Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Marketing, Principles of Management
on Mar 4th, 2014 | 0 comments
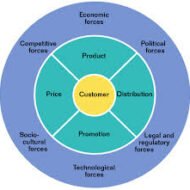
Key Components of Marketing System The core marketing system of a company comprises the suppliers, company, marketing intermediaries and target customers. The success of the company is also affected by competitor’s presence and other segments of public. The management has to watch and plan for all these factors to serve and satisfy the specified set of needs of a chosen target market. Supplier Selection: A company has to choose suppliers who offer the best mix of quality, delivery schedule, guarantee and low cost. Say, a firm involved in manufacturing confectioneries has to procure sugar, cocoa, caramel, milk powder; Labor, equipment, fuel, electricity and other factors of production are also to be obtained. If the company’s product has a good market, it can opt for continuous production. If it is a growing firm, it cannot go for voluminous production, but only supply goods against confirmed orders. In either case, the choice of suppliers is determined by one major factor called ‘cost’. Of course, one can never compromise on quality and so the company has to decide whether to purchase the inputs or make its own. Pic Courtesy : 5 Steps to Successful Supplier Selection The relationship of a company with the suppliers should be of a long-term nature, since any sudden change in the supplier’s environment will have a substantial impact on the company’s marketing operations. Sudden supply shortages, labor strikes and other events can interfere with the fulfillment of delivery promises to customers. This will result in sales decline in the short run and loss of goodwill in the long run. Back orders lead to loss of customers and in course of time their trust. The business firms must plan for alternate source of supply to avoid the risk of over-dependence on any one source of supplier. Company The marketing department has to work in tandem with the other departments of the company namely, finance, production, personnel and research and development, while designing and implementing its marketing plans. Finance department – has to be consulted regarding the availability and deployment of funds to carry out the marketing plans. Production department – to gauge market demand and to decide on the supply of products based on demand. R and D – new product development. Equally important is Digital Marketing which is considered to be an integral part of your promotional activities – What you are seeing above is a depiction of tools that help you in marketing your products online. Marketing intermediaries: Channel members are the link between the company and the customers. Agents and middlemen find customers who are wholesalers or retailers to take on the title and sell the merchandise. Also there are physical distribution firms who assist in stocking and moving goods from the warehouse to the destinations. The marketing executives have to deal with these intermediaries prudently in order to enhance the operational efficiency of the marketing function. Logistic firms, shippers and airliners help to move the goods from one location to another. Competitors: All the business firms in a particular market segment vie for the same resources and customers. A car manufacturing company in an automobile industry has to compete with other car manufacturers as well as with two wheelers. This implies that competition may come in different forms and each company has to identify potential threat from competitors, study their activities and capture their moves to win over the competition. Public: A company has to keep a close watch on people’s preferences to satisfy their requirements and also it is expected to give back something to the society in the form of social welfare measures. Employees belonging to different culture groups with differing attitudes,...

Posted by Managementguru in Financial Accounting, Financial Management
on Feb 20th, 2014 | 0 comments
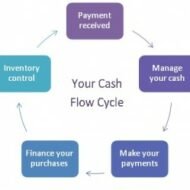
Debtor Management or Receivables Management Profit is directly proportional to the volume of sales, provided all your business transactions are cash based. Is it possible for a manufacturer, wholesaler or retailer to carry on his business without offering credit in this competitive business environment? The answer is a definite “no”, because extension of credit improves your sales and thus your profit. Problems arise only when a firm is not able to recover the debt within the stipulated period of time from the customers. What is receivables management or debtors’ management? It covers two aspects- one, the kind of money that is being invested in debt rotation; second, the risk factor which includes loss of money or the opportunity cost foregone by the organisation. Had these funds not been tied in receivables, the firm would have invested the same elsewhere and earned income thereon. A transaction entirely through cash is definitely a possible option, but whether it is lucrative in the long run must be subject to consideration. When customers are not offered credit, they choose concerns that extend credit facilities and thus you may lose your earlier customers and also exposed to the risk of declining sales proportions. Credit Sales In credit sales, the supplier offers credit for a specific time period, which is an investment from the angle of supplier and largest single source of short term financing from the angle of the customer. The supplier should be able to recover the amount of interest on the credit investment he has made. How? Recovery of debt within the stipulated credit period Taking interest from the customer for the period of delay Volume sales Surplus capital to offset these negative impacts on rotation of funds Proper formulation and execution of credit policies by the finance manager Discipline in collection policy and its execution. Discounts Cash discounts, quantity discounts and trade discounts are offered by many firms to the customers to encourage credit sales, favoring bulk purchases. A firm cannot be expected to survive long by pursuing the policy of cash sales while similar firms can overtake it by adapting to liberal credit policies. The main aspects of receivables management decisions are as follows: Time period of credit Credibility of the customer Cash discounts Trade discounts Learn the basics of the Income Statement, Balance Sheet and Cash Flow Statement and understand how they fit together. Credit Policy Credit policy on one hand stimulates sales and so also its gross earnings, but on the other may be accompanied by added costs, such as: 1) Clerical expenses involved in investigating additional accounts and servicing added volume of receivables, 2) increased bad-debt losses due to credit extension to less credit worthy customers, 3) higher cost of capital. Incremental earnings from increased sales should be matched with incremental costs that arise due to credit terms, to avoid funds being tied up in receivables. In course of time it would deprive you of your profits. The pivotal consideration of your credit policy would be the selection of credit worthy customers or debtors. If your funds become sticky, recovery becomes next to impossible and you need to proceed legally to claim your rights. Properly maintained accounting records and vouchers will stand as a testimony in your favor, in the court of...




