Posted by Managementguru in Business Ethics, Business Management, Principles of Management, Strategy
on Mar 15th, 2014 | 0 comments
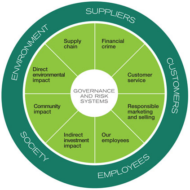
Social Value of Corporate Companies Economic Responsibilities: Ethical and discretionary responsibilities of a business firm are listed in the order of priority. First, a firm has to satisfy its economic responsibilities, followed by fulfilling legal responsibilities in order to survive in the market. Only then, it can think about or focus on purely voluntary actions pertaining to ethical consideration. In this competitive market situation, a business unit has to concentrate on profit making, the primary motive behind any business activity. However; it is easier said than done. You cannot hit the bull’s eye at the very first attempt. A firm has to become economically stable first; only then, it integrates social commitments in its agenda. Arguments for social responsibility: Public image: Socially responsible firms gain more customers and employees feel proud to work for such organizations. Handling the government regulations with ease: Government is a massive institution with long arms. It seeks to regulate business in public interest. Before government stretches its long arms, business persons should discharge their obligations to society. Business is resourceful: With a pool of resources, such as capital, labor and expertise, business is in a better position to tackle social problems and work for social goals. Let business try: It is that many other institutions have failed in handling social problems. So why should not a business enterprise handle social problems? Prevention is better than cure: Social problems have to be handled by the management at some point of time or the other. Problems with labor unions should be handled in a diplomatic way, so that they will not develop into serious social breakdown that consumes most of the management’s time. As a token of gratitude: Business units benefit from society. Based on the commonly accepted principle, that one owes debts of gratitude towards those who benefits us, the corporations have debts that it owes to society. Arguments against social responsibility: Profit maximization is the ultimate goal: Business units are accused of having profit maximization as their goal. Since business operates in a world of poverty and hunger, the economic efficiency of business is a matter of priority and should be the sole mission of business. Society has to pay the cost: The costs of social responsibility will be passed on to the society and the question is can the society bear these additional costs? Lack of social skills: Managers are here to solve economic problems and they do not possess knowledge or skills to provide the right solutions for social problems. Business has enough power: Business already is wielded with enough social power. The society should not take any steps, which will make it stronger. Social overhead costs: Costs on social responsibility is considered a social cost, which will not immediately benefit the business. Why spend money on an object, the benefits of which will be relished only in the future. Lack of broad support: The idea of business involvement in achieving social goals is not widely supported by many groups in society. Business and society are interlinked in many ways and the business has to handle the societal aspects with great care or else it may have to face the consequences arising out of such misappropriation or...

Posted by Managementguru in Economics
on Feb 16th, 2014 | 0 comments

Science of Macro Economics: Macroeconomics is the branch of economics that studies the behavior and performance of an economy as a whole. The part of economics concerned with large-scale or general economic factors, such as interest rates and national productivity. The sales and profit quotient of business enterprises in a market is dependent on the vigor of the overall economy to a greater extent. During expansion, the real GDP can accelerate to 4 to 5 % a year and during recessions the pace of growth declines for an extended period. The overall economic growth is subject to many cyclical fluctuations and the reasons for change in the pace and pattern of economic scenario still remains a mystery. Macroeconomic Concept What are the fundamental concerns of macro economics? Business Cycles: Business cycles are rhythmic patterns of expansion and contraction due to inflations and recessions. It is still an intriguing factor that unemployment persists even during times of expansion and production of goods and services fall down during cyclical downturn making millions of people lose their job. If macroeconomics can find the appropriate solution to these problem situations, better will be the prospects of many people’s lives and fortunes. Monetary and fiscal policies should be formulated in the light of reducing the severity of business cycles. The purpose of monetary policies is to stabilize the prices by managing the expansion and contraction of the volume of money in circulation, full employment and stability of exchange rates. Fiscal Policy: Fiscal policy is linked with the government’s stand on public revenue, expenditure and debt. The idea is to reduce inequalities in income and wealth and develop a socially optimum investment pattern. Resources available in a country influence the kind of investment pattern. Developing countries like India has its focus of activity centered on telecommunication and power generation through information technology and alternate fuel resources. Availability of skilled labor is an additional plus in countries like India and China and many countries prefer to outsource their business processes to offshore companies present here. Tax Structure: Tax structure is a source of revenue generation aimed at economic stability. During inflation, an increase in tax rates will reduce the buying power of people thereby reducing the prices in the economy. A reduction in tax rates during depression will encourage economic investment and consumption. Generous subsidies and reforms in industrial policies alone cannot bring about the desired growth in the economy. A nation should aspire to increase its growth ratio by providing the necessary infrastructure. Economic scholars of each nation have to vigilantly analyze the previous patterns of business cycles for the benefit of the society and this kind of review will lead to dependable forecasts on the basis of which proactive measures could be devised. Note: What is VAT: VAT is a multi-point levy where the tax paid on local purchases from the registered dealer can be set off against the tax payable on the sale of goods, other than special...




