Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Decision Making, Management Accounting, Project Management
on Apr 1st, 2014 | 0 comments
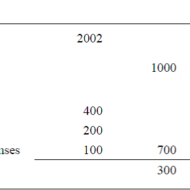
ACCOUNTING AND DECISION MAKING – IDENTIFYING THE PROBLEM SITUATION Learn accounting and finance basics so you can effectively analyze business data to make key management decisions. Business owners are faced with countless decisions every business day. Managerial accounting information provides data-driven input to these decisions, which can improve decision-making over the long term. Fig 1.1- ACCOUNTING INFORMATION FOR A SINGLE PRODUCT The above illustration clearly depicts that there has been a loss of Rs.100 in one year’s time for this particular product. The reason can be attributed to the increase in the “cost of goods” whereas other expenses have remained the same in both the years. For a single product manufactured, the problem is identifiable and solvable. But when the organization is producing a range of products, you need to apply some accounting technique by which the product losing money is identified and suitable measures are taken to cut down the escalating cost. Fig 1.2- Accouning Information for a Product Range The above illustration compares and contrasts the relationship of three products a company manufactures. It is seen that products P1 and P2 are doing well. Though the cost of sales has gone up for P1 and P2, the sales volume has also increased thus increasing the gross profit over the period of time. Here the product that has to be dealt with is P3 whose sales volume has drastically gone down, yet with the same cost of sales. When there is an increase in cost of sales, two things have to be considered. Identifying the problem-product Either cut down the production cost or increase the selling-price if the product has a real demand in the market. Uses of Accounting Data: Accounting information helps the management to arrive at make or buy decisions, to outsource production of certain components to cut down or control costs, to expand the production, to increase the sales volume or to downsize their project capacity. Techniques like Break-Even Analysis, Costing and Budgeting aid in going for the right production-mix, marketing-mix and sales target plans for the respective financial years. Aggregate Planning: As we all know planning is the key to the future and financial planning has to be given utmost importance for a production process. Aggregate planning involves translating long-term forecasted demand into specific production rates and the corresponding labor requirements for the intermediate term. It takes into consideration a period of 6 to 18 months, breaking it into work modules weekly or monthly and planning for the specific period in terms of men, material and...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Entrepreneurship, Labor Management, Operations Management, Principles of Management
on Mar 31st, 2014 | 0 comments
Operations Research-Emphasizing the need of Math in Management Business is all about “demand versus supply”. And as is always the case, industries operate in a tight situation, with limited resources and heavy demand, trying to make the ends meet. The production of required quantity with the available resources needs an approach that is quantitative and logical as well. This can be obtained by weighing the odds and choosing the right kind of decision that suits your business plan, be it production, distribution, marketing, selling or any business situation, where there is a need to compare and contrast between alternating decisions, to arrive at an optimal solution. High end mathematical concepts in Operations: Operations research comes into the picture in such situations, wherein, high end mathematical concepts and models are applied to problem situations, to first define the problem and then extract the best possible solution by quantifying the resources available. Quantitative data is then converted into linear equations to maximize the productivity and profit. Profit maximization is generally aimed by most of the firms that operate with limited potential and operations research helps to achieve this through optimal use of the available resources. Application of Scientific Methods: The emphasis is on application of scientific methods, use of quantitative data, goals and objectives and determination of the best means to reach them. Once the data is collected, it is carefully evaluated and the relationship among data is established, which helps in defining the problems and goals. The problem is represented logically to decide the course of action. Say, for example, Linear Programming represents each and every problem situation in the form of a linear equation and tries to allocate resources in an optimal fashion. Alternate decisions are evaluated and the decision that yields the best result in terms of productivity and profit is considered. Measure of Effectiveness: How do you measure profit? The measure of effectiveness will be determining the rate of return on investment, and every possible solution can be weighed against this measure. Theories of probability are also used to predict the success rate of the combinations of variables executed in different ways. But one has to understand that only some variables are controllable and others are not. Say, if the economy experiences inflation or recession, your predictions will undergo a drastic review in purview of the fluctuations in the economy. Similarly availability of labor is always a constraint, either labor is not available or they demand more pay. Simplex Methods: Since voluminous data is involved, computers with multi processors are used to manipulate the data. Mathematical tools like simplex methods, integer programming, graphical methods, transportation and assignment techniques, simulations, game theory and queuing theory can be very well applied to solve complex problem situations with ease. Today’s business world demands more sophistication in terms of technical updations. Evolution of Opeartions Research Techniques: Operations Research dates back to the Second World War period, and the accelerated growth of this discipline in recent years can be attributed to the fact that, researchers have found this useful in solving economic and political problems too. At the same time, critics point out that, application of operations research proves advantageous only to those people who are accustomed to the usage of rapid computing machines and understand the complex mathematical formulae and relationships. Note: Energy: The oil industry was one of the earlier users of operations research techniques to help manage their refinery processes, and operations research technologies are heavily used by all the major oil companies. Manufacturing: Manufacturing organizations continue to use operations research to optimize factory operations. Transportation: Operations researchers execute logistics for air traffic control, trucking, and railroads. Real-time dispatching and delivery truck...

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Financial Management, Management Accounting, Principles of Management
on Mar 29th, 2014 | 0 comments

Profitability ratios are metrics that assess a company’s ability to generate income relative to its revenue, operating costs, balance sheet assets, or shareholders’ equity. Profitability ratios show how efficiently a company generates profit and value for shareholders. Accounting Basics for Success in Business and in Life! In general two groups of profitability ratios are calculated. Profitability in relation to sales.Profitability in relation to investments. Profitability Ratios can be Classified into five types Gross profit margin or ratioNet profit margin or ratioOperating profit margin or ratioReturn on AssetsReturn on Equity 1. GROSS PROFIT MARGIN OR RATIO It measures the relationship between gross profit and sales. It is calculated by dividing gross profit by sales. Gross profit margin or ratio = Gross profit X 100 / Net salesGross profit is the difference between sales and cost of goods sold. 2. NET PROFIT MARGIN OR RATIO It measures the relationship between net profit and sales of a firm. It indicates management’s efficiency in manufacturing, administrating, and selling the products. It is calculated by dividing net profit after tax by sales. Net profit margin or ratio = Earning after tax X 100 / Net Sales 3. OPERATING PROFIT MARGIN OR RATIO It establishes the relationship between total operating expenses and net sales. It is calculated by dividing operating expenses by the net sales. Operating profit margin or ratio = Operating costs X 100 / Net sales (0r) Cost of goods sold + Operating expenses * 100 / Net sales Operating expenses includes cost of goods produced/sold, general and administrative expenses, selling and distributive expenses. 4. RETURN ON ASSETS Return on assets is the ratio that is used to measure the company’s ability to generate profit by using its whole resource, the assets. It shows the percentage of the net income or net profit comparing to the average total assets. Return on assets shows how efficient the company is in using the assets to generate profits in a period of time. The high return on assets usually shows that the company performs well in making a profit from the assets it has. Return on assets can be calculated by comparing net income or net profit after interest and tax in the period to average total assets. Return on Assets = Net Profit / Average Total Assets 5. RETURN ON EQUITY Return on equity is the ratio that is used to measure the company’s ability to generate profit by using its investors’ money. It shows the percentage of the net income or net profit comparing to the average total equity. Return on equity shows how efficient the company is in using the investor’s money to generate profits in a period of time. The high return on equity usually shows that the company performs well in making profits from its investors’ money. Return on equity can be calculated by comparing net income or net profit after interest and tax in the period to average total equity. Return on Equity = Net Profit / Average Total...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Decision Making, Marketing, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Strategy
on Mar 23rd, 2014 | 0 comments

Smart Objectives for Success An objective describes something which has to be accomplished and defines what organizations, functions, departments, teams and individuals are expected to achieve. Objectives may be operational or developmental. When the contribution is oriented towards the accomplishment of corporate objectives, in the light of the organization’s mission, core values and strategic plans, it is termed as operational; personal or learning objectives that involve the improvement of knowledge, skills and performance of individuals is termed as developmental. Objectives must be SMART: S-scientific M-motivating A-achievable R-realistic T-time bound Objectives that are mostly confined to the near future may be termed-short term objectives, which are accomplished in the stipulated time duration. Say, for example, 1000 units of pet bottles have to be produced in a week’s time. If the firm is focused on the overall production plan for the forthcoming year, then it is termed as long term objective. In a production environment, a firm has to initially go for an aggregate plan, where the production capacity of the plant is determined to make the project feasible. The firm has to make doubly sure, whether it is resourceful in terms of physical, financial and human aspects. The work centers are allotted with jobs in a mock trial to check man versus machine co-ordination and compatibility. Pic Courtesy: Digital Information World Proper Planning: Objectives are achieved only when there is proper planning. The top management must take the pains to clearly explain the objectives to all the employees across different levels of organization to facilitate smooth functioning. When the employees understand what is expected of them, the performance gets oriented towards accomplishing the objectives; the employees get proper direction and focus. Delivering Happiness: A Path to Profits, Passion, and Purpose Think of this, what will happen to the sales volume, if the marketing manager does not properly educate his team about the targets to be achieved for that quarter? Definitely there will be a dip in the sales owing to the lethargic and irresponsible attitude of the manager. Ultimately, the organization stands to suffer a loss in terms of time and cost of recruiting a new person to head the marketing department. Right Person for the Right Job: Organizations have to be meticulous while choosing people for the post of managers. The chosen persons must be able to identify themselves with the organization and its objectives, so that they could be a source of inspiration for people down the line. Right people for the right job, at the right place and right time is the success mantra. Objectives have to be periodically revised in the light of changing economic, political and technological developments. How to Stop Worrying and Start Living If not the objectives might become obsolete and in due course you will get stranded amidst the roaring competition. The process of business management aims at managing people and other resources to make a modest profit. How to achieve success in an open market? By clearly setting objectives that serve as tools of motivation and persuasion, a firm can evolve and contribute strategic inputs that make the objectives realistic and...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Ethics, Business Management, CSR, Entrepreneurship, Principles of Management
on Mar 15th, 2014 | 0 comments
![Code of Ethics]()
Institutionalize Your Code of Ethics Business Ethics is a term we often come across in the world of corporate business. Ethics generally distinguishes between the right and the wrong. But you might argue, what is right for one person may not be for the other. “True! But there are certain principles that are widely accepted by everyone that guides the behavior of individuals or a business enterprise. Shall we say that Business Ethics is an UNWRITTEN CODE OF CONDUCT which governs the conduct of a business enterprise and also helps it in reaching the right decision? CSR CORPORATE SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY comes into the big picture when you talk about business or professional ethics. When a person gears up himself to start a business, he studies the market as to how supportive it would be to carry on his business. He segments the market, evaluates the demography, approaches financial institutions like banks for loans, creates a big cacophony about the government’s red tapism to acquire licenses to do his business and when all these criteria accords a green signal he ventures into the market with a confidence that is backed up by all the above factors. Say by the end of the first year, he has done great business and the time has come for income tax or sales tax payments, a small voice cuckoos from within, asking him to think twice or to venture the possibilities of EVADING TAX. Once he tastes the essence of success and the POWER OF MONEY he deviates from the RIGHT CONDUCT and BEHAVIOR. He conveniently abstains himself from performing his duties towards customers, employees, government, share holders, stake holders and others. Mind you, being ethical is a statutory phenomenon and not a thing to be taken for granted. If your motivation and effort is oriented only TOWARDS PROFIT, thriving longer in the market will become a matter of concern. Every action has an equal and opposite reaction: “Whatever is that you take, you have to repay.”This is applicable both in personal life as well in business. Yogis’ have ascertained the fact time and again that you have to dissolve your karma or past actions to be a liberated soul. Neo world scientists also second this thought,” every action has an equal and opposite reaction. “Being ethical is not that demanding or tough as you have conceived it to be. In simpler terms, it even teaches you to be highly compassionate towards your fellowmen. Various aspects affecting ethical behavior in a business organization would be: Policies regarding moral duty and obligation Accounting ethics Corporate culture Ethics in management development programmes Dealing with “gray areas” Disciplinary procedures Review and updating the ethical code Increased concern about the well informed public Government regulations Value based management practices Enlightening the managers of top cadre Rewards and recognitions for people with right conduct and the list goes on and on. Corruptions, Bribery, Black marketing are some of the JARGONS that are strictly prohibited words and actions in the dictionary of ethics. Sound ethical practices not only create an IMAGE for your company, but also the recognition among your own employees that you could relish. Being ethical is not that difficult, only that it calls for undeterred determination and inbuilt...









