Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Decision Making, Marketing, Operations Management, Project Management
on May 7th, 2014 | 0 comments
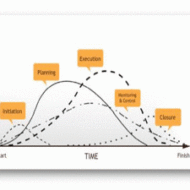
Project Formulation and Project Life Cycle What is a Project? “A temporary endevour leading to a product / service or result ” A project is any series of activities and tasks that: • Have a specific objective to be completed within certain specifications • Have defined start and end dates; • Have funding limits (if applicable); and • Consume resources (i.e. money, time, equipment). Characteristic Features of a Project: • Has a mission or a set of objectives. Once the mission is achieved the project is treated as completed. • Has to terminate at some time or the other (temporary in nature) • The project is one single entity and its responsibility is assigned to one single agency. • Calls for team-work, the members of the team may come from different organizational units, different disciplines, and geographic regions. • Has a life cycle represented by growth, maturity and decay. • Is unique and no two projects are similar, even though the plants set up are identical. The organizations, the infrastructure, the location and the people make the project unique. • Change is a natural phenomenon with every project throughout its life span. Some changes may not have any major impact, but some may change the very nature of the project. • The happenings during the life cycle of a project are not fully known at any stage. As time passes, the details are finalized successively. • Is always customer-specific. The requirements and constraints within which a project must be executed are stipulated by the customer. • Is a complex set of things. Projects vary in terms of technology, equipment and materials, machinery and people, work ethics and organizational culture. • A substantial portion of the work in a project is done by sub-contracting. The greater the complexity of a project, the greater will be the extent of work performed by subcontractors. • Is exposed to risk and uncertainty and the extent of these depend upon how the project moves through the various stages in its life span. • A well defined project has lesser risk and uncertainty, whereas an ill-defined project faces greater degree of risk and uncertainty. Project Life Cycle: The Project Life Cycle refers to a series of activities which are necessary to fulfill project goals or objectives. The different phases are as follows: a) Concept or initialization phase In this phase, the project idea emerges and the #management decides on the need for a project. A project which is well conceived can be later implemented successfully. b) Project Definition Phase •The techno-economic viability of the project is checked •The technical configuration of the project is identified •The performance requirements, sub-systems, key equipments etc.- purchased •The cost estimates with limits are identified •Schedule of implementation is identified c) Growth or Organisation Phase Organizations, during this phase, undertake the following actions: a) Establishing the infrastructure and enabling services for the project b) Project engineering and design c) Setting up Project Organization and staffing d) Appointing a project manager e) Preparing schedules and budgets f) Obtaining necessary licenses and clearances from the Government g) Raising finance h) Developing systems and procedures for monitoring and reviewing project progress i) Procedures for inviting tenders and awarding contracts j) Site preparation and development k) Procuring equipment and materials l) Work packaging This phase covers both paper work connected with project planning and also implementation activities. Planning is necessary to avoid crisis management; it makes the implementation phase to run smoothly. d) Implementation Phase The activities include: 1) The preparation of specifications for major equipment and machineries, 2) Placing orders with vendors for the supply of...


