Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Change management, Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 31st, 2014 | 0 comments
India often looks at Japanese or American models to comprehend the concepts of management. In reality, Indian scriptures can be considered as treasuries of management. The Bhagavat Gita, the Vedas and the Epics highlight the true spirit of working together and the need for de-stressing the self for enhanced performance levels. The idea of NISHKAMYAM (to perform one’s own work without expecting a result) is truly said to be the highest ideology preached by Lord Krishna. What Induces Stress? A dynamic condition in which an individual is presented with an opportunity or confronted with a demand, related to what she or he desires and for which the outcome is uncertain but important, can be called a stressful situation. The consequences of stress in an organizational set up express themselves in the form of physiological, psychological or behavioral symptoms, which are harmful to the individuals who experience high levels of stress. Symptoms of stress: AnxietyDepressionIncreased job dissatisfactionAbsenteeismDecline in productivityRapid turn overHigh blood pressureHeart diseasesHead aches Stress Can be Motivating: While long term stress is harmful to the individual and organization as well, it is said that short term stress serves the purpose of task accomplishment by individuals or groups, within the stipulated time. It serves as a motivation factor rather than a causative agent of frustration. It has been proved by scientists and medical researchers that stress has a direct effect on the metabolism of a person, that causes increase in heart and breathing rates, increase in blood pressure, thus inducing heart attacks. Equally important are the behavioral and attitudinal changes that are created by stress, which cannot be overlooked. Job Satisfaction: Psychological symptoms arise due to job-related dissatisfaction, boredom, work pressure, irritability and procrastination. Sometimes forceful involvement may also lead to decreased job satisfaction. The job to be carried out can be finished at the particular time if the individual is able to give one’s best shot. But when it is performed under stress, they complete the job with dissatisfaction. When the incumbent is asked to perform a task that lacks clarity, naturally ambiguity arises in his mind followed by anxiety. Behavioral Symptoms of Stress Changes in productivity levels, absence, and rapid staff turnover are stress symptoms of behavioral nature. It might be expressed even in the form of increased smoking, consumption of alcohol etc., Say for instance, in production department, when there is a need to supply a product in a very limited time, the workers may be active initially, but the performance slows down when they get totally tired or dissatisfied with the work. Again the demand by the superior adds additional stress that reaches unmanageable levels. Similarly, people taking care of administration, banking, marketing and other office related works fall a prey to stress. How to manage stress? From an organization view point, it is believed that a limited amount of stress may work wonders in terms of performance, with stress acting as a “positive stimulus”. But even low levels of stress are likely to be perceived as undesirable from an individual’s stand point. How could be the notion of management and individuals be different on the acceptable levels of stress? It does not solve the purpose. Individuals have to understand that, they have to live up to the expectations of the management in order to enhance their credit ratings, in terms of promotion and pay. They have to understand that challenges are to be perceived as opportunities to prove their mettle. Self and situational analysis, work analysis, time management and physical well- being are some techniques that practically solve problems of stress. “De-stressing the Self” Techniques for Employees Organisations can reduce stress of the employees...

Posted by Managementguru in Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 19th, 2014 | 0 comments
You Can Delegate Authority, but Not Responsibility Responsibility of a Manager: A corporate manager is accorded with the huge responsibility of leading his subordinates in the right direction, by giving proper insights on the tasks to be accomplished. The success rate depends on how well he delegates his authority down the line to get things done. The art of delegation results not only in down sizing his work pressure but also in the empowerment of subordinates, that elevates them to a higher plane of understanding and achievement. An Excerpt from The Art of Delegation: Developing This Essential Managerial Skill Delegation helps you handover the authority of certain tasks to capable team members so that you free up your time to work on more pressing issues. But you still remain responsible to get those completed in proper way. Hence it is essential to have a status check or communication with the team member on regular basis. Accountability of Subordinates: The subordinates, when entrusted with the responsibilities of performing a task by themselves and the necessary authority to make decisions within the area of their assigned duties, are obliged to perform. The necessary assistance and training for the new assignment has to be planned for, by the manager to make them perform as per the expected standards. The thing is right people should be chosen for the entrusted job. They should possess the zeal and enthusiasm to deliver the desired output. Some people perform beyond expectations and they should be rewarded with additional responsibilities. Whatever the case may be, it is a wise thing to delegate simple assignments at the initial stage, and proceed with more challenging jobs depending upon the caliber of the incumbent. THE ENTREPRENEUR’S GUIDE TO DELEGATION Clear and Clever Delegation: Clear and clever delegation facilitates to build a formal organization structure, where the subordinates are trained well and they look up to the manager for direction and guidance. Although the authority is delegated, the manager is held accountable and answerable to the management for the performance output or the end result. Some managers hesitate to delegate, just for the reason that their weaknesses might get exposed. Some don’t have confidence in their subordinates. Some even fear that they might lose their power if the subordinate is very shrewd and exceeds the expectations. Managers fail because of poor delegation; the reasons being personal attitude of managers in delegating authority. Let us understand some of the basic principles to be adhered to while delegating: The authority delegated to subordinates should be adequate enough to ensure their ability to accomplish the expected results. Authority can be delegated but responsibility can never be delegated. Responsibility of subordinates is “performance” and that of managers is “responsibility for the action of their subordinates”. One cannot be held responsible for a task if he has only limited authority. There need to be a balance between authority and responsibility. The presence of a single superior will invoke greater feeling of personal responsibility among the subordinates. Lack of receptiveness on the superior’s part will incur greater loss in terms of performance and efficiency. Instead, a manager should develop a trustful attitude towards his subordinates and should have the patience to explain the policies, objectives and guidelines and give sufficient authority to perform a duty. HOW WELL EMPLOYEES KNOW ABOUT YOUR ORGANIZATION? Although initially the efforts taken to train a subordinate is time consuming, the more empowered he becomes, less is your time taken to accomplish the enterprise objectives. The superior must be able to create a climate of mutual trust and goodwill, to make delegations effective in the light of expected...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Organisational behaviour
on Feb 25th, 2014 | 0 comments

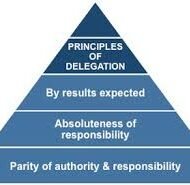
Before embarking on the subject let us find out what delegation is and how the process occurs in an organization. What is Delegation: A manager or a superior cannot think of doing all the jobs by himself. It becomes therefore necessary to delegate some of the jobs to his subordinates to ease the pressure and assign the required authority to carry on with those tasks. This downward pushing of authority is called delegation of authority. Art of Delegation Delegation takes place when one person gives another person the right to perform work on his behalf and in his name. It is the process of entrusting part of the work by the superior to his subordinates. How to Master the Art of Delegation? PROCESS OF DELEGATION 1. Step one is Assigning Responsibility: The superior directs the subordinate to perform a task with due assistance and training. 2. Step two is Granting Authority: To accomplish the task some authority has to be given to the subordinate to procure the essential resources from the organization like materials, equipment, labor etc., 3. Step three is Creating Accountability: The subordinate is expected to accomplish the task within the stipulated time period and report to the manager regarding the acquisition, use and replacement of resources. ADVANTAGES OF DELEGATION It reduces the work pressure of the manager Leads to better decisions Speeds up decision making It improves the morale of the employees Creates a feeling of mutual trust between the superior and subordinates Helps to create a formal organization structure BARRIERS TO EFFECTIVE DELEGATION Fear of being exposed: Some superiors fear that their weaknesses might be exposed Difficulty in briefing the actual requirement- depends on the quick wit of the employees Lack of confidence in subordinates Fear of loss of power“I am OK you are OK “ attitude of the managers PRINCIPLES OF DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY Principle of Delegation by Results Expected: The authority assigned to the subordinates should be sufficient enough to ensure their ability to accomplish the results expected.Principle of Absoluteness of Responsibility: One has to understand that responsibility can never be delegated and that the superiors are responsible for the activities of their employees and the performance of the employees has to be absolute towards their superior’s expectations.Principle of Parity for Authority and Responsibility: There should be a perfect balance between assigned authority and responsibility. One cannot be held responsible for a task where he has limited authority and too much of authority with too little responsibility can prove to be dangerous.Principle of Unity of Command: If there is a single superior to listen to, conflicts will be greatly reduced and it will be easy for the subordinate to have a personal rapport with the superior.Authority Level Principle: A manager who has the authority to make certain decisions must necessarily use his discretion and should not try to overlook or pass it on to the top management.Principle of Functional Definition: The objectives, tasks, responsibility and authority must be clearly stated to the individuals involved to facilitate improved performance to accomplish enterprise objectives. Managers fail because of poor delegation. Their personal attitude comes to the forefront which makes things quite difficult. Lack of receptiveness: Some managers are not open to ideas and suggestions from the other endWillingness to let go: A superior must have the willingness to delegate authority for positions which he had left long ago.Willingness to trust subordinates: A trustful attitude makes the proceedings smoothWillingness to establish and use broad controls: The superior must establish some standards to which the objectives or tasks can be compared to and control mechanisms must be installed for evaluation purposes. Feedback from subordinates is the most important criterion that determines the effective functioning of the organization. HOW TO MAKE DELEGATION EFFECTIVE? Right person for the right jobGive sufficient authorityFree flow of informationEstablish proper controlsReward the subordinatesMake the nature and scope of the tasks clearMake the subordinate understand...






