR module where policies and programmes are laid down by the HR department for the benefit of the human resource personnel. Employment and compensation are chiefly dealt with in personnel administration. While business firms in the corporate environment are in constant demand of man power, finding the right person for the right job is always a testing task for them. Right from job analysis to HR planning, recruitment, selection, placement, induction and orientation, HR department is held accountable to define and develop these operative functions. Mere acquisition and incorporation of human resource is not adequate, the organizations have to engage themselves in empowering their employees through competent training, motivation and refining their social relations. Job Assessment: Job assessment has to be done for fixing compensation that includes wages and salary administration, incentives, bonus, fringe benefits and social security measures. The shifting business environment and consumer requirements compel the organizations to restructure and re-engineer their organizational functions. These moves can be viewed as strategic responses reflecting from all domains of an organization, namely product, marketing, manufacturing etc., where people are the centre of focus. Human resource development: This is easier said than done. Firms are trying to evolve and employ various methodologies of training to enhance the performance levels to the desired standards. Performance cannot be achieved by coercion or bureaucracy, as the work force is protected by numerous enactment of labor laws enforced by various governments. Training and development is a separate entity by itself and is a continuous process that aims at the development of the organization as a whole and also facilitates employee career planning and development. Industrial relations: The following factors have to be scrutinized by the management to maintain good personal relations with the employees. Motivation Morale Job satisfaction Communication Grievance handling Discipline procedure Quality of work life Employee participation All said and done, the organizational health can be measured by checking the effectiveness of HR management through aspects like HR audit and research that aid the firms to analyze and understand the extent to which they are efficient in utilizing human resource for the benefit of their organization. The experience of a human resource manager comes in handy at situations like these, where he has to don different roles to suit the occasion. Personnel role-advisor for top management, policy maker, counselor to employees, spokesman of the company, change analyst, liaison Welfare role-researcher, catering man, motivator Clerical role-time keeping, wages and salary administration, record maintenance, human engineering Fire fighting legal role-negotiator, trouble shooter, peace maker, problem solver, grievance handling. The management employs scientific, analytical, psychological and social techniques to build the business around human resource, who are the real value additions to the...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 13th, 2014 | 0 comments
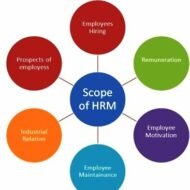
Scope and Characteristics of HRM 1. Personnel aspect: concerned with manpower planning, recruitment, selection, placement, transfer, promotion, training and development, lay off and retrenchment, remuneration, incentives, productivity, etc.; 2. Welfare aspect; dealing with working conditions and provision of amenities such as canteens, crèches, rest and lunch rooms, housing, transport, medical assistance, education, health, safety, recreation facilities, etc.; and 3. Industrial Relations aspect: the legal part which covers union-management relations, joint consultation, collective bargaining, grievance redress and disciplinary procedures, settlement of disputes, etc. Small Business Management and Marketing Essentials CHARACTERISTICS OF HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT: 1. It is an art and a science: The art and science of HRM is indeed very complex. HRM is both the art of managing people by recourse to creative and innovative approaches; it is a science as well because of the precision and demanding application of theory that is required. 2. It is pervasive: Development of HRM covers all levels and all categories of people, and management and operational staff. No discrimination is made between any levels or categories. All those who are managers have to perform HRM. It is pervasive also because it is required in every department of the organisation. All kinds of organisations, profit or non-profit making, have to follow HRM. 3. It is a continuous process: First, it is a process as there are number of functions to be performed in a series, beginning with human resource planning to recruitment to selection, to training to performance appraisal. To be specific, the HRM process includes acquisition (HR planning, recruitment, selection, placement, socialisation), development (training and development, and career development), utilisation (job design, motivation, performance appraisal and reward management), and maintenance (labour relations, employee discipline, grievance handling, welfare, and termination). Second, it is continuous, because HRM is a never-ending process. 4. HRM is a service function: HRM is not a profit centre. It serves all other functional departments. But the basic responsibility always lies with the line managers. HRM is a staff function – a facilitator. The HR Manager has line authority only within his own department, but has staff authority as far as other departments are concerned. 5. HRM must be regulation-friendly: The HRM function has to be discharged in a manner that legal dictates are not violated. Equal opportunity and equal pay for all, inclusion of communities in employment, inclusion of tribal’s and farmers in the benefits and non-violation of human rights must be taken care of by the HRM. 6. Interdisciplinary and fast changing: It is encompassing welfare, manpower, personnel management, and keeps close association with employee and industrial relations. It is multi- disciplinary activity utilising knowledge and inputs from psychology, sociology, economics, etc. It is changing itself in accordance with the changing environment. It has travelled from exploitation of workers to treating them as equal partners in the task. 7. Focus on results: HRM is performance oriented. It has its focus on results, rather than on rules. It encourages people to give their 100%. It tries to secure the best from people by winning the whole hearted cooperation. It is a process of bringing people and organization together so that the goals of each are met. It is commitment oriented. 8. People-centred: HRM is about people at work both as individuals and a group. It tries to help employees to develop their potential fully. It comprises people-related functions like hiring, training and development, performance appraisal, working environment, etc. HRM has the responsibility of building human capital. People are vital for achieving organizational goals. Organizational performance depends on the quality of people and employees. 9. Human relations philosophy: HRM is a philosophy and the basic assumption is that employees are human beings and not a factor of production like...




