Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Financial Accounting, Financial Management, Principles of Management
on Apr 8th, 2014 | 0 comments

Interest Free Sources and Unsecured Interest Bearing Sources A firm obtains its funds from a variety of sources. Some capital is provided by suppliers, creditors, and owners, while other funds arise from earnings retained in business. In this segment, let me explain to you the sources of short-term funds supplied by creditors. Characteristics of short-term financing: Cost of Funds: Some forms of short-term financing may prove to be expensive than that of intermediate and long-term financing while some short-term sources like Accruals and Payables provide funds at no cost to the firm. Rollover Effect: Short-term finance as the name indicates must be repaid within a period of one year – though some sources provide funds that are constantly rolled over. The funds provided by payables, may remain relatively constant because, as some accounts are paid, other accounts are created. Clean-up: This happens when commercial banks or other lenders demand the firm to pay-off its short term obligation at one point in a financial year. Goals of Short-Term Financing: Funds are needed to finance inventories during a production period. Short term funds facilitate flexibility wherein, it meets the fluctuating needs for funds over a given cycle, commonly 1 year. To achieve low-cost financing due to interest free loans. Cash flow from operations may not be sufficient to keep up with growth-related financing needs Interest Free Sources: Accounts Payable Accounts payable are created when the firm purchases raw material, supplies, or goods for resale on credit terms without signing a formal note for the liability. These purchases on “open account” are, for most firms, the single largest source of short-term financing. Payables represent an unsecured form of financing since no specific assets are pledged as collateral for the liability. Even though no formal note is signed, an accounts payable is a legally binding obligation of a firm. Postponing payment beyond the end of the net (credit) period is known as “stretching accounts payable” or “leaning on the trade.” Possible costs of “stretching accounts payable” are Cost of the cash discount (if any) forgone Late payment penalties or interest Deterioration in credit rating Accruals: These are short term liabilities that arise when services are received but payment has not yet been made. The two primary accruals are wages payable and taxes payable. Employees work for a week, 2 weeks or a month before receiving a paycheck. The salaries or wages, plus the taxes paid by the firm on those wages, offer a form of unsecured short-term financing for the firm. The Government provides strict rules and procedures for the payment of withholding and social security taxes, so that the accrual of taxes cannot be readily manipulated. It is however, possible to change the frequency of paydays to increase or decrease the amount of financing through wages accrual. Wages — Benefits accrue via no direct cash costs, but costs can develop by reduced employee morale and efficiency. Taxes — Benefits accrue until the due date, but costs of penalties and interest beyond the due date reduce the benefits. Unsecured Interest Bearing Sources: Self-Liquidating Bank Loans The bank provides funds for a seasonal or cyclic business peak and the money is used to finance an activity that will generate cash to pay off the loan. Borrowed Funds → Finance Inventory → Peak Sales Season → Receivables → Cash → Pay Off the Loan. Three types of unsecured short-term bank loans: Single payment note – A short-term, one-time loan made to a borrower who needs funds for a specific purpose for a short period of time. Line of Credit – An informal arrangement between a bank and its customer specifying the maximum amount of...

Posted by Managementguru in Financial Accounting, Financial Management, Management Accounting
on Apr 3rd, 2014 | 0 comments
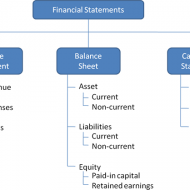
Ratio Calculation From Financial Statement Profit and Loss a/c of Beta Manufacturing Company for the year ended 31st March 2010. Exercise Problem1 Kindly download this link to view the exercise. Given in pdf format. You are required to find out: a) #Gross Profit Ratio b) #Net Profit Ratio c) #Operating Ratio d) Operating #Net Profit to Net Sales Ratio a. GROSS FORFIT RATIO = Gross profit ÷ #Sales × 100 = 50,000 ÷ 1,60,000 × 100 = 31.25 % b. #NET PROFIT RATIO = Net profit ÷ Sales × 100 = 28,000 ÷ 1,60,000 × 100 = 17.5 % c. OPERATING RATIO = #Cost of goods sold + Operating expenses ÷ Sales × 100 Cost of goos sold = Sales – Gross profit = 1,60,000 – 50,000 = Rs. 1,10,000 Operating expenses = 4,000 + 22,800 + 1,200 = Rs. 28,000 Operating ratio = 1,10,000 + 28,000 ÷ 1,60,000 × 100 = 86.25 % d. OPERATING NET PROFIT TO NET SALES RATIO = Operating Profit ÷ Sales × 100 Operating profit = Net profit + Non-Operating expenses – Non operating income = 28,000 + 800 – 4,800 = Rs. 32,000 Operating Net Profit to Net Sales Ratio = 32,000 ÷ 1,60,000 × 100 = 20 % What is a Financial statement? It is an organised collection of data according to logical and consistent #accounting procedure. It combines statements of balance sheet, income and retained earnings. These are prepared for the purpose of presenting a periodical report on the program of investment status and the results achieved i.e., the balance sheet and P& L a/c. Objectives of Financial Statement Analysis: To help in constructing future plans To gauge the earning capacity of the firm To assess the financial position and performance of the company To know the #solvency status of the firm To determine the #progress of the firm As a basis for #taxation and fiscal policy To ensure the legality of #dividends Financial Statement Analysis Tools Comparative Statements Common Size Statements #Trend Analysis #Ratio Analysis Fund Flow Statement Cash Flow Statement Types of Financial Analysis Intra-Firm Comparison Inter-firm Comparison Industry Average or Standard Analysis Horizontal Analysis Vertical Analysis Limitations Lack of Precision Lack of Exactness Incomplete Information Interim Reports Hiding of Real Position or Window Dressing Lack of Comparability Historical...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, CSR, Principles of Management
on Feb 26th, 2014 | 0 comments
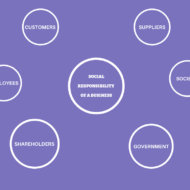
According to Raymond Bauer, “Social responsibility is seriously considering the impact of the company’s actions on the society. It may also refer to the person’s obligation to evaluate in the decision making process, the effects of both his personal and institutional decisions and actions on the whole system, according to Keith Davis and Cobert Blomstorm. A) SOCIAL OBJECTIVES OF BUSINESS: 1. The focus should be on quality, safety, service and security which lead to customer satisfaction. Quality– Product superiority and durability Safety– Products should not cause any harm to the consumers Service– After sales service is the link that builds a long standing relationship between the company and customers Security– Sense of satisfaction and belief on the company’s brand 2. The business has social responsibility of giving adequate opportunities to the members of the society. If everybody aims at white collar job, how does a nation grow economically? Developing economies should promote and encourage entrepreneurs to create more “Job Opportunities.” This especially suits countries like India and China where the pressure of population is very high. 3. Mass production facilitates in factorizing the economy of scale and at the same time aids in providing with quality goods at reasonable prices to the consumers. We see big chain of retail shops like Cosco and Wal-Mart in the US have made this possible where consumers can avail discount for bulk purchase. In India, Big Bazaar is a forerunner in this kind of retail marketing which enhances the material well being of a community and raises the average standard of living of the people. 4. Another main objective of business would be to control the percentage of pollution in air, water and land. Discharge of effluent in a lake or a river by the industrial enterprise may result in water pollution and also affects the plant, animal life and fish and birds to a considerable extent. Stringent laws must be in place to avoid such incidences and protect the society. B) RESPONSIBILITY TO CONSUMERS There is only one valid definition of business purpose: “to create a customer”, the customer is the foundation of a business and keeps it in existence. The responsibilities of a business towards its customers would be: Increased productivity in order to make goods available for the consumers at the right time at right prices; this solely depends upon the increased efficiency of functioning of the businessConstantly strive to improve the quality of goodsR & D to improve product quality and to come out with better and new productsProper distribution structure to reach even the remotest of locationsRemove hoarding, black marketing, profiteering by middlemen or anti-social elementsProvide them with the required after sales serviceEnsure that the product supplied has no adverse effectSufficient information about the product has to be given to the consumers regarding the adverse effects and precautions to be taken while using the productNo misleading product information through improper advertisements or otherwiseTo provide an opportunity for being heard and to redress consumer grievances Consumer courts are becoming popular in India for handling consumer grievances swiftly and efficiently. It is but a sad thing that many people do not know that they can address issues relating to quality, quantity or service. The businesses should understand the consumer needs and take necessary measures to satisfy those needs. C) REPONSIBILITY TO THE COMMUNITY To prevent environmental pollution and to preserve the ecobalanceAssisting in the overall development of a localityUse alternate energy resourcesContributing to research and developmentRehabilitate the population displaced by the operation of the businessDevelopment of economically backward areasPromotion of small scale industriesContributing to the national effort It is gratifying to see that many leading corporate icons of...

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Economics
on Feb 17th, 2014 | 0 comments
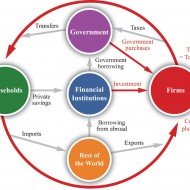
National Accounting Concepts Why knowing about national accounting concepts is important? National income data are of great importance for the economy of a country. In modern days they are regarded as the accounts of an economy, which are known as social accounts. Social accounts tell us how the aggregate of a nation’s revenue, output and product result from the income of different individuals, products of industries and transactions of international trade. National policy formulations: The computation of national income forms a basis for a nation to develop its policies for important spheres of action such as employment policies, monetary policies and fiscal policies that determine the growth of an economy. These figures enable us to know the direction which the industrial output, investment, saving etc. take and proper measures can be adopted to bring the economy on the right path. Facilitates Planning: Gross Domestic Product Gross National Product Net Domestic Product Net National Product Per Capita Income Disposable Personal Income All these factors comprise the national income and indicate the money value of the flow of goods and services available annually in an economy. Also this statistics helps a nation for proper economic planning. The per capita income refers to the earning capacity of individuals in an economy and more the per capita income, higher is the economic welfare of a country. Uncontrolled population growth and unemployment are major reasons for low per capita income. The wealth cannot be evenly distributed owing to high birth rates and low mortality rates and making the ends meet with the available scant resources becomes a major problem for developing countries. Distribution of income From the data pertaining to wages, rent, interest and profits, we learn of the disparities in the incomes of different sections of the society. Similarly the regional distribution of income is revealed. It is only on the basis of these that the government adopts measures to remove inequalities in income distribution and attempts at regional equilibrium. There have been differences of opinion regarding ‘nation’ in the concept of national income. In the calculation process, the term ‘nation’ has to be defined exactly as to whether it is the geographical entity of the country to be taken up for computing national income or the incomes earned by the nationals including those residing abroad. Further, since everything has to be equated to the money value, services produced in the economy out of love for humanity cannot be brought under the term national income. Besides, there is an overlapping of occupations, especially in the rural sector of certain countries, which makes it difficult to know about incomes from various...








