Posted by Managementguru in Human Resource, Labor Management, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Training & Development
on Mar 18th, 2014 | 0 comments

Evolution and Growth of Human Resource Management It is very interesting to trace out the evolution and growth of Human Resource Management. People – The Principal Resource The principal resource of any organization is people and managing people is the most important and challenging aspect of an organization. What we call human resource management today, dates back to 1800 b.c.,which is evident from the inscriptions of Babylonian code of Hammurabi and Kautilya’s Arthasashtra, which explains in detail the importance of selection, incentives, performance evaluation, quality of a manager and wage rates. So,we understand that the concept of managing people has existed even in the previous eras through ancient literature and philosophy. India, China and Greece have been the origin points of human resource management concepts. Evolution of Human Resource Management Industrial Revolution Till, 1930’s, there was no such department called “personnel management” that was considered necessary to cater to the needs and welfare of the labor society. The factory manager was acting as a link between the workers and the management, and most of the time he had to comply with the rules of the management to satisfy them, even if it were against the welfare of the workers. Also proper attention was not given to areas like, worker safety, security and living conditions. Industrial revolution saw mass exodus of workers to urban areas in search of jobs. Need for Employment Department Application of science and technology in production made the rich owners even richer; the poor workers were not paid adequately and their life became miserable. Since the owners lost direct contact with the employees, managers came into the picture to take over control of production and administration. Machines ruled the industry and importance of labor got reduced. This condition existed for sometime until the advent of new and improved management concepts by people like F.W.Taylor who is considered to be the father of scientific management and B.F.Goodrich who was instrumental in forming the “employment department” which can be considered the fore runner of present human resource department. Introduction of Scientific Management Scientific methods were introduced to make the workers perform the job with ease and perfection. It also saved enormous time and reduced the monotony of work. job-designs, job-specification, training and development and human relations were given due importance and the owners slowly started realizing the importance of labor. Through 1940’s to 1970’s behavioral approach was applied to professional management, the major architects being Abraham Maslow, Herzberg and Douglas McGregor. This approach suggested managers to modify their leadership styles to suit the type of followers and motivate the workers. Consequences of World War I and II World War I and II also had profound influence on Human resource development. The concepts of role playing, improved training methods, supervision and group discussions came into the fray. The advent of labor unions also established a clear pathway for the workers to claim their rights, ably supported by the labor laws enacted by various governments. International labor organization was formed in 1919 which created sensation in the worker community all over the world. All said and done, empowerment of workers has been achieved only in developed nations where “job security” is no more a great concern because job opportunities are more. But in unorganized and small sectors, employers continue to exploit workers because “supply” is more than “demand”. The responsibility to develop and empower the employees solely lies on the shoulders of human resource department. It should try to address the problems of workers to the management and amicably settle issues relating to wages, welfare, safety and security. → Objectives and Functions of...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 17th, 2014 | 0 comments
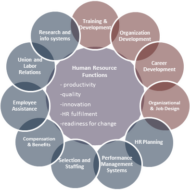
Personnel or Human Resource Management: is the strategic approach to the management of an organization’s most valued assets – the people. Human resource is always in great demand as competent or skilled labor is in short supply. It is important to remember that no one is born with the value of excellence, as the acquisition is gradual in nature and only possible through proper training and one’s own cognitive perception. It is not that people have to belong to the elite group to make their mark in the respective fields. The best leaders and managers often are ordinary people creating amazing results and astounding success. Try some of these golden etiquettes for achieving excellence in the management of human resource: Clear objectives have to be set with the consensus of the employees Recognize the progress Confront problems Manage with flexibility Understand the value of quality Manage time for better results Enhance decision-making skills by delegating authority Master stress Motivate people Think like a winner Pursue a participative style of leadership To achieve the goals of the organization, the HR department will have to reorient itself on the following lines. It is very important that ‘Right people are chosen for the Right job’. During the induction stage, employee attitudes must be shaped in harmony with the culture of the organization. Dynamic training system should be introduced which is supposed to be a continuous process rather than a sporadic exercise. Quality of Work Life: Organization should ensure satisfactory quality of work life in order to minimize the sense of alienation, found in the workplace. It should contribute to an atmosphere to improve self-discipline, self-motivation and self realization for the purpose of production optimization in terms of both quantity and quality. The presence of a fair performance appraisal system will facilitate the growth prospects of employees in terms of career advancement and development. Fair Compensation: Institutions must work out a fair compensation package for all categories of workmen so that they may be able to receive the living wages instead of subsistence-level wages. The accent should be on production and productivity, without any compromise. Opportunities are aplenty, particularly for experienced personnel as the industries offer wide job prospects for the prospective candidates. Now-a-days job hopping is rampant which is a serious issue to be managed. A number of organizations offer bonus in the form of stock that interjects a feeling of oneness, which ensures alignment of interest between employees and the management. Favored position in terms of enhanced performance from the work force is possible only if the management comes down to embrace and lend their ears to certain rational demands form the other end. Security of Employment Increased wages Employee ownership Participation and employment Internal promotions Information sharing Incentives etc., The personnel function can 1) Attract attention to indicate the importance attached to management’s process and the various policies, practices and systems that support the process. 2) Provide necessary information and expertise on best practices in rival companies to benchmark the process and provide with analytical support for diagnosing and recounting solutions to problems arising in the employee management relation. 3) Engage in business decisions and accelerate change that is consistent with the underlying values of the company. Note: The laws and matters relating to wages and bonus come under the purview of the Ministry of Labor and Employment. The Minimum Wages Bill was passed by the Indian Dominion Legislature and came into force on 15th March,...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Human Resource, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 13th, 2014 | 0 comments
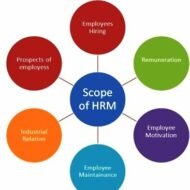
Scope and Characteristics of HRM 1. Personnel aspect: concerned with manpower planning, recruitment, selection, placement, transfer, promotion, training and development, lay off and retrenchment, remuneration, incentives, productivity, etc.; 2. Welfare aspect; dealing with working conditions and provision of amenities such as canteens, crèches, rest and lunch rooms, housing, transport, medical assistance, education, health, safety, recreation facilities, etc.; and 3. Industrial Relations aspect: the legal part which covers union-management relations, joint consultation, collective bargaining, grievance redress and disciplinary procedures, settlement of disputes, etc. Small Business Management and Marketing Essentials CHARACTERISTICS OF HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT: 1. It is an art and a science: The art and science of HRM is indeed very complex. HRM is both the art of managing people by recourse to creative and innovative approaches; it is a science as well because of the precision and demanding application of theory that is required. 2. It is pervasive: Development of HRM covers all levels and all categories of people, and management and operational staff. No discrimination is made between any levels or categories. All those who are managers have to perform HRM. It is pervasive also because it is required in every department of the organisation. All kinds of organisations, profit or non-profit making, have to follow HRM. 3. It is a continuous process: First, it is a process as there are number of functions to be performed in a series, beginning with human resource planning to recruitment to selection, to training to performance appraisal. To be specific, the HRM process includes acquisition (HR planning, recruitment, selection, placement, socialisation), development (training and development, and career development), utilisation (job design, motivation, performance appraisal and reward management), and maintenance (labour relations, employee discipline, grievance handling, welfare, and termination). Second, it is continuous, because HRM is a never-ending process. 4. HRM is a service function: HRM is not a profit centre. It serves all other functional departments. But the basic responsibility always lies with the line managers. HRM is a staff function – a facilitator. The HR Manager has line authority only within his own department, but has staff authority as far as other departments are concerned. 5. HRM must be regulation-friendly: The HRM function has to be discharged in a manner that legal dictates are not violated. Equal opportunity and equal pay for all, inclusion of communities in employment, inclusion of tribal’s and farmers in the benefits and non-violation of human rights must be taken care of by the HRM. 6. Interdisciplinary and fast changing: It is encompassing welfare, manpower, personnel management, and keeps close association with employee and industrial relations. It is multi- disciplinary activity utilising knowledge and inputs from psychology, sociology, economics, etc. It is changing itself in accordance with the changing environment. It has travelled from exploitation of workers to treating them as equal partners in the task. 7. Focus on results: HRM is performance oriented. It has its focus on results, rather than on rules. It encourages people to give their 100%. It tries to secure the best from people by winning the whole hearted cooperation. It is a process of bringing people and organization together so that the goals of each are met. It is commitment oriented. 8. People-centred: HRM is about people at work both as individuals and a group. It tries to help employees to develop their potential fully. It comprises people-related functions like hiring, training and development, performance appraisal, working environment, etc. HRM has the responsibility of building human capital. People are vital for achieving organizational goals. Organizational performance depends on the quality of people and employees. 9. Human relations philosophy: HRM is a philosophy and the basic assumption is that employees are human beings and not a factor of production like...






