Posted by Managementguru in Financial Accounting
on Feb 24th, 2015 | 0 comments

What are known as Final Accounts? Trading, profit & loss account and balance sheet, all these three together, are called as final accounts. Final result of trading is known through Profit and Loss Account. Financial position is reflected by Balance Sheet. These are, usually, prepared at the close of the year hence known as final accounts. They serve the ultimate purpose of keeping accounts. Their purpose is to investigate the consequence of various incomes and expenses during the year and the resulting profit or loss. 1. Trading and Profit and Loss A/c is prepared to find out Profit or Loss. 2. Balance Sheet is prepared to find out financial position of a concern. Trading Account Trading refers buying and selling of goods. Trading A/c shows the result of buying and selling of goods. This account is prepared to find out the difference between the Selling prices and Cost price. Profit and Loss Account Trading account discloses Gross Profit or Gross Loss. Gross Profit is transferred to credit side of Profit and Loss A/c. Gross Loss is transferred to debit side of the Profit Loss Account. Thus Profit and Loss A/c is commenced. This Profit & Loss A/c reveals Net Profit or Net loss at a given time of accounting year. Trading Profit And Loss CMD from knoxbusiness Balance Sheet Trading A/c and Profit & Loss A/c reveals G.P. or G.L and N.P or N.L respectively; besides the Proprietor wants i. To know the total Assets invested in business ii. To know the Position of owner’s equity iii. To know the liabilities of business. Definition of Balance Sheet The Word ‘Balance Sheet’ is defined as “a Statement which sets out the Assets and Liabilities of a business firm and which serves to ascertain the financial position of the same on any particular date.” On the left hand side of this statement, the liabilities and capital are shown. On the right hand side, all the assets are shown. Therefore the two sides of the Balance sheet must always be equal. Capital arrives Assets exceeds the liabilities. BUY “ACCOUNTING CONVENTIONS AND CONCEPTS” OBJECTIVES OF BALANCE SHEET: 1. It shows accurate financial position of a firm. 2. It is a gist of various transactions at a given period. 3. It clearly indicates, whether the firm has sufficient assents to repay its liabilities. 4. The accuracy of final accounts is verified by this statement 5. It shows the profit or Loss arrived through Profit & Loss A/c. PREPARATION OF FINAL ACCOUNTS Preparation of final account is the last stage of the accounting cycle. The basic objective of every firm maintaining the book of accounts is to find out the profit or loss in their business at the end of the year. Every businessman wishes to find out the financial position of his business firm as a whole during the particular period. In order to accomplish the objectives for the firm, it is essential to prepare final accounts which include Trading, Profit and Loss Account and Balance Sheet. It is mandatory that final accounts have to be prepared, every year, in every business. Trading and profit & loss accounts are prepared, after all the accounts have been completely written and trial balance is extracted. Before preparing final accounts, it becomes obligatory to scritinize whether all the expenses and incomes for the year for which accounts are prepared have been duly provided for and included in the accounts. Form of Final Accounts: There is a standard format of final accounts only in the case of a limited company. There is no fixed prescribed format of financial accounts in the case of a proprietary concern and partnership...

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Decision Making, Management Accounting, Project Management
on Apr 1st, 2014 | 0 comments
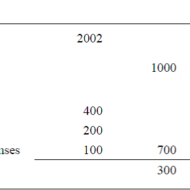
ACCOUNTING AND DECISION MAKING – IDENTIFYING THE PROBLEM SITUATION Learn accounting and finance basics so you can effectively analyze business data to make key management decisions. Business owners are faced with countless decisions every business day. Managerial accounting information provides data-driven input to these decisions, which can improve decision-making over the long term. Fig 1.1- ACCOUNTING INFORMATION FOR A SINGLE PRODUCT The above illustration clearly depicts that there has been a loss of Rs.100 in one year’s time for this particular product. The reason can be attributed to the increase in the “cost of goods” whereas other expenses have remained the same in both the years. For a single product manufactured, the problem is identifiable and solvable. But when the organization is producing a range of products, you need to apply some accounting technique by which the product losing money is identified and suitable measures are taken to cut down the escalating cost. Fig 1.2- Accouning Information for a Product Range The above illustration compares and contrasts the relationship of three products a company manufactures. It is seen that products P1 and P2 are doing well. Though the cost of sales has gone up for P1 and P2, the sales volume has also increased thus increasing the gross profit over the period of time. Here the product that has to be dealt with is P3 whose sales volume has drastically gone down, yet with the same cost of sales. When there is an increase in cost of sales, two things have to be considered. Identifying the problem-product Either cut down the production cost or increase the selling-price if the product has a real demand in the market. Uses of Accounting Data: Accounting information helps the management to arrive at make or buy decisions, to outsource production of certain components to cut down or control costs, to expand the production, to increase the sales volume or to downsize their project capacity. Techniques like Break-Even Analysis, Costing and Budgeting aid in going for the right production-mix, marketing-mix and sales target plans for the respective financial years. Aggregate Planning: As we all know planning is the key to the future and financial planning has to be given utmost importance for a production process. Aggregate planning involves translating long-term forecasted demand into specific production rates and the corresponding labor requirements for the intermediate term. It takes into consideration a period of 6 to 18 months, breaking it into work modules weekly or monthly and planning for the specific period in terms of men, material and...

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Financial Management, Management Accounting, Principles of Management
on Mar 27th, 2014 | 0 comments
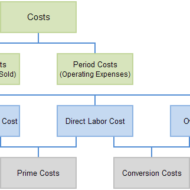
Costing is the technique and process of ascertaining cost whereas cost accounting is the application of costing and cost accounting principles, methods and techniques to the science, art and practice of cost control and ascertainment of profitability.






