Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Financial Accounting, Financial Management, Principles of Management
on Mar 27th, 2014 | 0 comments

An Analysis to Understand the Art of Accounting Objectives of an Accountant: The pure objective of an accountant would be to record all business transactions that are monetary in nature, in order to ascertain if the company has earned profit or suffered loss during a financial year. The financial position of the company as on a particular date can thus be understood from the accounting journals and ledgers. We are talking about the conventional purpose of accounting. But with the lapse of time, more and more is being expected from accounting, in that, it has to meet the demands and requirements of tax authorities for the purpose of income tax and sales tax returns, government regulations, investors, owners and the management. Thus it can be aptly defined as the art of recording, classifying and summarizing events in a significant manner, that involve money transactions and/ or events that are of financial character, for interpretation. Systematic records for future reference: Book keeping is an accounting practice that tells us how to keep a record of financial transactions. A firm deals with its customers and suppliers, where numerous business transactions take place every day. It is not possible for us to remember every transaction, which we might need it for our reference at a future date. Especially, if it happens to be a credit sale, definitely the necessity of systematic book keeping arises. The owner would like to know, what amount is due from whom, from time to time. To know the financial position of the firm: Every merchant is in business to earn profits. So systematic recording of factual and financial information will facilitate the owner to understand where he stands financially at the end of a financial year, what is his net profit and to pull the ropes tight if credit margin is wide. Further more, he can also understand the nature of his business growth by comparing the accounting records of two consecutive years. Taxation purposes: Some people evade tax, but no one can avoid tax. The main source of revenue generation for government is tax payments from business merchants and corporate companies. You need to pay a percentage as tax, in accordance with profit arising from sales. The accounting records that you maintain contain facts that are taken into account by the taxation authorities as a basis for assessment. https://amzn.to/2sl5aL7 Good evidence in the court of law: To prove your genuinity, in case of some disputes between yourself and the customer or supplier, your records and vouchers, if authentic and valid, are going to speak for you in the court of law as solid evidence. Accounting also answers some of these questions: How well the different departments of business have performed all along? What is the most profitable product line? What are the products whose production has to be increase and what is to be stopped in order to avoid losses? Is the cost of production reasonable or excessive? Is there a need to revise policy decisions to improve the profitability? What will be the future plans of business in the wake of existing results presented to the management? Overall, is the firm proceeding towards the right direction in terms of productivity, profitability and growth? Accounting is not only about recording and classifying, the interesting features being analysis and interpretation, which are the key factors for the development of the organization as a whole. Note: The Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAG),is the head of the Supreme Audit Institution of India (SAI) CAG is the sole auditor of the accounts of the Central (Union) Government and the State Governments. CAG is also responsible for the audit...

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting
on Feb 21st, 2014 | 0 comments
Functions of Accounting: a. Recording: Accounting records business transactions in terms of money. It is essentially concerned with ensuring that all business transactions of financial nature are properly recorded. Recording is done in journal, which is further subdivided into subsidiary books from the point of view of convenience. b. Classifying: Accounting also facilitates classification of all business transactions recorded in journal. Items of similar nature are classified under appropriate heads. The work of classification is done in a book called the ledger. c. Summarizing: Accounting summarizes the classified information. It is done in a manner, which is useful to the internal and external users. Internal users interested in these informations are the persons who manage the business. External users of information are the investors, creditors, tax authorities, labor unions, trade associations, shareholders, etc. d. Interpreting: It implies analyzing and interpreting the financial data embodied in final accounts. Interpretation of the data helps the management, outsiders and shareholders in decision making. Limitations of Accounting: Accounting information is expressed in terms of money. Non monetary events or transactions, however important, are completely omitted. Fixed assets are recorded in the accounting records at the original cost, that is, the actual amount spent on them plus all incidental charges. In this way the effect of inflation (or deflation) is not taken into consideration. The direct result of this practice is that balance sheet does not represent the true financial position of the business. Accounting information is sometimes based on estimates; estimates are often inaccurate. Accounting information cannot be used as the only test of managerial performance on the basis of more profits. Profit for a period of one year can readily be manipulated by omitting such costs as advertisement, research and development, depreciation and so on. Accounting information is not neutral or unbiased. Accountants calculate income as excess of revenues over expenses. But they consider only selected revenues and expenses. They do not, for example, include, cost of such items as water or air pollution, employee’s injuries, etc. Accounting Made Easy Accounting like any other discipline has to follow certain principles, which in certain cases are contradictory. For example current assets (e.g., stock of goods) are valued on the basis of cost or market price whichever is less following the principle of conservatism. Accordingly the current assets may be valued on cost basis in some year and at market price in another year. In this manner, the rule of consistency is not followed...

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Financial Accounting
on Feb 21st, 2014 | 0 comments
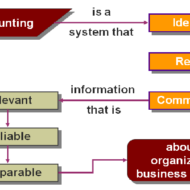
Characteristics and Objectives of Accounting What is Accounting: According to American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA), “Accounting is the art of recording, classifying and summarizing in a significant manner and in terms of money transactions and events which are, in part at least, of a financial character and interpreting the results thereof.” American Accounting Association (AAA) has defined accounting as “the process of identifying, measuring and communicating economic information to permit informed judgements and decisions by users of the information.” Characteristics of Accounting: i. Accounting is the art of recording and classifying different business transactions. ii. The business transactions may be completely or partially of financial nature. iii. Generally the business transactions are described in monetary terms. iv. In accounting process, the business transactions are summarized and analyzed so as to arrive at a meaningful interpretation. v. The analysis and interpretations thus obtained are communicated to those who are responsible to take certain decisions to determine the future course of business. The Small Biz Doers’ Guide to Small Biz Accounting Objectives of accounting: a. To record the business transactions in a systematic manner. b. To determine the gross profit and net profit earned by a firm during a specific period. c. To know the financial position of a firm at the close of the financial year by way of preparing the balance sheet d. To facilitate management control. e. To assess the taxable income and the sales tax liability. f. To provide requisite information to different parties, i.e., owners, creditors, employees, management, Government, investors, financial institutions, banks etc. ...






