Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Training & Development
on Apr 5th, 2014 | 0 comments
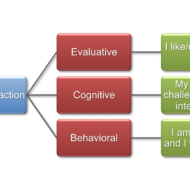
Attitude and Job Satisfaction What is attitude? Attitudes are evaluative statements or judgments concerning objects, people or events –Stephen Robbin. They also represent an ‘affective orientation towards an object.’ It simply means what one feels and thinks about something. Elements of attitude: Cognitive components – opinion or belief Affective components – emotion or feeling Behavioral components – intention to behave The interaction of these three components determines the way in which an individual develops an attitude towards something. Sources: Society Friends Teachers Family Members It also forms on the basis of the level of admiration we have over an object or persons. People also try to imitate others and attitudes are gradually formed on that basis also. In some attitudes formed are less stable, in some they even dominate the whole life. Types: Organizational behavior uses the concept of attitudes in relation to nature of the job and its influence on the performance of the persons. Accordingly, Job Satisfaction Job Involvement and Organizational Commitment, are the three kinds of attitude a person could have with respect his / her job or organization. Job Satisfaction: In “Job Satisfaction “, Stephen P. Robbins writes about five factors which make a person satisfied with his or her job. These factors are Mentally challenging work Equitable rewards Supportive working conditions Supportive colleagues and Personality-job fit. Cranny, Smith and Stone define job satisfaction as employees’ emotional state concerning the job, considering what they anticipated and what they actually got out of it. In fact, an employee with low expectations can be more satisfied with a certain job than someone who has high expectations. If one’s expectations are met or surpassed by the job, then one is happy and satisfied with the job. Job Involvement: Job involvement has been defined as an individual’s psychological identification or commitment to his / her job. As such individuals who display high involvement in their jobs consider their work to be a very important part of their lives- In other words for highly involved individuals performing well on the job is important for their self esteem. Organizational Commitment: Three important elements of a committed individual would be Identification with the organization’s goals and/or mission Long-term membership in the organization and intention to remain with the organization, often termed loyalty High levels of extra role behavior- behavior beyond required performance- Often denoted to as citizenship behavior or pro-social behavior. Cognitive Dissonance Theory: Leon Festinger developed this theory which explains the relationship between attitude and behavior. It refers to”any incompatibility that an individual might perceive between two or more of his or her attitudes, or between his or her behavior and attitudes.” Attitude Surveys: This is a tool that helps to collect information about the levels of attitude among the people. In most companies these kinds of surveys are conducted with the help of different rating scales like Likert scale offering five or seven alternative choices for each of the statement developed for attitude measurement. Summary: Research conducted on attitude and job satisfaction in Indian workers has made clear certain points as given below: Attitude is positively correlated with efficiency Absenteeism will bring down satisfaction levels Unions, negatively affect the employee attitude and job satisfaction Attitude researches and surveys will improve...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Human Resource, Motivation, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 10th, 2014 | 0 comments

Employee Morale – Role and Effect What is Morale? Morale is a word that conveys different meaning to different people. It might imply the following meanings: 1. Mental Attitude or Mind set from a psychologist’s perspective 2. A feeling of togetherness from an individual’s point of view 3. Group consent in terms of a business environment etc. Morale can be defined as ” an attitude of mind which conditions how well or how badly duties are performed”- W.H.Walley It can also be defined as ” the collective attitudes of workers towards one another, the employer, the management, or their work”-J.C.Denyen Morale is ” the capacity of group of people to pull together persistently and consistently in pursuit of a common purpose”-Dr.Deighton Morale is thus the undercurrent in an organisation that determines the performance levels of the employees as it dictates employees’ enthusiasm, voluntary conformance with regulations and orders and willingness to co-operate with fellow workers to accomplish the enterprise objectives. Poor morale is evident from in-subordination, discouragement and dislike of job, company and associates. Nature of Morale What it is? : Emotional by nature , a state of well- being and an attitude of mind. What it does? : Directly related to quality of work, enthusiasm, motivation, productivity, discipline, co-operation and initiative. Where it resides? : In the minds, attitudes and emotions of employees as individuals and as groups. Whom it affects? : Employees and executives during their interaction and ultimately the customers and the community. What it affects?: Willingness to work and placing the enterprise objective behind self interest. To summarise, the ill effects of Bad Morale would be Reduced productivityIncreased absenteeismAntagonism towards managementToo much of complaints and grievancesIncreased employee turn-overFriction between employeesAlcoholismAccidentsIncreased lethargy In contrary High Morale leads to Willing co-operation towards enterprise objectivesLoyalty to the managementGood behaviour in conformance with the rules and regulationsStrong and coherent groups leading to organisational staminaPrioritising jobs and placing self interest behind organisational objectivesIncreased sense of participationPride in organisation Picture Courtesy: extramadness.com Ways to Improve Employee Morale From the workers’ point of view: Fair compensation and bonusSatisfactory working conditions conforming to safety and securityTreated with dignityEfficient and amiable leadershipScope for expressing their views for improvementAcceptable working hoursEnsuring economic security From the management’s view point Co-operation from the employeesStability of tenureIncreased productivityLow cost per unitLoyalty of the workers Is it possible to measure Employee Morale? Level of productivity: When the morale is low due to different reasons, higher is the chance of absenteeism, accidents and grievances since the employees try to overlook their responsibilities towards the organisation. Therefore it is the responsibility of the management to settle and score issues relating to employees or unions then and there to avoid those issues blowing out of proportion. Morale Surveys These are generally conducted by individual organisations to find out if the employees are satisfied with their job and task and how they feel about it. This is considered to be a fairly important measure to gauge the kind of relationship the employees have with the management. Surveys also indicate whether the channel of communication is open between the superiors and sub-ordinates and serves as an emotional release for the workers to express their real feelings. Types of Morale Surveys: Objective Surveys: Objective type of questions are given to the employees for answering but the flaw is that, the management representative writes the answers and this does not give a chance for the workers to express their feelings. Descriptive Surveys: Here the employees write their answers to queries asked which are more descriptive in nature and reflects the actual feelings of each individual. Projective Surveys: Sometimes psychological tests are conducted to bring out the hidden feelings from tight lipped employees or who fear the management. The management must be aware of the following morale...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Motivation, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 9th, 2014 | 0 comments
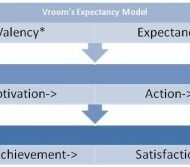
Herzberg and Victor’s Motivation Models Herzberg’s Hygiene Factor Theory Psychologist Fredrick Herzberg asked a basic question to 200 accountants and engineers in firms in and around Pittsburg-“What do people want from their jobs’? He used the critical incident method of obtaining data for analysis. “Think of a time when you felt exceptionally good or exceptionally bad about your job, either your present job or any other job you have had”. The responses obtained were fairly consistent in that, good feelings were associated with job content and bad feelings with job context. The ones on the right side of the table are intrinsic factors leading to job satisfaction and acted as motivators and ones on the left side lead to job dis-satisfaction and were termed as hygiene factors. Hygiene Factors: One has to understand that hygiene factors need not always cause dis-satisfaction; when the managers handle the situation in an amicable manner in terms of company policy, supervision, working conditions, salary and administration, things will be in the right direction but, even if they are adequate, people are never satisfied. These are called Hygiene factors and managers must try to eliminate factors that create discontent among the workers. If we want to motivate people, the real motivators are achievement, recognition, responsibility and growth. We must change the job design in such a way that the work arising out of the job should be challenging, exciting and should offer them a sense of achievement, recognition and growth. HYGIENE FACTORS MOTIVATORS Company policy Achievement Relationship with superiors Recognition Working conditions Work itself Salary Responsibility Relationship with peers Advancement Personal life Growth Relationship with subordinates Status Security CRITICISM: The factors which one particular group of individuals finds to be dis-satisfying may not be applicable for everybody. Factors which are beyond the scope of employees such as policy formulations cannot be considered as hygiene factors. VICTOR H. VROOM’S EXPECTANCY MODEL Valency*Expectancy=Motivation By increasing the positive value of the outcomes through such means as better communication about the outcomes, values and actually increasing them, i.e., the rewards and also by increasing the expectancy of the person by making him believe that the work will really lead him to the desired outcome, organizations can make a strong connection between the work and the...






