Posted by Managementguru in How To, Intellectual Property Rights, Marketing, Sales, Strategy
on Apr 3rd, 2015 | 0 comments
What is Brand Identity? Definitions Business Dictionary: The visible elements of a brand (such as colors, design, logotype, name, symbol) that together identify and distinguish the brand in the consumers’ mind. Investopedia: How a business wants a brand’s name, communication style, logo and other visual elements to be perceived by consumers. Kapferer’s Brand Identity Prism Model: The brand identity prism by Kapferer describes the brand through six different facets. The identity of a brand describes what makes it stand out and special, as well as the attractiveness of the brand. By the brand’s physique the physical appearance is meant. This includes a prototype of the brand: the product that represents the brand’s qualities.The brand personality connects the brand with human characteristics to differentiate. It is the way a brand speaks to its customers.Every brand tries to build a relationship with its customers. This relationship is more obvious for service brands, but product brands like Porsche and Morgan build relationships with their clients The question here is what role does the brand occupy in the relationship. It could be being a friend or being dominant.The culture of the company is reflected by the values the brand is communicating. Values can be linked for example to the origin of the company and their heritage.The reflection of a brand can be seen as the typical user of the product it is the outward mirror of the brand. It therefore often gets confused with the target market.The self-image is the way customers see themselves when using the brand and how this makes them feel. (Kapferer, 2012) Pic Courtesy: Marketing91 What are the top 3 things that make customers loyal to a brand? Quality – Quality in business, engineering and manufacturing has a pragmatic interpretation as the non-inferiority or superiority of something; it is also defined as fitness for purpose. Quality is a perceptual, conditional, and somewhat subjective attribute and may be understood differently by different people. Customer Service – The process of ensuring customer satisfaction with a product or service. Often, customer service takes place while performing a transaction for the customer, such as making a sale or returning an item. Customer service can take the form of an in-person interaction, a phone call, self-service systems, or by other means. Price – For many consumers, price is a very important attribute. The attribute price can indeed be more important on decision making than that of quality, brand name and others. We can conclude that consumer consideration to decide product brand is mainly based on price. The main question is how consumer brand decision is effected by price fluctuations. Does consumer move to another brand as price rises? Branding Gone Bad : Pizza Hut Tries to Lose the Pizza For some bizarre reason, Pizza Hut made an attempt to rebrand in 2009 by calling themselves “The Hut.” As a result, the fast food chain received a significant amount of ridicule from the public, and had to revert back to the original name. Although the company may deny rumors regarding the name change, photographic evidence of the redesigned logo are still circulating online. When British Airways Removed the Union Jack In 1997, British Airways executive Bob Ayling stated, “Perhaps we need to lose some of our old-fashioned Britishness and take on board some of the new British traits.” The company then embarked on a project that saw the Union Jack tail fin flag being replaced with other designs. After receiving numerous complaints from customers, this decision was reversed in 2001 when Ayling was replaced by Rod Eddington, and the Union Jack was once again painted on the fleet’s tail fins. Source: Six Examples of Branding Gone Wrong How Important is Brand...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Decision Making, Principles of Management, Productivity
on Feb 26th, 2014 | 0 comments
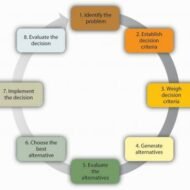
The Process of Decision Making There is a need to broaden our understanding about decision-making process. Decision making is not an independent entity and relies upon many other factors like precedence, social processes and random eventualities. It has three components; identification of the issue, the possible course of action and choosing the best amongst the choices of action available. The decision-making process is continuous since the business environment is dynamic and constantly poses challenges to the decision makers. Organizations are viewed as “Garbage can models” of decision making, in which actions, decisions and outcome are randomly mixed in the flow of events. With this introduction let us proceed to know more about the nature and types of decision making. NATURE OF DECISION-MAKING: 1. It is closely related to solving problems and issues 2. It is associated with all the important management functions like planning, organizing and controlling 3. Fayol and Urwick feels that decision-making is concerned only to the extent that it affects delegation and authority 4. Chester I Bernard in his “Functions of the Executive” says that the process is nothing but narrowing down of choice 5. Herbert A Simon considers decision-making as a process of intelligence, design and choice activities 6. According to Peter Drucker, it is a central part of the management process THE DECISION-MAKING PROCESS: The following steps are involved in the process of decision-making Recognizing the problem: Think about this; if there is a decline in the sales volume of your company or say if the value of your stock decreases, you are forced to make decisions to manage the contingency. In such situations, the first step would be to recognize or identify the problem area. A problem identified is half done. In this instance, the reason might be competitor strength or lack of necessary investment in the key strategic business units. Deciding priorities among the problems: A manager need not and cannot look after all the problems prevailing in the organization. He should know how to delegate authority and the responsibility that goes along with it. Subordinates can be entrusted with the handling of small and trivial problems while the manager can handle very important ones that might affect the functioning of the firm. He should ask the following questions to diagnose the situation. 1. What is the real problem? 2. What are the causes and effects of the problem? 3. Is this problem very important? 4. Can sub-ordinates handle this problem? 5. Which is the most pressing problem to be solved? Diagnosing the problem: Now the manager must start diagnosing the problem. Each and every individual has a different perspective and perceive the problem from a different angle. This depends upon the background orientations and training. The right way of approach for any manager would be to systematically analyze the problem for identifying the alternative courses of action. Developing alternative courses of action: This step involves creativity and innovative capabilities as the manager has to think from all possible angles and directions. Managers holding senior corporate positions are exposed to more of this kind of atmosphere where they are forced to make quick decisions in accordance with what the situation demands. Outside expert consultants are also put into use by some companies for developing choice alternatives. The following are the five PSYCHOLOGICAL STEPS for developing alternatives: 1. Saturation– A manager must be thoroughly familiar with the problem 2. Deliberation– Analyzing the problem from several points of view 3. Incubation– Temporarily switching off the conscious search to relax for the purpose of clear thinking 4. Illumination– A flash of light may occur after sometime giving him the right insights and ideas. 5. Accommodation– The ideas are made into a concrete proposal Evaluating the alternatives: The pros and cons of each and every choice is thoroughly subjected to scrutiny in terms of cost, time, risk, results expected, deviations anticipated...




