Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 2nd, 2014 | 0 comments
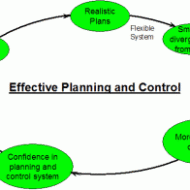
Principles of Planning and Forecasting The guidelines of principles of planning are as follows: 1. Principle of primacy of planning: As discussed earlier planning is the prime function of management and precedes all the other functions. 2. Principle of verifiable objectives: The objectives set must be clear, achievable and verifiable in order to attain a feasible management model. 3. Principle of planning premises: The contributing factors in the external environment are government policies, economic factors, market standing, and consumer preferences etc. that decide the success of planning. Planning is done based on these assumptions but nevertheless, all the factors external to the business have to be thoroughly analyzed to ensure concrete planning. 4. Principle of limiting factor: Cost is one of the major limiting factor; production cost has to be factorized to ensure economy of scale and potential resources needed for a business in the likes of men, material and other physical resources have to be taken into consideration. 5. The commitment principle: Planning and decisions whether short term or long term is valid only for a particular period. The long term plan is nothing but the future impact of today’s decisions. Decisions concerning new product development by a company aims at creating an impact for the next 15 years or so while decisions concerning sales target has to be accomplished on a periodic basis- monthly or quarterly. 6. Principle of flexibility: A plan should be flexible and give room for contingencies like losses incurred through unexpected events. 7. Principle of navigational change: Plans while suggested to have built-in flexibility are also subjected to periodical review in the light of environmental fluctuations. A business can not stick to a long term plan devised originally since it is equally important to check on events and expectations periodically. FORECASTING AND PLANNING: Forecasting is a management technique that relies on both past experiences and present assumptions to predict the future. Again this serves as an important premise for the planning process. The conditions of the external environment though out of one’s control, if properly estimated, can lead an organization to produce wonderful results. TYPES OF FORECSATS: Economic forecast: To gauge the general economic scenario and its effect on sales. Technological forecast: To predict what new technologies can be developed, when and how to bring feasibility to the operations involved. Competition forecast: To look into the competitor strength and tactics and know where one stands. Social forecast: To predict the attitude of people and social conditions. Supplier’s forecast: Reveals the response of suppliers. FORECASTING TECHNIQUES: 1. Quantitative time series analysis: Monthly sales data is plotted in a chart and the past data helps in consolidating the sales volume and fluctuations in sales. Sales trend is determined and the assumption is that, the future will reflect the past and present trend and hence can be projected. If there is a lull in sales, reasons for the decline can be known by taking feedback from various quarters like, suppliers, consumers and employees. 2. Derived forecast: The forecast done for a specific purpose may be reused for another purpose. For example a census data can help you to determine the demography of a particular geographical area that might help you to reach your target customers. 3. Casual methods: If the underlying cause for the variable can be determined, the forecast can be arrived mathematically and produce quite accurate results. Social media marketing is very popular now a days and instantly you know how many hits are received for a particular product and the ratio of conversion into sales. 4. Brain storming: People with knowledge and expertise assemble in order to discuss the pros and cons of a particular idea, be it the launch of a new product, product promotion or withdrawal of a product line. 5. Delphi method: In this method, each and very expert is contacted independently and opinions are drawn...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Principles of Management
on Feb 26th, 2014 | 0 comments
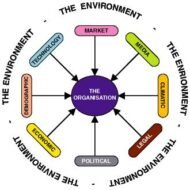
Factors of External Environment of Business What do you mean by Business Environment: The sum total of all things external to firms and industries that affect the functioning of the organization is called Business Environment. Elements of Business Environment 1. ECONOMIC 2. SOCIAL 3. CULTURAL 4. POLITICAL 5. LEGAL 6. TECHNOLOGICAL 7. DEMOGRAPHIC 8. GEOGRAPHICAL 9. ECOLOGICAL 1. Economic Environment This refers to all economic factors that influence and affects the very survival of an organization. Can be classified into · Economic factors affecting demand · Competitive forces Economic factors affecting demand The existence of an organization depends on the demand for its products or services. The customers’ ability to buy and willingness to pay determine the demand factor. The buying power is determined again by · Employment · Income taxes · Saving and · Prices The money acquired by an individual through employment is utilized for paying taxes which is the first priority and then comes saving or spending. In developing countries like India, much importance is attached to the habit of saving in the form of insurance policies or mutual fund deposits or investment on immovable assets. This makes the economy strong and stable even during times of recession, whereas we witness the economy of some developed countries entirely shaken when there is an economic depression. Sub Prime Lending Sub prime lending may prove to be disastrous for a growing or grown nation when the money is lent by the banks to third parties without proper securities or collaterals. While the initiative is intended to increase the growth rate or GDP, the end result may not live up to the expectations when the money is parted to individuals or firms with poor financial credentials. Disposable Income Disposable income also decreases when the tax rate increases and his/her ability to buy is reduced. Equally important is the willingness to by because the fact that an individual has the ability does not mean that he or she will buy. Willingness is affected by the preferences for products and the expectation about future factors like the price fluctuation, increase in one’s own income, general economic trend and so on. Competitive forces Firms have to first survive in order to succeed in the market. To accomplish this they exert competitive force on each other through one or the other following methods. · Price cutting · Promotion-advertising, personal selling · Design, feature and packing · Number and type of customer services offered give a cutting edge to firms competing in the race. 2. Social and Cultural Environment The social environment depends upon the · The class structure · Mobility · Nature of the social organization and · Development of social institutions People always have the unending desire to move from one occupational category to another and this is the main reason for high job turn over in IT industries for various reasons like pay, promotions, job satisfaction etc., This is the same reason which can be attributed to the failure of many good projects that go underway due to lack of continuation of the same initiative with which it was started. The above said process is more prevalent in urban societies than rural where scope of mobility is much the less among farmers, artisans and those engaged in traditional crafts and cottage industries. 3. Political Environment A smart manager has to be on tenter hooks to gauge the trends in political scenario that directly or indirectly affect the functioning of the firm. The political weather is highly unpredictable and may be classified into · Long-term changes · Quick changes · Cyclical changes · Regional changes Now-a-days we see that the economic depression in...




