Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Change management, Human Resource, Organisational behaviour
on Jul 25th, 2014 | 0 comments

EQ or EI When we talk about IQ or Intelligence Quotient, another entity which is indispensable to the smooth running of your business comes into the picture. Yes, I’m talking about Emotional Quotient or EQ, also called as Emotional Intelligence or EI. The concept of emotional intelligence is a blanket term that covers a broad collection of individual skills and dispositions, usually referred to as soft skills or inter and intra-personal skills. One must be adept at handling situations which warrant application of EI and at the same time strong in his/her basic IQ. Answer these simple questions and please don’t think way too extensively. Simple thinking will do… 1. How do you put a giraffe into a refrigerator? The correct answer is: Open the refrigerator put in the giraffe and close the door. This question tests whether you tend to do simple things in an overly complicated way. 2. How do you put an elephant into a refrigerator? The wrong answer is: Open the refrigerator put in the elephant and close the door. The correct answer is: Open the refrigerator, take out the giraffe, put in the elephant and close the door. This tests your ability to think through the repercussions of your actions. 3. The Lion King is hosting an animal conference; all the animals attend except one. Which animal does not attend? The correct answer is: The Elephant. The Elephant is in the refrigerator. This tests your memory. OK, even if you did not answer the first three questions, correctly, you still have one more opportunity to show your abilities. 4. There is a broad, deep river you must cross. But it is inhabited by hungry crocodiles. How do you manage it? The correct answer is: You swim across. All the Crocodiles are attending the Animal Meeting! This tests whether you learn quickly from your mistakes. This EXERCISE is cited just to show that logic or reasoning is an important element in management; at workplace or home. Parallel Thinking Just that you have to prune your memory to enhance your parallel thinking. In general parallel thinking is a further development of the well-known lateral thinking processes, focusing even more on probabilities—looking for what can be rather than for what is. Be Mindful of Others’ emotions: Emotional intelligence can be defined as the ability to monitor one’s own and other people’s emotions, to discriminate between different emotions and label them appropriately and to use emotional information to guide thinking and behavior. Emotional intelligence involves being MINDFUL of emotions and how they can affect and interact with traditional intelligence (e.g., impair or enhance judgment, etc.). One must also be able to develop and maintain healthy interpersonal relationships apart from being intelligent. It involves a lot of psychology which is in-built in our mechanism and heightened by our exposure to various work situations and challenges. An examination of more than 300 top-level executives from fifteen global companies showed that six emotional competencies distinguished stars from the average. Influence Team leadership Organizational Awareness Self-confidence Achievement Drive and Leadership Using Emotional Intelligence on the Job Emotional awareness is being in touch with the feelings of others. Well, if you say that “Emotions don’t go well with Logic”, and “Emotions can’t be mixed with Business”, I’d like to remind you “A controlled mind and cheerful spirit” are crucial when it comes to employee engagement and sustaining their morale. Even though your employees are well trained and technically experts in their own area, it takes that extra something for them to work whole-heartedly for their principals. They have to identify themselves with the organization and its objectives, in particular with the key persons...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Decision Making, Entrepreneurship, Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 20th, 2014 | 0 comments
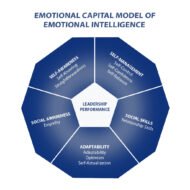
Emotional Intelligence for Effective Inter Personal Relationships What is Emotional Intelligence : an ability or capacity to perceive, assess, and manage the emotions of one’s self, and of others. Role of Emotions: Emotions play a critical role in organizations where there is a need for people to work in groups or teams. A leader who is strong in mind and thoughtful can perceive, observe and direct the emotions of the team members through proper channels. Such a leader is said to be “emotionally intelligent”. No! It is not about intelligence quotient but emotional intelligence. Empathy is the ultimate quality expected in leaders and managers rather than being rated high in the IQ scale.The capacity to perceive, scrutinize and manage one’s own emotions and that of others is one major factor of advantage in the concept of emotional intelligence. An emotionally intelligent person can institutionalize and manage change as well as make powerful decisions. Grooming of Human Mind and Skills: Human resource management throws up a real challenge to corporate organizations, where human minds and skills have to be groomed for the purpose of transcending their performance to remarkable levels in order to satisfy the production requirements. This is possible only when an organization has a leader who can draft and amalgamate the process of relationship management and skill development without a glitch for the benefit of the organization . Transformational leadership with constructive attitude and open approach is well appreciated and accepted by the worker force. What are the distinct features of emotional intelligence? High perception Being insightful Sensitive to the needs and requirements of the employees Self-control Self-awareness Open communication Empathy Change management skills Effective decision making Ever sanguine Instrumental in developing interpersonal skills Breaks the conventional rules Aggressive and daring in his approach Socially popular and easily gain acceptance Motivation driver The rational quotient behind emotional intelligence helps people to think and act smart even during nerve-racking situations.Emotional intelligence helps people to think and act in a logical manner in stressful situations that can divert their energy into positive thinking. A leader with high emotional intelligence can work efficiently with his team members. The spirit of exuberance from the leader acts as a positive signal and takes the pressure off the employees’ mind. It is this ability to identify and understand the emotions of people working under him makes him a comrade rather than a commando. Why EI is Necessary? Emotional intelligence is necessary for top level executives at management level to stand out and succeed. An ordinary employee who does mundane job everyday is expected to be technically sound and well-trained. The same criterion can never be applied to a manager or a chief executive who is bound to manage both formal and informal teams working under the same roof. Only persons who are emotionally sound can uphold the proceedings with dynamism and verve. By motivating human personnel you can get things done in a smooth manner: Give them a fresh start to prove themselves in case if they fail at the first attempt Anger management of self/others Channelize the emotions of self/others and create positive vibes Perceive the problems from various angles to get a complete picture Understanding the root of the problem Treating work as fun Thinking out of the box – parallel thinking and creative thinking must be encouraged amongst the employee group. People with high emotional intelligence are the ones needed in business community as big corporate organizations always find it difficult to manage human resource. The management has to devise a system that takes into account the intricacies of human mind and assigning right people to handle the perplexities....

Posted by Managementguru in Change management, Organisational behaviour
on Feb 23rd, 2014 | 0 comments
Resistance to change should be considered as a good sign and can be compared to fever while there is a bodily infection. It creates a platform for the firm to find out the causes for resistance and hence the solution. Causes for Resistance to Change Individual Resistance A. Economic factors: When pay is tied up with productivity, resistance arises. B. Habit: It is the habit of humans to resist anything new. C. Fear of the unknown: Freshers always have a feeling of insecurity and uncertainty when they join an organization. D. Change affects emotions and sentiments: People are disturbed both emotionally and sentimentally when there is a change. E. Lack of clarification: People interpret change in different ways; so there is a need for the organization to clarify as to the nature of the change and its implied consequences or implications. F. For the sake of opposing: Illogical and weird opinions are given by the employees just for the sake of opposing. Resistance to change Organizational Resistance A. Built-in-Mechanism: People working in groups experience shock when there is a structural change introduced in the system as they are tuned to a set of rules and procedures. B. Group norms: This also acts as a strong source of resistance acting as a constraint C. Threat to expertise: Technological innovations pose new threats everyday to the non-technical persons D. Threat to established power relationship: If the powers are re-assigned amongst the managerial cadre there arises unrest E. Threat to established resource allocation: Budget reallocations are resisted by departments that are not favored How to Overcome Resistance to Change? Education and Communication: The logic of change must be conveyed to the employees in a convincing manner and full facts must be communicated without an iota of doubt. Participation: It becomes difficult for individuals or groups to resist change when they are made to act as change agents Facilitation and Support: Change agents can offer counseling, training etc to pacify the employees Use of Group Force: Groups can exert more pressure on attitudes, values and behavior and hence, if the group cohesiveness is strong, the change is easier to achieve. Leadership for Change: A strong leader-manager can create a climate for psychology support from subordinates Negotiation: The key persons or individuals whom the management think are potential change agents can be rewarded and brought to the negotiating table Manipulation: Twisting information, creation of false rumors, withholding undesirable information are some of the tactics of manipulation that decrease the intensity of resistance to change. Coercion: Application of force that includes threats of transfers, delay in promotions, negative performance evaluation can decrease the resistance and also the credibility. Manipulation and coercion must be considered as last options to reduce the pressure as generally people will welcome any change that is positive and beneficial to the organization in the long run. It is the responsibility of the management to project the change in a gradual and convincing manner to the...






