Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Principles of Management, Project Management, Strategy
on Mar 16th, 2014 | 0 comments

Strategy Implementation Organizational objectives must be accomplished by strategic planning and thinking that makes your organization unique and also helps to have a competitive edge. What are the elements that are part of this planning strategy? Proper allocation of resources An appropriate organization structure Efficient human resource personnel An effective management information system A feasible budgeting system A good reward system Periodic strategy review system There are many more aspects that can be attributed to broadly define strategic planning and execution. The success or failure of this exercise is in the hands of managers, who should be adequately prepared for the planning process. The objectives of the organization must be well defined and clear so that the people in the organization can evolve the necessary plans to accomplish those objectives. The action plans are then formulated based on these initially formed plans. So, the planning premises form the base on which the organization is built. Strategic business units must be identified and nurtured to add value to the organization. Why strategic planning becomes a failure in some of the organizations? Lack of proper training in strategic planning, and the key persons are the managers at all levels. Vague goals and objectives don’t make them meaningful and strategic excellence cannot be achieved. Long term goals not subjected to periodic review. If there is fluctuation in the political, economic or social environment, that is detrimental to the industry in which the firm operates, the goals can be reviewed and a revised strategic plan can be devised for the long term health of that organization. Poor budget planning. To enjoy a sustainable competitive advantage in the market, you need to have a good financial backup to give shape to your plans. The strategic plans must be supported by specific action plans. It is a pity that in many organizations, there is neither co-ordination nor co-operation between the peers to make the strategic plans successful. Integrating these various functional groups becomes a tough task for the management. Simple but effective measures: Above all odds, a company can make things work, if the management is wise enough to follow these First and foremost thing to be done is to communicate the strategic plans to all the managers who are key decision makers. The management must make sure that everybody involved in the strategic implementation understand those strategies. Well devised action plans that contribute to the accomplishment of the firm’s objectives must be laid down. A well defined span of management that makes communication flow easy and simple. Revising the strategies in lieu of the contingencies. A conducive organizational climate that is devoid of conflicts and pressure Involvement of top management to ensure success. Thinking Out of the Box: You need “thinking managers“, to make your organization grow. The modern business management lays great emphasis on “getting people together” to accomplish the goals and objectives. How do you get people to work together? They should have a common business ideology that binds them to work for the upliftment of the organization. Although top level management cadre is responsible for formulating strategic plans, organizations must understand that the idea also reaches the lower level management in the right sense. That facilitates smooth execution delivering the expected result. Benefit from this Free Udemy Course on Marketing Strategies https://www.udemy.com/one-minute-marketing-lessons-30-quick-marketing-strategies/...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 6th, 2014 | 0 comments
Critical Factors Influencing Corporate Management A corporate management is said to be capable only if it is able to integrate, coordinate and direct the functional capabilities towards overall objectives and common goals of a firm, that have a bearing on an organization’s capacity and ability to implement its strategies. Multitudinous factors affect the functioning of corporate general management system. It differs with each organization with differing objectives and mode of operations. Key Factors or Contributors: The firms must evolve an effective system for corporate planning. The objectives must be realistic and achievable and clear and complete communication of plans to various levels of organization helps in execution of action plans by the respective departments. A pucca management information system is necessary that integrates all the levels through a network of computers, facilitating information processing and task implementation. If the firm is oriented towards a god deal of risk-propensity, chances of rewards are also quite high. You cannot beat your competitors unless you possess a better shade of entrepreneurship in you than others. Competency development backed up by strategy formulations, in the wake of challenges and opportunities in the external environment is well appreciated. Why everybody always talk about strategy? It is one thing that warrants for a sure success, it implies that you are smart enough to think ahead of time, what others have failed to. Don’t you want to set a path forward for the future generations to come? Values that are unique to your organization add to the image of your company. Say, if you project “quality”, as your prime value system, definitely it is going to attract consumers who are very particular about quality unmindful of the price. Slowly the idea gathers momentum and your company’s image gets a boost. But don’t forget that you have to fulfill your commitments in terms of quality without any compromise. Reward systems must be worked out to gear up the morale of top managers who are the achievers of your management objectives. Their track records and degree of commitment should be analyzed to decide on pay and promotions. A favorable organizational climate is inevitable for the organization to progress in the desired direction without any internal politics and power struggles. The role of top management is very crucial in that, it has to identify people with vested interests and bring them back into the groove by making necessary changes in the organization structure or go for weeding out actions if things go out of control. Ultimately, the overall objectives of the organization is what that matters, and people must be trained to accept the organizational changes which form a part of the developmental procedures of management. Social responsibility is much talked about these days, and the corporate firms are in a position to discharge their duties pertaining to social welfare, as part of their corporate management programme.It has become a regular feature of the management process to part with a share of their profit towards a social cause. Corporate management is a comprehensive process that covers all aspects of the management with growth as its motto and social conscience as its...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 3rd, 2014 | 0 comments
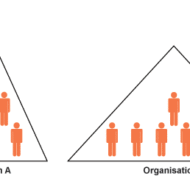
Levels of Organization An organization is a network consisting of people interacting to accomplish the enterprise objectives. The inter relationship is always complex as groups tend to develop conflicts and difference of opinion among themselves and in between. Hence the structure of an organization should be designed to clarify who is to do what task and who is responsible for what results and to furnish decision-making devoid of uncertainty. Organization implies to Recognizing and classifying the required activities Grouping of activities in order to achieve the objectives Appointing a manager and assigning him with the necessary authority to lead each group The provision for co-ordination vertically and horizontally “Organization is the establishment of authority and relationships with provision for coordination between them, both vertically and horizontally in the enterprise structure,” According to Koontz. FORMAL ORGANISATION It implies a formalized intentional structure of roles or positions. Formal organization must be flexible. The formal structure is laid down by the top management The levels are designed on the basis of specialization Purely task oriented and not people oriented Rules are very stringent and everyone is expected to follow them without fail INFORMAL ORGANISATION A network of personal and social relations arising spontaneously as people associate with one another and not restricted by the formal rules or structure. One important aspect of organizing is the establishment of department. Department designates a distinct area, division, or branch of an organization over which a manager has authority for the performance of specified activities. Spontaneous in nature More people oriented Based on religion, culture, common problems faced by the workforce etc., Membership is voluntary and the same person can be a member of many groups. ORGANISATION LEVELS AND SPAN OF MANAGEMENT Why there is a need to organize? To co-ordinate the activities of the people involved in the organization’s functions for which there needs to be certain levels established to facilitate the co-operation effective. There are two types of spans, 1. Wide span 2. Narrow span Pic Courtesy: LumenLearning WIDE SPAN: Wide span of management has fewer organizational levels with more number of sub-ordinates reporting to a superior. Though it proves advantageous for the superior as delegation becomes part of the process and hence work is shared, care must be taken in selecting the right people for completion of tasks and clear policies must be made to avoid confusion. There is this tendency of overloaded superiors to become decision bottlenecks and there exists the danger of superior’s loss of control too. This kind of management needs exceptionally qualified managers to lead the respective groups. NARROW SPAN: Narrow span of management involves many organizational levels with fewer number of employees reporting to a superior. This facilitates close supervision, close control and fast communication between superiors and subordinates. On the contrary, superiors tend to get too involved in subordinates’ work and this kind of management incurs higher costs due to many levels in the organization and there is excessive distance between the lowest and top most levels. FACTORS DETERMINING AN EFFECTIVE SPAN: 1. Training of Subordinates: Well trained subordinates save much time and energy of the superiors and training has to be a continuous process as the technological policies and procedures are subjected to change periodically. 2. Clarity of Delegation of Authority: Clarity implies direction and guidance from the manager’s end to the subordinate. A manager has the responsibility of clearly explaining the task and the methods involved to complete the task in a suitable manner to his subordinates. In cases of machine handling, “On the Job Training” becomes inevitable. If not, the work will not be completed as per the schedule due to lack of clarity. 3. Clarity of Plans: In a production environment, the workers have to be...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Principles of Management
on Mar 3rd, 2014 | 0 comments
Centralization and De-Centralization Concepts CENTRALIZATION: The term “centralization” has several meanings: Centralization of Performance: Say, if the operations of a company is restricted to a single geographical location, it characterizes centralization of performance. Departmental Centralization: Specialized activities are carried out by a single department, say, maintenance of a whole plant, staff recruitment by HR department etc., Centralization as an aspect of management: This implies restricted delegation and exclusivity of decision-making by the top management. According to Allen, “Centralization is the systematic and consistent reservation of authority at central point in an organization.” According to Weihrich and Koontz, “Centralization (as an aspect of management) is the tendency to restrict delegation of decision-making. What are the special circumstances that force the managers to reserve authority and centralize decision making powers? 1. To facilitate personal leadership 2. To provide for integration 3. To handle emergencies 4. To utilize resources effectively and instantaneously. DECENTRALISATION: It is the tendency to disperse decision making authority in a structured and organized manner. It can be viewed as a philosophy rather than a principle where-in “discretion” plays a major role in deciding which decisions to push down into the organization structure and which to hold near the top. Capital expenditure, Investment analysis and major policy decisions have to be dealt with, by the top management. It is the systematic effort to delegate to the lowest levels of authority except that which can be exercised at central points. TYPES OF DECENTRALIZATION: Three approaches to the concept are: 1. PROFIT CENTRES 2. COST EXPENSE CENTRES 3. INVESTMENT CENTRES Profit Centre: Here the organization is split into divisions on a “product basis” and is given full authority to handle its own scheduled operations, right from placing orders to negotiating the sale of its finished products. Cost Expense Centre: Whenever it is easy to determine the cost of operations, cost centres are established. Cost centres run on “budgets” which acts as a control tool to run the units within the specified budgetary limits. Investment Centre: Useful in the case of big multi-product enterprises where product performance is measured by decentralizing the investment aspect. Each strategic business unit is responsible for the acquisition, use and disposition of fixed resources. Advantages of Decentralization: Managers and executives are relieved form excessive work pressure Even low level employees are involved in decision making thus bringing the decision making process closer to the scene of action. It facilitates product-diversification Creates an opportunity for learning Ensures effective control When a big organization is divided into relatively smaller units, it becomes flexible and also effects close control. Disadvantages of Decentralization: · Conflict arises between people belonging to different levels of the organization · Rising cost · Lack of co-ordination between production and marketing departments · No defined leadership Contingency Factors in Decentralizing: 1. Organizational goals 2. Organizational size 3. Geographical dispersion 4. Technical complexity of tasks 5. Time frame of discussions and decisions 6. Subordinates’ take on issues 7. Planning and control procedures 8. Environmental factors 9. Knowledge and experience of managers Effective Decentralization can be accomplished by · Establishing appropriate centralization · Developing efficient managers · Proper provision for communication and co-ordination · Establishing adequate controls Top management must be willing to delegate authority towards decision making; Middle management must be willing to accept responsibility that is being delegated. Only then effective decentralization is...

Posted by Managementguru in Operations Management, Project Management
on Feb 24th, 2014 | 0 comments
Significance of Operations Management: Business firms need to formulate brilliant operations strategies in order to survive in the market for long. Focus on finance and marketing alone is not sufficient to compete in the global market. The emergence of innovative products and processes from leading companies in different parts of the world is a clear-cut evidence to prove the significance of operations function. Operations management is gaining importance, thanks to public awareness on quality and its applicability in service operations too. Advent of Industrial Revolution: Until the advent of machinery, each and every nation was dependent on agriculture, which was the prime economic activity. After the industrial revolution of the eighteenth century, mechanization in a large scale converted agricultural economy to an industrial economy. Slowly scientific principles were introduced into production activities to make it more systematic and thus “Production Management” evolved. Now service operations have also gained momentum and since the concepts and techniques of production management are applicable to service operations too, it is rightly called as “Operations Management.” Operations management functions at three different levels. Strategic levelTactical levelOperational level Strategic level: At the strategic level, the operations manager must have a long term vision, as to shape up the company’s success in the light of strategic decisions taken, with the approval of the top management. His area of concern would be, New product developmentNew process developmentProduct re-designProcess re-designProcess layoutProduct layoutFacility locationAggregate capacity planningPlanning co-ordination with finance and marketing departments Tactical level: At the tactical level, the operations manager is concerned about the planning and scheduling operations of the desired output. His area of concern would be: Designing a suitable inventory systemPlan for the work force and train them effectivelyQuality control systemMaintenance andReliability assurance system. Operational level: At the operational level, the job of the operations manager is to accomplish the “set targets”, by performing various coordinating and controlling functions. His area of concern would be: Ordering materials at the right timeScheduling productionScheduling workers as per production requirementControlling quality of goods and services producedFollow up of various schedules for proper implementationMaintaining and updating equipment and system reliabilityOn the job skill development of workers, etc. These functions are by no means exhaustive, but only indicative. The process of planning and control operations is not done in water tight compartments, but are interactive and integrative feeding on one another and also aligned in line with the overall corporate objectives. The strategies are evolved for the purpose of efficient utilization of the available resources as well as to predict the changes in the external business environment that calls for suitable action to limit their impact on the goals of the organization, in terms of cost, quality and...










