Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Decision Making, Marketing, Strategy
on Jul 7th, 2014 | 0 comments

What is Portfolio Analysis ? Portfolio Planning is best advised for diversified companies than the more product coherent ones. Portfolio analysis plays a vital role in planning and implementation of various #strategic business units of the organization as a whole. Portfolio planning recognizes that diversified companies are a collection of businesses, each of which makes a distinct contribution to the overall corporate performance and which should be managed accordingly. Companies dealing with a wide #product range and divisions are expected to redefine their strategies for each of the SBU’s or Strategic Business Units. Then they classify these units on a portfolio grid according to the competitive position and attractiveness of a particular product market. What are strategic business units? A strategic business unit is a fully functional and discrete unit of the business that builds its own strategic vision and direction. Within large companies there are smaller specialized divisions that work towards specific projects and #objectives. The strategic business unit, often referred to as an SBU, remains an important element of the company and is accountable to their head office about their operational status. Typically they will operate as an independent organization with a specific focus on target markets and are large enough to maintain internal divisions such as finance, HR, and so forth. Being Strategic: Thinking and Acting with Impact Types of Portfolio Planning: Analytical Planning: Planning is only at the initial level where traditional administrative tools are used. Process Planning: Here planning is a central part of the ongoing #management process and strategic mission is explicit in activities. Advantages of Portfolio Planning: It promotes substantial improvement in the quality of strategies formulated both at the business and corporate levels.It provides a guideline for adopting their overall management process to the needs of each business.It provides selective #resource allocation to the various SBUs.It furnishes companies with a greatly improved capacity for strategic control when portfolio planning is applied intelligently and with attention to its limitations and problems. Since the road to portfolio planning is a long one, companies often face difficulties trying to implement it and cannot realize the full potential of the approach. In implementing portfolio planning, there is a tendency for the focus to be shifted towards #capital investment rather than resource allocation. #Resource Development is the key: Become a Product Manager | Learn the Skills & Get the Job Implementing Corporate Level and Business Level Strategies: Corporate level #strategy is concerned with the strategic decisions a business makes that affect the entire organization. Financial performance, mergers and acquisitions, #human resource management and the allocation of resources are considered part of corporate level strategy.Business level strategy focuses on how to compete in a particular product/market segment or industry. Competitive advantages and distinctive competencies thus become dominant strategic concerns at this level.At the functional level, the primary focus of strategy is efficiency. Boston Consulting Group Matrix: The business policy portfolio models are most popular and useful to understand the firm’s strategic concerns and choices. They define the firm’s scope or domain by highlighting the inter-relatedness of the diverse factors, such as: #Market Growth#Market ShareCash and Cash flow patternsCapital Intensity#Product Maturity BCG Matrix #Stars– Star category represents high growth and high market share– High investments are needed to maintain the share– High cash flow outward movement in this category to maintain status– Usually in the end of the ‘Growth’ #Product Life Cycle stage– Represents emerging and good business for the company, though they need alot of attention and priority #Cash Cows– Represents low growth, high market share– This is the best quadrant of the portfolio as the company basically enjoy the ‘milk’ of success– This is where the...

Posted by Managementguru in Video Lecturers
on Apr 20th, 2014 | 0 comments

Strategic Management Video Lecture by David Kryscynski This is the introduction lecture for Strategic Management. Very Innovative and Informative video. A List of Strategic Management Terms Business – A strategy that pertains to single departments or units within a company.Combination – A type of grand strategy that employs several different grand strategies at once.Concentration – A growth strategy that extends the sale of current products or services to a company’s current market.Differentiation – A business strategy that strives to make the company’s product or service unique.Diversification – A growth strategy that moves a company into a similar kind of business with new or different products or services.Divestiture – A type of defensive strategy in which a company sells some part of its business, often an unprofitable part.Evaluating – The process of continuously monitoring the company’s progress toward its long-range goals and mission.Focus – A business strategy that directs marketing and sales towards a small segment of the market.Formal – The type of planning that involves systematic studying of an issue and the preparation of a written document to deal with the problem.Formulating strategy – Developing the grand- and business-level strategies to be used by the company.Functional – A strategy which involves short-range operational plans which support business strategies by emphasizing practical implementation.Goal – A concise statement that provides direction for employees and set standards for achieving the company’s strategic planGrand – A type of strategy that provides overall direction for the company.Growth – A type of grand strategy developed when a company tries to expand sales, products, or number of employees.Implementing – Putting a strategy to work after it has been formulated.Intermediate – Covers the time span between short-range and long-range, usually 1-3 years or 1-5 yearsLiquidation – A type of defensive strategy in which the entire company is sold or dissolved.Long Term– A three-to-five year period of time, but possibly as far as 20 years into the future.Mission Statement – A brief summary explaining why a company exists.Operational – Short-range planning that focuses on forming ideas for dealing with specific functions in the company.Overall Cost Leadership – A business strategy that is designed to produce and deliver a product or service for a lower cost than the competition.Planning – The process that businesses use to decide the company’s goals for the future and the ways to achieve those goals.Policy – A broad general guide to action that establishes boundaries within which employees must operate.Procedure – A detailed series of related steps of tasks written to implement a policy.Retrenchment – A type of strategy that aims to reverse negative trends in a company, such as losses in sales.Rule – A specific and definite corporate action that employees must follow.Short Term– A one-year period of time.Stability – A type of strategy that aims to keep the company operating at the same level that it has for several years.Strategic – Long-range planning done by the highest management levels in the company.Strategic Management – The application of the basic planning process at the highest levels of the company.Strategy – An outline of the basic steps management is going to take to achieve a goal.SWOT Analysis – The most utilized process for determining a company’s overall health; it involves analyzing internal strengths, internal weaknesses, external opportunities, and external threats.Turnaround – A type of defensive strategy that is used to regain success.Vertical Integration – A growth strategy that moves a company into a market it previously served either as a supplier or as a customer. Take The Test to Check Your Strategic...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Decision Making, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Strategy
on Mar 24th, 2014 | 0 comments
STRATEGIC PLANNING Strategic planning is the primary step in the process of strategic management [Strategic management is a comprehensive topic that covers almost all the functional aspects of the organization] which can be outlined from at least two perspectives: First, strategy is the “broad programme for defining and achieving the objectives of an organization and implementing its mission”. Secondly, “It is the pattern of the organization’s response to the external environment over a period of time”. A strategy that takes a broad and typically long range focus is called strategic planning. MBA Application Strategies for Top Business Schools Strategic planning is the process that classifies the long range goals of the organization and opts for the precise means (strategies and polices) for achieving these goals, allocates resources, and develops long range plans to reach the destination. Watch this Video to Understand the Overview of Strategic Planning Process Time-Horizon: Strategic planning takes into account the extended time horizon. There may not be any immediate impact out of strategic planning, but the consequences in the long-run prove to be gradual and significant as well. It provides with the necessary action plans to make a difference in vital areas concerning development. You can always associate innovativeness with strategy since it explores new paradigms and tries to enhance the impact. When the size of organizations expands, they are broken down into strategic business units (SBU’S) for the purpose of functional excellence. These units are expected to operate as if they were relatively independent businesses. WHY STRATEGIC LEADERSHIP IS IMPORTANT A Tailor Made Approach: A tailor made approach is essential when it comes to strategy development the systematic analysis of the factors associated with customers and competitors (the external environment) helps the organization to meet the challenges of modern society. More and more organizations are focusing on formal approaches and concepts for planning their long range process. Specifically these challenges are a result of increasing rate of change, the complexity of manager’s jobs, the increasing importance of fitting the organization into external environment, and the increasing lag between the preparation of plans and their implementation in future. Resource Allocation: Strategic planning is an organization’s process of defining its strategy or course, and making decisions on resource allocations to pursue this strategy. Managers must be adequately geared up for strategic planning. The goals of the organization must be made plain and not unclear. Each business unit should be categorized based on its performance level to decide on the resource share to be allocated. You need to infuse cash flow into ineffectual units and divest funds from dying units into other profitable ones. The ultimate aim is to build up star performers that will be the perennial source of income or revenue generation. There should be a strong linkage between planning and control. The assessment of strategic plans of the business units must be made periodically and effectively. TOP FIVE REASONS WHY STRATEGIC PLANS FAIL SWOT Analysis: SWOT analysis is a strategic planning technique used to evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses/Limitations, Opportunities, and Threats. Planning is the primary step for control as it provides several standards and benchmarks of control. Planning extracts commitment. Some times planning highlights the objectives only and the planning premises may not be fully reliable. Threats are to be considered as challenges and must be converted into opportunities. Two heads are better than one is the philosophy of brain storming where a group of people with knowledge and expertise assemble to lay out clear plans that will steer the organization smoothly even in times of rough...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Entrepreneurship, Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Startups
on Mar 22nd, 2014 | 0 comments

Why mission statements are important? Before going into that, let me first briefly tell you what a mission statement is. Contact Us for Promotions & Partnerships Firms in corporate business arena perform different business activities to earn profit as well as to retain their market share and stand. How does the general public know what they are up to? Is it really necessary for the firms to expose the nature of their activities to outsiders! Well, by explicitly defining the mission of your company, you stand a chance to gain identity, character and image and there is nothing to lose. A mission statement defines the basic reason for the existence of the organization and it clearly reflects your corporate philosophy. The management’s actions also might reflect their mission, in which case the mission statement is not explicitly defined and sometimes it could be deduced from the press statements released by the CEO. Whether defined or not defined, each and every organization has a definite mission that is clearly communicated to all the employees for action. When defined, it also serves as a means to highlight the firm’s social responsibility. Following are the Distinct Characteristics that a Mission Statement Should Possess It should be precise: The mission should neither be narrow as to restrict the activities of an organization nor too broad to make the situation pointless. It should be crystal clear: It should be clear enough to lead to action and not high-sounding and adhere to cheap publicity. It should be feasible: The actions mentioned must be well within the reach of the company and should not be impossible. It should be realistic and achievable. As, credibility is involved, firms must exercise caution when they release their mission statements. Feasibility mainly depends on the resources available that facilitate the firm to work towards the mission. It should be motivating: Motivating both for the employees and the society. Employees must identify themselves with the organization and feel proud that it is worth working for the firm and customers should take pride in associating themselves with that firm. It should be distinctive: It should project your distinctive competence to sustain competitive advantage. Say, if you own a garment shop, you should talk about the range of clothes that you can offer for different sections of the society and you can name yours a “Family Shoppe”, so that people will understand the nature of your business. It should indicate major components of strategy: If the aim of your company is stability, growth, diversification or concentration, all those can be included in your mission statement. It should also indicate how objectives are to be accomplished: The time period, production target, product specialization, product or process differentiation, everything can find their place in mission statements for the benefit of the society and self. Strategic management involves intelligent and timely decision making and mission statements are nothing but components of strategic planning that help the managers to lead the firm with some distinct “ideology” in the form of mission statements. Some Interesting Mission Statements Google’s mission is to organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful. Nike-“Crush Reebok.” Wal-Mart-“To give ordinary folk the chance to buy the same thing as rich people.” Walt Disney-“To make people...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Organisational behaviour, Strategy
on Mar 2nd, 2014 | 0 comments
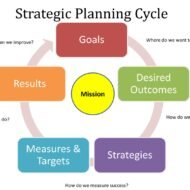
“Planning is bringing the future into the present so that you can do something about it now.” – Alan Lakein. Planning is absolutely essential and every minute you spend in planning saves 10 minutes in execution and gives 100 percent return on energy. We compare the advantages of planning against the consequences for your better understanding. Let’s See the Advantages of Planning First Facilitates opportunity analysis and presents an awareness of the external environmentMinimizes cost as it takes into account all the contributing and limiting factorsIncreases efficiencyRefines culture of an organizationProvides a good directionAlso establishes several measures of controlElicits commitment Disadvantages of Planning Time consumingInvolves excessive paper workSome times over emphasizes only the objectivesPlanning may become lop sided as it entirely depends on the mind set and attitude of people concerned with planningPlanning premises may not be fully reliable Steps to Make Planning Effective Every organization should have a separate planning department. A corporate planning department will take care of all the functions of an organization under one heading.Planning must be all pervasive and even the work force at the bottom level should understand the importance of planning and the planning perspective of the management.The goals must be verifiable and clearGive managers adequate tools and the freedom to trial and errorThe long term and short term goals should be combined together to form a inter locked system and must be viewed as one big single network.Goal setting must be practiced – participation by the employees must be made compulsoryA small idea could turn out into a big plan- don’t ignore suggestions from your subordinates and term them “silly.” What is Strategic Planning Strategic planning has a long term perspective and takes into account the extended time horizon.There may not be any immediate impact arising out of strategic planning, but the results can be experienced in the long run.It gives effort on vital areas. When the size of organizations is huge, they are broken down into STRATEGIC BUSINESS UNITS, treating them as individual businesses for ease of operation and decision making.It is a tailor made approach to match the functioning of an organization to the external environment for meeting the changes in the future. So, i is crystal clear that the advantages of planning outweigh the disadvantages and good plans never...










