Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 20th, 2014 | 0 comments
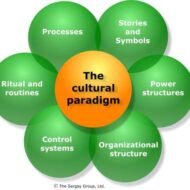
The Ideology of Corporate Culture What is Corporate Culture: the collective beliefs, value systems, and processes that provide a company with its own unique flavor and attitude. Management Attitude: Globalization has necessitated organizations existing in the corporate business world to respond in a unique way in an attempt to enjoy a competitive edge in the market. Corporate culture is a value that keeps an organization intact and helps in building team spirit amongst the members. It is not possible to specifically describe or delineate the concept of culture, yet, people are aware of its fine and striking presence. Let us say that each corporate firm has a dissimilar but unique culture which embraces the values, norms, beliefs and assumptions of the members of the organization and their behavior. It is also greatly induced by the leadership style and management attitude. Role of Culture: Why do organizations need culture as a milieu? Has culture any role in improving the output? Management uses culture as a means to reach out to the employees in an informal manner, to signify what is expected of them plus what is to be expected from the management. Culture cuts through all the levels of an organization and unites the members or employees, to work towards enterprise objectives in a remarkable manner. It is a sort of identity label on the organization and its interest to promote or espouse the value systems through out the organization. Corporate culture encompasses the following qualities enlisted: Quality driven Presence of an informal atmosphere Open communication Customer centric business model Proper and likable dress code Trust and confidence amid employees Value based management CEOs’ as strategic drivers in setting a candid corporate culture CEO’s naturalness and spontaneity with the employees Gratifying employee welfare and security measures Value systems indicated by the vision and mission statements Codified employee behavior Well devised operating strategies Greater autonomy tomanagers at different levels Rewards and recognitions and so on… https://blog.enplug.com/corporate-culture Corporate culture is considered to be a dogma, which many organizations utilize as a means to develop and amalgamate prospective employee groups. An employee learns all about the firm, its activities, the role he is supposed to play, information regarding his superiors, training, career advancements or promotions, pay, employee leave procedures and the long range goals of the organization during the time of induction. The firms should capitalize on this incubation period to spruce up the minds of the employees to act in accordance with the desired values expected by the management. Value Systems: It is inevitable for each and every organization to develop a value system over a period of time based on the founder’s outlook towards business and people working for him. This creates a strong or a weak culture which has an effect on the output or performance of the employees. This also serves as a clear indication whether the organization is proceeding in the right direction. We should never forget that a sound culture eventually aims at achieving the end goals of an organization. The cultural framework of an organization facilitates this process to materialize in a smooth manner. Though intangible in nature, it wields its negative power, when not nurtured appropriately. Flourishing organizations always have pride in their robust cultural back ground, which is a mark of distinction. It definitely shapes up an organization to deliver performance that matches and often surpasses the industry standards. The head of an organization has an important role as a leader as well as a change agent in taking his organization to the next level. The mutual faith and trust between the superior and his subordinates is the anchor point of an organization. Culture – An Intervention Technique: The culture of an...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 6th, 2014 | 0 comments
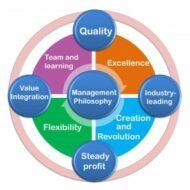
Corporate Philosophy of Management CORPORATE PHILOSOPHY OF MANAGEMENT calls for creating a framework of values, beliefs and ethical standards which are considered to be vital for an effective management. They must be embedded in formal and informal philosophical statements which are then communicated to the fraternity of that organization. From a broader perspective, the LEADER has to have a VISION as to where he is heading his company in the next three to four years. Corporate Objectives provide vision as well as direction and map for bold decisions to be taken regarding NEW MARKETS MARKET SHARE PRODUCTS SERVICES etc. , Now the organization is in a position to decide and prioritise the VALUES AND COMPETENCIES it expects from its managers. For example, if the situation favors the business expansion to new markets, say, European or Asian, then an organization has to develop competence in areas like LANGUAGE AND CULTURE, besides marketing and business skills. Different Philosophies of Management: Well, you might have been inspired with JAPANESE PHILOSOPHY OF MANAGEMENT, EASTERN OR WESTERN PHILOSOPHY OF MANAGEMENT t. But what is the fun? If you don’t have A SOUND MANAGEMENT PHILOSOPHY of your own, to simply put it, you don’t have a broad set of principles to back up your management development process which is a generic one. Ideally speaking, you should be able to develop a concrete SYSTEM that is made up of FOOL PROOF policies and procedures; try to develop a professional team of executives who can take up your vision to the next level; these measures will prove worthwhile in the long run. You are left without any choice but to develop “truly” INTERNATIONAL MANAGERS who could transcend nationally and the location of any specific job consideration. This is what Ideal management philosophy means to me, A holistic vision of the future A solid set of principles(values, beliefs) Sound policy definition Management development programmes Autonomy to my work force Always “yes “to new technology Development of women managers Flexible leadership Social responsibility Contribution to the growth of my Country’s economy Strategic Perspective: Major environmental shifts now demand a more strategic perspective from those who manage and lead in organizations; “GLOBALISING” in the quest for major market share brings in new opportunities for growth and prosperity. Organizations are now espousing values that regard people, not as costs to be minimized, but AS “ASSETS TO BE MAINTAINED AND DEVELOPED.” An open systems approach of management is likely to overcome many of the problems created by the piecemeal approach. Instead of looking at management development in isolation, see it as an integral part of a wider organizational system that takes care of the processes through which people working for the firm take care of themselves leading to self...

Posted by Managementguru in Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 1st, 2014 | 0 comments
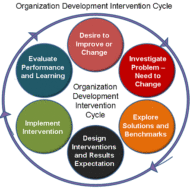
Organizational Development Training and development is an important aspect of human resource development. However the traditional methods and approach of T&D has its own limitations in that the focus is on individual development and behavior modification. This has seldom produced organizational development and hence in 1960’s an integrated approach called the ‘OD’ or organizational development was developed. Meaning and definition of organizational development (o.d.) “A process used to enhance both the effectiveness of an organization and the well being of its members through planned interventions.” OD is the systematic application of behavioral science knowledge for the purpose of improving productivity, efficiency, effectiveness and overall health of the total organization. The applied interventions attempt to modify the beliefs, assumptions, values, attitudes and standards of both the individuals and groups thereby transforming the organizational culture for the betterment of system as a whole. FEATURES OF ORGANIZATIONAL DEVELOPMENT: HUMANISM: The focus is on the employees, their attitude and inter-personal relationships. An organization is a network of people whose emotions, outlook and cohesiveness are more important than monetary and other physical aspects because it is they who take the organization to the next higher level. This is made possible by open communication, free and frank discussions of problems with employees by the managers, inter-personal trust and above all, sense of belongingness, comradeship and team spirit. PROBLEM-SOLVING NATURE: The purpose of an OD intervention is to solve a problem. The employees themselves are given the opportunity to identify the problem by Survey Feedback and find a suitable solution through analysis. This is a cyclic process and also called as “Action Research”. SYSTEMS APPROACH: OD is concerned with not the structure or persons per se, but with the interplay of structure and persons. LEARNING THROUGH PARTICIPATION: The participants of the learning process are none other than the employees. They unlearn old things and learn new things by identifying, analyzing and finding the right solution to the bottlenecks. TOP MANAGEMENT SUPPORT AND INVOLVEMENT: OD intervention is successful only when top management involvement is full-fledged and ensures participation from all levels of managers and all departments in such an exercise. MULTIPLE INTERVENTIONS: Intervention takes place at various levels, individual as well as group and the purpose is molding desirable work culture and leadership styles suitable for the organization. ROLE OF CONSULTANT: Employing an external consultant will be more appropriate as he is less susceptible to influences and more objective. He acts as the change agent facilitating co-ordination and stimulation. CONTINGENCY PLANS: Alternate plans are also devised if in case the original plan fails; the idea is one that of trial and error, hence the need for contingency plans and approach to OD problem. RENSIS LIKERT’S OD FRAMEWORK: Rensis Likert’s 4 system OD framework aims at moving towards truly participative system. Care and caution must be adhered to steer the system gradually from where the organization now works. He also introduced diagnostic analysis to find what causes the current problem. His three part diagnostic analysis includes: A. OUTPUT CAUSES: Low productivity, absenteeism, declining profit B. INTERVENING CAUSES: Organization structure, control, policy and leadership C. ROOT CAUSES: Attitude, motivation level, empowerment and organization culture Tips for Organization Development OD CULTURE: “The OD paradigm values human and organizational growth, collaborative and participative processes and a spirit of enquiry.” Brown and Covey have made some attempts to identify OD values from the following: Norms and Values: Respect for people: People are the most important of all resources. So giving due respect and importance to people induces the creativity and innovation in them. Trust and Support: Trust, openness and supportive climate improve organization culture and empowerment. Power Equalization: This emphasizes hierarchical authority, control and centralization. Confrontation: Do not...






