Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Economics, Principles of Management, Strategy, Technology
on Mar 26th, 2014 | 0 comments
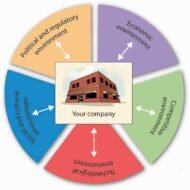
Technological Impact on Business Environment and Society The tremendous technological growth that is being witnessed is made possible through extensive programmes of technological research being conducted by many types of researchers working within universities, business, and non-profit research organizations. Technological developments are strong and all pervasive forces of the business environment. Technology is the scientific knowledge to practical problems. Technology feeds on itself and it affects business in two major ways: Through its impact on society in generalThrough its direct influence on business operations and activities. Technology and Economic Growth: Technology affects society. In fact, we feel its effect in our everyday lives. It affects economic growth, our standard of living and our culture. However, some of the effects of technology are highly beneficial and some detrimental. These effects on members of the society may in turn affect business practices. We are surrounded by so much of technology, that we take it for granted and usually do not realize how much it affects us until we have to do without electricity, water, transport or telephone. Technological developments have raised the standard of living. In spite of inflationary pressure and considerably a high degree of unemployment, generally families eat better, wear a wider variety of clothing, and live in more comfortable homes. Technology and Lifestyle: Technology also influences basic aspects of our culture, including religion, education, mobility, health care, art, language, laws and their enforcement. For example, technological advances in health care allow physicians to treat their patients in a virtual environment through video conferencing, which again is helpful in legal environment too for the judges to proceed with investigations on hard core criminals, who need not be produced before the court for security reasons. Creative Destruction: Every new technology is a force involved in creative destruction. Say, television hurts movies, synthetic fibers are considered rival for cotton fiber. The discovery of new technology even sometimes affects economic growth-TV with its high entertainment value takes away productive hours of mankind. Each new technology creates major long term consequences, which are not always foreseeable. How do you justify nations spending more money to develop missiles, nuclear weapons and bombs for the sake of security? Developing nations have to buy technology from foreign countries, as they are not resourceful in terms of capital needed for Research and Development, expertise, patents, licenses, and equipments and so on. This transfer of technology involves huge costs as a result of which a vicious circle is formed, in which weak technology creates dependence and dependence creates weakness. Conserve, Reduce, Recycle: The recent trend can be enumerated through this slogan, “Conserve, reduce and recycle”. The stress today is on clean production measures, advanced robotics, zero-emition vehicles, material recycling and alternative fuels and materials. This change towards love for environment by the technologists is a sure sign of positive...

Posted by Managementguru in Human Resource, Motivation, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Stress Management, Training & Development
on Mar 19th, 2014 | 0 comments
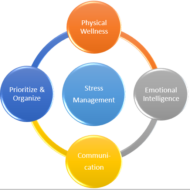
Did you know that without your knowledge, your health might be deteriorating due to pressure at work. Effective stress management is the only way out to become happier, healthier, and more productive. Whatever we do or say has a direct effect on our physiological processes as it affects our psyche-both positive and negative. While positive vibes act as a booster to our health, enhances the morale causing increased productivity which is “THE CONTRIBUTION FACTOR” in corporate organisations, negative vibes causes distress to the party affected and in-turn the organisation. Though in a small way, which is enough to cause great distress waves amonsgt the entire organisation through grapevine. Morale Surveys Therefore, it becomes necessary that every organisation takes some time to understand and analyse the mind-set of their employees to maintain the entire health of their firm. This can be done through surveys or questionnaires which serve as best platforms that shoulder employees’ opinion. On the side of the individual, he also should spare some time, from time-to-time to analyse his attitude towards the organisation and his/her colleagues and how it affects his/her performance. Management scholars say that “SELF-APPRAISAL” is the best tool for enhanced organisational performance and productivity. What is Stress? It is very important to understand what stress is, to combat it. Stress is nothing but a condition where people get excited emotionally or in other words ” a disturbed mental state” affecting the well-being. The causal agents may be physiological which can be medically treated or emotional which we are more worried about as emotionally unstable individuals cannot think properly which again leads to physical distress. It becomes therefore vital to know how we perceive and interpret things through our cognitive skills, again influenced by environmental factors to a considerable extent. People, particularly working in corporate environment and IT industry are subjected to much stress and they don’t know how to find a vent to their feelings or when there is no adequate support from the family side. What are the Ways Out? So, what is it we do at times like these? Not to bother. The mantra is “RELAX” to the maximum possible extent. First thing extract yourself away from the scene of action so that you could breathe some fresh air. Then think calmly and try to isolate the bug that is bothering you. Here the problem is the bug and analyse how far you have become vulnerable to the situation. Gauge the amount of damage done and rate the problem in terms of ” recoverable by myself- no help needed”, ” recoverable- but with external support”. Remember, for every problem there is a solution. It may not be tailor- made, but definitely passable with little bit of compromise from our end if necessary. 10 Yoga Poses You Should Do Everyday to Combat...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 13th, 2014 | 0 comments
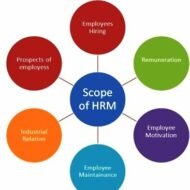
Scope and Characteristics of HRM 1. Personnel aspect: concerned with manpower planning, recruitment, selection, placement, transfer, promotion, training and development, lay off and retrenchment, remuneration, incentives, productivity, etc.; 2. Welfare aspect; dealing with working conditions and provision of amenities such as canteens, crèches, rest and lunch rooms, housing, transport, medical assistance, education, health, safety, recreation facilities, etc.; and 3. Industrial Relations aspect: the legal part which covers union-management relations, joint consultation, collective bargaining, grievance redress and disciplinary procedures, settlement of disputes, etc. Small Business Management and Marketing Essentials CHARACTERISTICS OF HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT: 1. It is an art and a science: The art and science of HRM is indeed very complex. HRM is both the art of managing people by recourse to creative and innovative approaches; it is a science as well because of the precision and demanding application of theory that is required. 2. It is pervasive: Development of HRM covers all levels and all categories of people, and management and operational staff. No discrimination is made between any levels or categories. All those who are managers have to perform HRM. It is pervasive also because it is required in every department of the organisation. All kinds of organisations, profit or non-profit making, have to follow HRM. 3. It is a continuous process: First, it is a process as there are number of functions to be performed in a series, beginning with human resource planning to recruitment to selection, to training to performance appraisal. To be specific, the HRM process includes acquisition (HR planning, recruitment, selection, placement, socialisation), development (training and development, and career development), utilisation (job design, motivation, performance appraisal and reward management), and maintenance (labour relations, employee discipline, grievance handling, welfare, and termination). Second, it is continuous, because HRM is a never-ending process. 4. HRM is a service function: HRM is not a profit centre. It serves all other functional departments. But the basic responsibility always lies with the line managers. HRM is a staff function – a facilitator. The HR Manager has line authority only within his own department, but has staff authority as far as other departments are concerned. 5. HRM must be regulation-friendly: The HRM function has to be discharged in a manner that legal dictates are not violated. Equal opportunity and equal pay for all, inclusion of communities in employment, inclusion of tribal’s and farmers in the benefits and non-violation of human rights must be taken care of by the HRM. 6. Interdisciplinary and fast changing: It is encompassing welfare, manpower, personnel management, and keeps close association with employee and industrial relations. It is multi- disciplinary activity utilising knowledge and inputs from psychology, sociology, economics, etc. It is changing itself in accordance with the changing environment. It has travelled from exploitation of workers to treating them as equal partners in the task. 7. Focus on results: HRM is performance oriented. It has its focus on results, rather than on rules. It encourages people to give their 100%. It tries to secure the best from people by winning the whole hearted cooperation. It is a process of bringing people and organization together so that the goals of each are met. It is commitment oriented. 8. People-centred: HRM is about people at work both as individuals and a group. It tries to help employees to develop their potential fully. It comprises people-related functions like hiring, training and development, performance appraisal, working environment, etc. HRM has the responsibility of building human capital. People are vital for achieving organizational goals. Organizational performance depends on the quality of people and employees. 9. Human relations philosophy: HRM is a philosophy and the basic assumption is that employees are human beings and not a factor of production like...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Labor Management, Organisational behaviour
on Mar 7th, 2014 | 0 comments

People Management and Trade Unions Need for Trade Unions Why do employees join trade unions is an important question. Most of the workers are members of any one of the trade unions. One of the major objectives of trade unionism is to promote industrial democracy. This objective is achieved when trade union is an organization of the workers, for the workers and by the workers”. In practice this rarely happens and instead unions become an oligarchy. Union leaders by and large, show authoritative behavior with less participation, openness and transparency. Decision-making is centralized, elections are often postponed and positions are filled repeatedly by nominations. Rank and file is pampered with promises and seldom gets near to decision-making process. Positions get worse when unions are guided by outside leaders and regulated by the policies of political parties. Ideology of Trade Unions Absence of democratic leadership reduces the effectiveness of trade unions and prevents the development of trade union leadership from among the workers within the industries. In due course, trade unions become obsessed with political ideology or personal interest ousting the welfare of the workers. Before we move on to the functions of trade unions, let us understand the reasons for the existence of such organizations. To get a common platform to air ones views, aims, ideas and feelings and obtain recognition and status among fellow workers. Make use of the principle of unity for the purpose of securing good working conditions, higher economic compensations, better career prospects and welfare needs. Security of employment and protection against calamity of accident, death and social security after retirement. Restrict management action which is against the interest of the workers. Functions of a Trade Union The internal functions of a labor union includes better wage claim, to ensure better working conditions, reasonable work etc.,The external functions include conducting night school, games, sports and other recreational activities. These two functions may be grouped as economic and social functions. Many unions try to capture political power through election, so that they can influence upon the programmes and policies of government in favor of labor. This function is known as political function. Under the legal functions, the interpretation of law takes the major share. A jist of the main purpose of trade organizations: To improve the standard of living and working condition of the workers. To protect the security of workers’ employment. To ensure better health, reasonable working hours and welfare measures. To improve the political status. To raise the vocational status. To bring better participation in the management. To inculcate the feeling of self respect and confidence among worker force. To bring industrial peace and harmony. As long as unionism is considered as an anathema by the management, there will be lack of harmony and mutual trust between the management and labor force. Management must not consider labor unions as a legal obligation as it does not develop faith and goodwill. Instead the union has to be viewed as a partner in trade to live with and work with. Union must also recognize that work is worship and the survival and success of organization depends on the very survival and success of the workforce. Once the team spirit is built up no unreasonable demands will be raised and union leaders must view strikes and lock outs as last resorts to put pressure on management. The Trade Unions Act, 1926– An act to provide for the registration of Trade Unions and in certain respects to define the law relating to registered Trade...

Posted by Managementguru in Economics, International Business
on Feb 16th, 2014 | 0 comments

Economic Growth Strategies A Purview on Economic Growth Strategies for Developing Countries A developing country is one where the per capita income is low relative to that of fully developed countries. In human terms developing countries typically have major population percentage with poor health, low levels of literacy, inadequate dwellings and meager diets. The key to development rests on four fundamental factors namely human resources, natural resources, capital formation and technology. Human resources: A lot of poor countries are forever running hard just to stay in place. Even as a developing nation’s GDP rises, so does its population. So it becomes a mammoth task for such nations to overcome poverty with birth rates so high. Equitable distribution of wealth cannot happen in an economy unless and until it becomes self sufficient. One strategy will be to curb the population, even if such actions run against prevailing religious norms. Strategies for Developement Economic planners in developing countries lay great emphasis on the following strategies of development with regard to human capital: Control disease and improve health and nutrition Improve education, reduce illiteracy and train workers Above all, do not underestimate the importance of human resources. Literate people are knowledgeable and resourceful; their analytical skills help them to weigh the pros and cons of specific social situations that affect their standards of living. Asian countries like India and China with exploding population figures are in a situation to invest their human capital for productive purposes. Pinning Your Way to Profit With Pinterest Natural Resources: Some developing nations with meager endowments of natural resources such as land and minerals have to divide the available resources among the dense population. Perhaps the most valuable of all the resources would be arable land, as most of the people in developing countries employ themselves in farming, which is the primary economic activity. Hence the productive use of land with appropriate conservation, fertilizers and tillage will go- far in increasing a poor nation’s output. More over land ownership patterns are a key to providing farmers with strong incentives to invest in capital land’s yield. When farmers own land, they are more willing to make improvements, such as irrigation systems and undertake appropriate conservation practices. The governments have to think in these lines if their economy is based on agricultural activity: Farmers should be appraised about modern farming techniques and provided with farming equipments and fertilizers at subsidized rates. Note:-nothing should be given as free as freebies make them lethargic and unmotivated. Much of cultivable lands are being destroyed for commercial purposes which have to be checked. Power generation and supply should be copious and uninterrupted as farming, solely is dependent on availability and usage of ground water. Pumping of water is done through jet pumps and electric motors. Budding population can make a marked difference in the field of farming, as it is impossible for a nation to generate white collar jobs for everyone and it definitely elevates the capacity of youth from being mere employees to that of owners. Organic farming has found a place for itself in international market and human capital of developing nations can be employed in research and development of new strains that will facilitate to capture the global market. Capital formation: Rates of productive capital formation are low in developing countries because of deprived income; little can be saved for the future. The financing of growth in poor countries has always been an unstable link in the productive mechanism. Countries should definitely have a balanced and cautious approach when they plan to finance ambitious development programmes as they will be forced to borrow heavily from other developed countries or the World Bank. Technological change and innovations: This is...










