Posted by Managementguru in Human Resource, Quotes and Quotes Only, Training & Development
on Jul 6th, 2014 | 0 comments

Popular HR Quotes by Industry Experts and Management Scholars We have compiled 50 top notch hr quotes from doyens in the field of business and management that will sure fire inspire you with creative ideas. 1. “Great Vision Without Great People Is Irrelevant.” -Jim Collins, Good To Great 2. “Human Resources Isn’t A Thing We Do. It’s The Thing That Runs Our Business.” -Steve Wynn, Wynn Las Vegas 3. “You Need To Have A Collaborative Hiring Process.” -Steve Jobs, Apple 4. “You Can’t Teach Employees To Smile. They Have To Smile Before You Hire Them.” -Arte Nathan, Wynn Las Vegas 5. “Never Hire Someone Who Knows Less Than You Do About What He’s Hired To Do.” -Malcolm Forbes, Forbes Top 50 HR Quotes 6. “When Hiring Key Employees, There Are Only Two Qualities To Look For: Judgement And Taste. Almost Everything Else Can Be Bought By The Yard.” John W. Gardner 7. “Recently, I Was Asked If I Was Going To Fire An Employee Who Made A Mistake That Cost The Company $600,000. No, I Replied, I Just Spent $600,000 Training Him. Why Would I Want Somebody To Hire His Experience?” -Thomas John Watson Sr., Ibm 8. “It’s More Than Just Selling Pizzas. It’s Being A Good Fit For The Community. We Hire Based On The Betterment Of The Community As Much As Anything.” -Mark Starr, David’s Pizza. 9. “You Can Have The Best Strategy And The Best Building In The World, But If You Don’t Have The Hearts And Minds Of The People Who Work With You, None Of It Comes To Life.” -Renee West, Luxor And Excalibur Hotel 10. “I am convinced that nothing we do is more important than hiring and developing people. At the end of the day you bet on people, not on strategies.” -Lawrence Bossidy, Ge CURRENT TRENDS IN HRD 11. “Do Not Hire A Man Who Does Your Work For Money, But Him Who Does It For The Love Of It.” -Henry David Thoreau, Life Without Principle 12. “If You Think Hiring Professionals Is Expensive, Try Hiring Amateurs” -Anonymous 13. “The Key For Us, Number One, Has Always Been Hiring Very Smart People.” -Bill Gates, Microsoft 14. “Time Spent On Hiring Is Time Well Spent.” -Robert Half 15. “I Hire People Brighter Than Me And Then I Get Out Of Their Way” -Lee Iacocca, Ford 16. “You Cannot Push Anyone Up The Ladder Unless He Is Willing To Climb.” -Andrew Carnegie 17. “Management Is Nothing More Than Motivating Other People.” -Lee Iacocca, Ford 18. “There Are Few, If Any, Jobs In Which Ability Alone Is Sufficient. Needed, Also, Are Loyalty, Sincerity, Enthusiasm And Team Play.” -William B. Given, Jr. 19. “When People Go To Work, They Shouldn’t Have To Leave Their Hearts At Home.” -Betty Bender 20. “One Machine Can Do The Work Of Fifty Ordinary Men. No Machine Can Do The Work Of One Extraordinary Man.” -Elbert Hubbard 21. “To Find Joy In Work Is To Discover The Fountain Of Youth.” -Pearl S. Buck 22. “One Of The Symptoms Of An Approaching Nervous Breakdown Is The Belief That One’s Work Is Terribly Important.” -Bertrand Russell 23. “Opportunity Is Missed By Most People Because It Is Dressed In Overalls And Looks Like Work.” -Thomas A. Edison 24. “Far And Away The Best Prize That Life Offers Is The Chance To Work Hard At Work Worth Doing.” -Theodore Roosevelt 25. ”Being Busy Does Not Always Mean Real Work. The Object Of All Work Is Production Or Accomplishment And To Either Of These Ends There Must Be Forethought, System, Planning, Intelligence, And Honest Purpose, As Well As Perspiration. Seeming To Do Is Not Doing.” -Thomas A. Edison 26. “Going To Work For A Large Company Is Like...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Decision Making, Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Apr 19th, 2014 | 0 comments

Business Policies – Framing and Execution Business policies are the keystone in the arch of management and the life-blood for the successful functioning of business, because without well-laid down policies, there cannot be lasting improvements in the economic condition of the firm and labor-management relations. A policy is a positive declaration and a command to its followers. It translates the goals of an organization into selected routes and provides the general guidelines that prescribe and proscribe programmes, which in turn, dictate practices and procedure. Attainment of Objectives: Buisness policies are general statement of principles for the attainment of objectives which serve as a guide to action for the executives at different levels of management. They pave a broad way in which the sub-ordinates tread along towards accomplishing their objectives. Hierarchy: For each set of objectives at each level, there is a corresponding set of policies. The Board of Directors determine the basic overall corporate policiesThe top management decides on the executive corporate policiesManagers decide on the departments / divisional policiesMiddle managers handle the sectional policies Consistent Decisions contributing to the Objectives: The policies delimit the area within which a decision has to be made; however, they do allow some discretion on the part of the man on the firing line, otherwise, they would be mere rules. At the same time too much of discretion in policy matters may prove harmful to the accomplishment of organizational objectives and hence it is generally within limits. Mutual Application: Policies in general are meant for mutual application by sub ordinates. They are fabricated to suit a specific situation in which they are applied, for they cannot apply themselves. Unified Structure: Policies tend to predefine issues, avoid repeated analysis and give a unified structure to other types of plans, thus permitting managers to delegate authority while maintaining control. Policies for all Functional Areas: In a well-structured and managed organization, policies are framed for all functional levels of management. Corporate planningMarketingResearch and DevelopmentEngineeringManufacturingInventoryPurchasePhysical DistributionAccountingFinanceCostingAdvertisingPersonal SellingSpecial Promotion, are some areas that require clear-cut policies. Clear-Cut Guidelines: Policies serve an extremely useful purpose in that they avoid confusion and provide clear-cut guidelines. This enables the business to be carried on smoothly and often without break. They lead to better and maximum utilization of resources, human, financial and physical, by adhering to actions for...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Training & Development
on Apr 5th, 2014 | 0 comments
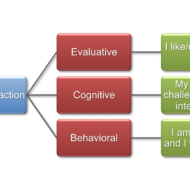
Attitude and Job Satisfaction What is attitude? Attitudes are evaluative statements or judgments concerning objects, people or events –Stephen Robbin. They also represent an ‘affective orientation towards an object.’ It simply means what one feels and thinks about something. Elements of attitude: Cognitive components – opinion or belief Affective components – emotion or feeling Behavioral components – intention to behave The interaction of these three components determines the way in which an individual develops an attitude towards something. Sources: Society Friends Teachers Family Members It also forms on the basis of the level of admiration we have over an object or persons. People also try to imitate others and attitudes are gradually formed on that basis also. In some attitudes formed are less stable, in some they even dominate the whole life. Types: Organizational behavior uses the concept of attitudes in relation to nature of the job and its influence on the performance of the persons. Accordingly, Job Satisfaction Job Involvement and Organizational Commitment, are the three kinds of attitude a person could have with respect his / her job or organization. Job Satisfaction: In “Job Satisfaction “, Stephen P. Robbins writes about five factors which make a person satisfied with his or her job. These factors are Mentally challenging work Equitable rewards Supportive working conditions Supportive colleagues and Personality-job fit. Cranny, Smith and Stone define job satisfaction as employees’ emotional state concerning the job, considering what they anticipated and what they actually got out of it. In fact, an employee with low expectations can be more satisfied with a certain job than someone who has high expectations. If one’s expectations are met or surpassed by the job, then one is happy and satisfied with the job. Job Involvement: Job involvement has been defined as an individual’s psychological identification or commitment to his / her job. As such individuals who display high involvement in their jobs consider their work to be a very important part of their lives- In other words for highly involved individuals performing well on the job is important for their self esteem. Organizational Commitment: Three important elements of a committed individual would be Identification with the organization’s goals and/or mission Long-term membership in the organization and intention to remain with the organization, often termed loyalty High levels of extra role behavior- behavior beyond required performance- Often denoted to as citizenship behavior or pro-social behavior. Cognitive Dissonance Theory: Leon Festinger developed this theory which explains the relationship between attitude and behavior. It refers to”any incompatibility that an individual might perceive between two or more of his or her attitudes, or between his or her behavior and attitudes.” Attitude Surveys: This is a tool that helps to collect information about the levels of attitude among the people. In most companies these kinds of surveys are conducted with the help of different rating scales like Likert scale offering five or seven alternative choices for each of the statement developed for attitude measurement. Summary: Research conducted on attitude and job satisfaction in Indian workers has made clear certain points as given below: Attitude is positively correlated with efficiency Absenteeism will bring down satisfaction levels Unions, negatively affect the employee attitude and job satisfaction Attitude researches and surveys will improve...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Change management, Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 31st, 2014 | 0 comments
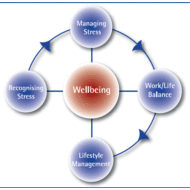
India often looks at Japanese or American models to comprehend the concepts of management. In reality, Indian scriptures can be considered as treasuries of management. The Bhagavat Gita, the Vedas and the Epics highlight the true spirit of working together and the need for de-stressing the self for enhanced performance levels. The idea of NISHKAMYAM (to perform one’s own work without expecting a result) is truly said to be the highest ideology preached by Lord Krishna. What Induces Stress? A dynamic condition in which an individual is presented with an opportunity or confronted with a demand, related to what she or he desires and for which the outcome is uncertain but important, can be called a stressful situation. The consequences of stress in an organizational set up express themselves in the form of physiological, psychological or behavioral symptoms, which are harmful to the individuals who experience high levels of stress. Symptoms of stress: AnxietyDepressionIncreased job dissatisfactionAbsenteeismDecline in productivityRapid turn overHigh blood pressureHeart diseasesHead aches Stress Can be Motivating: While long term stress is harmful to the individual and organization as well, it is said that short term stress serves the purpose of task accomplishment by individuals or groups, within the stipulated time. It serves as a motivation factor rather than a causative agent of frustration. It has been proved by scientists and medical researchers that stress has a direct effect on the metabolism of a person, that causes increase in heart and breathing rates, increase in blood pressure, thus inducing heart attacks. Equally important are the behavioral and attitudinal changes that are created by stress, which cannot be overlooked. Job Satisfaction: Psychological symptoms arise due to job-related dissatisfaction, boredom, work pressure, irritability and procrastination. Sometimes forceful involvement may also lead to decreased job satisfaction. The job to be carried out can be finished at the particular time if the individual is able to give one’s best shot. But when it is performed under stress, they complete the job with dissatisfaction. When the incumbent is asked to perform a task that lacks clarity, naturally ambiguity arises in his mind followed by anxiety. Behavioral Symptoms of Stress Changes in productivity levels, absence, and rapid staff turnover are stress symptoms of behavioral nature. It might be expressed even in the form of increased smoking, consumption of alcohol etc., Say for instance, in production department, when there is a need to supply a product in a very limited time, the workers may be active initially, but the performance slows down when they get totally tired or dissatisfied with the work. Again the demand by the superior adds additional stress that reaches unmanageable levels. Similarly, people taking care of administration, banking, marketing and other office related works fall a prey to stress. How to manage stress? From an organization view point, it is believed that a limited amount of stress may work wonders in terms of performance, with stress acting as a “positive stimulus”. But even low levels of stress are likely to be perceived as undesirable from an individual’s stand point. How could be the notion of management and individuals be different on the acceptable levels of stress? It does not solve the purpose. Individuals have to understand that, they have to live up to the expectations of the management in order to enhance their credit ratings, in terms of promotion and pay. They have to understand that challenges are to be perceived as opportunities to prove their mettle. Self and situational analysis, work analysis, time management and physical well- being are some techniques that practically solve problems of stress. “De-stressing the Self” Techniques for Employees Organisations can reduce stress of the employees...

Posted by Managementguru in Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Strategy, Training & Development
on Mar 31st, 2014 | 0 comments
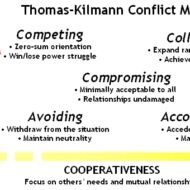
Conflict is a Part of Organizational Life Managers need to be alert to the presence of conflicts. Their focus should be oriented towards the goals to be accomplished. If there is a conflict, they should aim to resolve it smoothly by not over-reacting to the situation. They should take the help of persons who can best settle the issue, be ready to bargain and not issue orders. Their concentration should be on the problem and not on persons. True to the saying – Am I not destroying my enemies when I make friends of them?- President Abraham Lincoln Conflicts are Functional and Healthy: Conflicts in organisations are generally considered to be dysfunctional. On the contrary, many top executives of big companies view conflicts, as a means, to sufficiently analyse a problem and postpone decision making until all critical aspects of an issue are evaluated properly. Conflicts may occur within the individual, between individuals, between the individual and the group or between groups. There are many potential sources of conflict in today’s corporate organisations. The complex inter personal relationships and high degree of interdependence causes friction. Difference of Opinion: When many people must work together, conflict is inevitable, as it is human nature to clash and complain. Conflict is the personal divergence of interests between groups or individuals. The need to share scarce resources, difference in goals between organisational units, difference in values, attitudes and perception, ambiguously defined work responsibilities are some of the major sources of conflict. Functional Conflicts: Functional conflicts support the goals of a group, improve its performance and are constructive in nature. Dysfunctional conflicts hinder the performance of a group and are destructive in nature. It has not been precisely defined, as to what criterion demarcates functional from the dysfunctional. It is only the group’s performance and the delivered result or outcome that determines the nature of the conflict. Conflicts, irrespective of their type can bring these benefits to the firm: Bring hidden issues to the surface. Encourage creativity and innovation. Improves communication and make changes more acceptable. Increases group cohesion. Strategies to Resolve Conflicts: So, what kind of strategy do you think best suits in resolving conflicts? Avoiding or smoothing conflicts may be a temporary measure, only to bounce back in full force. Forcing might create undesirable consequences. The only option left is to confront the situation, face-to-face meeting of the conflicting parties for the purpose of identifying the problem and resolving it through an open discussion. Make Structural Changes to Lessen Conflicts: By making structural changes, conflicts can be managed. The objectives of a group are modified and then integrated to suit the purpose. Also changes in the structure of the organization, that is, clarification of authority-responsibility relationship, improving the working atmosphere, ambience and work locations help in resolving conflicts. Proper Communication: Lack of proper communication, ego clashes between the people in line and staff positions, a superior’s autocratic leadership style, differing educational backgrounds, lack of co-ordination between inter-departments are all rich sources of conflict. These can be resolved with the right kind of attitudinal approach and an open mind from the management’s...










