Posted by Managementguru in Business Ethics, Business Management, Principles of Management, Strategy
on Mar 15th, 2014 | 0 comments
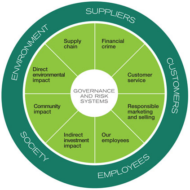
Social Value of Corporate Companies Economic Responsibilities: Ethical and discretionary responsibilities of a business firm are listed in the order of priority. First, a firm has to satisfy its economic responsibilities, followed by fulfilling legal responsibilities in order to survive in the market. Only then, it can think about or focus on purely voluntary actions pertaining to ethical consideration. In this competitive market situation, a business unit has to concentrate on profit making, the primary motive behind any business activity. However; it is easier said than done. You cannot hit the bull’s eye at the very first attempt. A firm has to become economically stable first; only then, it integrates social commitments in its agenda. Arguments for social responsibility: Public image: Socially responsible firms gain more customers and employees feel proud to work for such organizations. Handling the government regulations with ease: Government is a massive institution with long arms. It seeks to regulate business in public interest. Before government stretches its long arms, business persons should discharge their obligations to society. Business is resourceful: With a pool of resources, such as capital, labor and expertise, business is in a better position to tackle social problems and work for social goals. Let business try: It is that many other institutions have failed in handling social problems. So why should not a business enterprise handle social problems? Prevention is better than cure: Social problems have to be handled by the management at some point of time or the other. Problems with labor unions should be handled in a diplomatic way, so that they will not develop into serious social breakdown that consumes most of the management’s time. As a token of gratitude: Business units benefit from society. Based on the commonly accepted principle, that one owes debts of gratitude towards those who benefits us, the corporations have debts that it owes to society. Arguments against social responsibility: Profit maximization is the ultimate goal: Business units are accused of having profit maximization as their goal. Since business operates in a world of poverty and hunger, the economic efficiency of business is a matter of priority and should be the sole mission of business. Society has to pay the cost: The costs of social responsibility will be passed on to the society and the question is can the society bear these additional costs? Lack of social skills: Managers are here to solve economic problems and they do not possess knowledge or skills to provide the right solutions for social problems. Business has enough power: Business already is wielded with enough social power. The society should not take any steps, which will make it stronger. Social overhead costs: Costs on social responsibility is considered a social cost, which will not immediately benefit the business. Why spend money on an object, the benefits of which will be relished only in the future. Lack of broad support: The idea of business involvement in achieving social goals is not widely supported by many groups in society. Business and society are interlinked in many ways and the business has to handle the societal aspects with great care or else it may have to face the consequences arising out of such misappropriation or...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Human Resource, Leadership, Principles of Management
on Mar 1st, 2014 | 0 comments
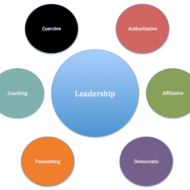
One of the key concepts of leadership is that everyone has innate leadership skills that can be ‘polished’ and developed. In excellent organizations, everyone, regardless of title or position, is encouraged to act like a leader. One of the principles of effective leadership is “to make sure that other people will be willing to follow you. Unfortunately, management education doesn’t place enough emphasis on leadership skills.” The functions of a leader can be defined as follows: 1. Taking the initiative – A leader initiates all actions necessary for the purpose of warranting the health and growth of the enterprise in a competitive economy. 2. He identifies group goals 3. He represents the organization 4. He acts as an arbitrator 5. To assign reasons for his actions 6. To interpret the objectives of organization 7. To guide and direct the organization 8. To encourage team work 9. He manages the organization Top 50 Quotes That Show the Road to Success This exemplary leadership model by kouzes and posner will give you a fair idea on how a leader should set behavioral and performance standards in an organization. Leadership Styles Every leader has his own style that can be defined as a leader‘s behavior towards group members. It refers to the pattern of behavior which a leader embraces in influencing the behavior of his subordinates in the organizational context. Different leadership styles can be categorized as follows. 1. Autocratic Leadership Autocratic leadership is also known as authoritarian, directive, leader centered or monothetic style. Under this style, leader concentrates all authority in himself, instructs a subordinate as to what to do, how to do it, when to do it etc. He also exercises close supervision and control over his subordinates. There are three categories of autocratic leaders a. Strict Autocrat – A strict autocrat believes on negative authority and gives orders which the subordinates must accept. He may also use his powers to disperse rewards to his group. b. Benevolent Autocrat – The benevolent style aids in accomplishing high productivity in many situations and he can develop effective human relationship. His motivational style is usually positive. c. Manipulative Autocrat – A manipulative autocrat leader is one who makes the subordinates feel that they are participating in decision making process even though he has already taken the decisions. 2. Participative Leadership This style is also called as democratic, consultative, group centered or ideographic style. A participative leader is one who consults and welcomes his subordinates to participate in decision making process. Under this style, subordinates are freely allowed to communicate with the leader and also with their fellow subordinates and take their own initiative. 3. Laissez Faire or Free-rein Leadership Under this style of leadership, the leader mostly depends upon the group and its members to establish their own goals and make their own decisions. The leader is passive and assumes the role of just another member in the group. Only very little control is exercised over group members. This style is also known permissive style of leadership. This style is appropriate only in certain situations where the manager can leave a choice to his groups. A leader is supposed to possess these discretionary skills required at different times and during interaction with different people… Qualities of a successful leader The following are the major innate qualities in a successful leader. 1. Physical features like height, weight, health and appearance 2. Intelligence 3. Emotional stability 4. Human relations 5. Empathy 6. Objectivity 7. Motivating skills 8. Technical skills 9. Communicative skills 10. Social...




