Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Decision Making, Management Accounting, Project Management
on Apr 1st, 2014 | 0 comments
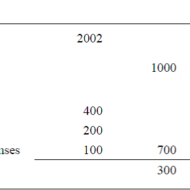
ACCOUNTING AND DECISION MAKING – IDENTIFYING THE PROBLEM SITUATION Learn accounting and finance basics so you can effectively analyze business data to make key management decisions. Business owners are faced with countless decisions every business day. Managerial accounting information provides data-driven input to these decisions, which can improve decision-making over the long term. Fig 1.1- ACCOUNTING INFORMATION FOR A SINGLE PRODUCT The above illustration clearly depicts that there has been a loss of Rs.100 in one year’s time for this particular product. The reason can be attributed to the increase in the “cost of goods” whereas other expenses have remained the same in both the years. For a single product manufactured, the problem is identifiable and solvable. But when the organization is producing a range of products, you need to apply some accounting technique by which the product losing money is identified and suitable measures are taken to cut down the escalating cost. Fig 1.2- Accouning Information for a Product Range The above illustration compares and contrasts the relationship of three products a company manufactures. It is seen that products P1 and P2 are doing well. Though the cost of sales has gone up for P1 and P2, the sales volume has also increased thus increasing the gross profit over the period of time. Here the product that has to be dealt with is P3 whose sales volume has drastically gone down, yet with the same cost of sales. When there is an increase in cost of sales, two things have to be considered. Identifying the problem-product Either cut down the production cost or increase the selling-price if the product has a real demand in the market. Uses of Accounting Data: Accounting information helps the management to arrive at make or buy decisions, to outsource production of certain components to cut down or control costs, to expand the production, to increase the sales volume or to downsize their project capacity. Techniques like Break-Even Analysis, Costing and Budgeting aid in going for the right production-mix, marketing-mix and sales target plans for the respective financial years. Aggregate Planning: As we all know planning is the key to the future and financial planning has to be given utmost importance for a production process. Aggregate planning involves translating long-term forecasted demand into specific production rates and the corresponding labor requirements for the intermediate term. It takes into consideration a period of 6 to 18 months, breaking it into work modules weekly or monthly and planning for the specific period in terms of men, material and...

Posted by Managementguru in Economics, Financial Management, Principles of Management
on Mar 15th, 2014 | 0 comments
Demand vs. Supply- Parameter deciding market equilibrium The success of economic freedom of a country is naturally reflected in the form of human prosperity. Countries like India are evidencing a consistent increase in their annual GDP rates which obviously must have reduced the population percentage living below poverty line; yet this has not been accomplished and the question is, is it really something to do with the economic model or is it the bureaucracy and inefficiency the root cause for the strain in the economy? Flow of Economic Activity: This discussion aims at shedding some light on the flow of economic activity in a free market economy. The elemental players or contributors in a free enterprise market economy are individuals and firms. Individuals who own or control resources (in the form of labor, capital or natural resources), sell these resources to firms and obtain money. These resources which serve as necessary inputs in the production process add value to firms. The money received by individuals is called factor payment which is utilized to fulfill their consumption demands of goods and services. Two distinct areas of interaction exist between the individuals and firms. One is the product market where the products are bought and sold and the other being a market for production factors, where the inputs such as labor, capital and natural resources are traded. What is the activity in a product market? Fundamentally business is all about demand vs. supply. The consumers’ demand has to be met with by the manufacturers. Profit is the primary motive of any firm and the priority of a firm lies in responding to the demands of the consumer market by supplying goods and services to the potential and prospective buyers. Input costs and production technology are the determinants of supply conditions. People’s preferences and earnings decide the elasticity of market demand. The price of the product and quantity sold is a result of the interaction between demand and supply. In a product market money flows from consumers to firms and goods and services flow from firms to consumers. What happens in a factor market? The reverse of those conditions in the product market are seen in a factor market. Here the individual becomes the supplier of production factors and hence the money flows from firms to individuals and factors of production from individuals to firms. Prices and profits control the flow of money and resources through the factor market and flow of money and goods through the product market. What is a Free Market Enterprise? Added advantage of a free market enterprise is that, the effortlessness with which one can enter and exit the market. The activity flow proves advantageous to each person involved .Firms make profits, individuals are satisfied of their consumption demand for goods and services, resource owners are compensated for their services. If an individual is not able to benefit by trading in these markets, he or she is not required to do so or free to leave the market which ensures that nobody is made worse off by voluntary trade in these markets. Essentially countries have to go in for suitable economic restructuring that promotes equality and even distribution of wealth. Wall Street protest in US is a clear-cut indication of strained market economy which is a result of people’s fury against the prevailing economic...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Principles of Management
on Feb 26th, 2014 | 0 comments
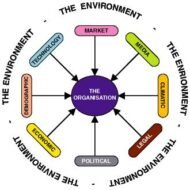
Factors of External Environment of Business What do you mean by Business Environment: The sum total of all things external to firms and industries that affect the functioning of the organization is called Business Environment. Elements of Business Environment 1. ECONOMIC 2. SOCIAL 3. CULTURAL 4. POLITICAL 5. LEGAL 6. TECHNOLOGICAL 7. DEMOGRAPHIC 8. GEOGRAPHICAL 9. ECOLOGICAL 1. Economic Environment This refers to all economic factors that influence and affects the very survival of an organization. Can be classified into · Economic factors affecting demand · Competitive forces Economic factors affecting demand The existence of an organization depends on the demand for its products or services. The customers’ ability to buy and willingness to pay determine the demand factor. The buying power is determined again by · Employment · Income taxes · Saving and · Prices The money acquired by an individual through employment is utilized for paying taxes which is the first priority and then comes saving or spending. In developing countries like India, much importance is attached to the habit of saving in the form of insurance policies or mutual fund deposits or investment on immovable assets. This makes the economy strong and stable even during times of recession, whereas we witness the economy of some developed countries entirely shaken when there is an economic depression. Sub Prime Lending Sub prime lending may prove to be disastrous for a growing or grown nation when the money is lent by the banks to third parties without proper securities or collaterals. While the initiative is intended to increase the growth rate or GDP, the end result may not live up to the expectations when the money is parted to individuals or firms with poor financial credentials. Disposable Income Disposable income also decreases when the tax rate increases and his/her ability to buy is reduced. Equally important is the willingness to by because the fact that an individual has the ability does not mean that he or she will buy. Willingness is affected by the preferences for products and the expectation about future factors like the price fluctuation, increase in one’s own income, general economic trend and so on. Competitive forces Firms have to first survive in order to succeed in the market. To accomplish this they exert competitive force on each other through one or the other following methods. · Price cutting · Promotion-advertising, personal selling · Design, feature and packing · Number and type of customer services offered give a cutting edge to firms competing in the race. 2. Social and Cultural Environment The social environment depends upon the · The class structure · Mobility · Nature of the social organization and · Development of social institutions People always have the unending desire to move from one occupational category to another and this is the main reason for high job turn over in IT industries for various reasons like pay, promotions, job satisfaction etc., This is the same reason which can be attributed to the failure of many good projects that go underway due to lack of continuation of the same initiative with which it was started. The above said process is more prevalent in urban societies than rural where scope of mobility is much the less among farmers, artisans and those engaged in traditional crafts and cottage industries. 3. Political Environment A smart manager has to be on tenter hooks to gauge the trends in political scenario that directly or indirectly affect the functioning of the firm. The political weather is highly unpredictable and may be classified into · Long-term changes · Quick changes · Cyclical changes · Regional changes Now-a-days we see that the economic depression in...

Posted by Managementguru in Economics, Financial Management, Management Accounting
on Feb 14th, 2014 | Comments Off on Concept of Cost
Cost-A Key Concept in Economics for Managerial Decision Making The concept of cost along with demand and supply constitute three of the basic areas of managerial economics. Analysis of cost is essential when it comes to large-scale production, where the firm is in a position to factorize the economies of scale. For a profit-maximizing firm, the decision to add a new product is done by comparing additional revenues to additional costs associated with that project. Aids in Decision Making Decisions on capital investment are made by comparing rate of return on investment with the opportunity cost of the funds used to make capital acquisition. Costs are equally important in non-profit sector. For example, to obtain funding for a new dam, a government agency has to demonstrate that the value of the benefits of the dam like flood control and water supply, will exceed the cost of the project. It is necessary that we define the term ‘cost’ for better understanding. The traditional definition tends to focus on the explicit and historical dimensions of cost. In contrast, the economic approach to cost emphasizes opportunity cost rather than historical and includes both explicit and implicit costs. Opportunity Cost: Opportunity costs are fundamental costs in economics, and are used in computing cost benefit analysis of a project. Such costs, however, are not recorded in the account books but are recognized in decision making by computing the cash outlays and their resulting profit or loss. Opportunity cost is the minimum price that would be necessary to retain a factor-service in it’s given use. It is also defined as the cost of sacrificed alternatives. For instance, a person chooses to forgo his present lucrative job which offers him Rs.50000 per month, and organizes his own business. The opportunity lost (earning Rs. 50,000) will be the opportunity cost of running his own business. Fixed and Variable Cost: A company’s total cost is composed of its total fixed costs and its total variable costs combined. Variable costs vary with the amount produced. Fixed costs remain the same, no matter how much output a company produces. Semi-variable is the type of costs, which have the characteristics of both fixed costs and variable costs. Fixed costs and variable costs comprise total cost. Total cost is a determinant of a company’s profits which is calculated as: Profits = Sales – Total Costs. The cost which remains same, regardless of the volume produced, is known as fixed cost. A variable cost is a corporate expense that changes in proportion with production output. Variable costs increase or decrease depending on a company’s production volume; they rise as production increases and fall as production decreases. Feel free to share this infographic on “Concept of Costs” Cost Reduction: Cut Costs and Maximise Profits: Be flooded with ideas on how to cut your...








