Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Human Resource, Labor Management, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management, Strategy
on Mar 18th, 2014 | 0 comments
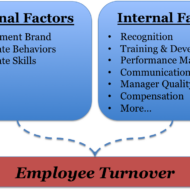
Smart Retention Strategies: Before going into the details of how to handle attrition, the first thing you must understand and realize is this. Each person working for you will have different expectations, perspectives and demands about his job, work environment and compensation respectively. Right at the time of recruiting and selecting the employee, his ideas must be taken into consideration and then it becomes the prerogative of the management whether to hire the person for that particular job. So the first step will be the right person for the right job, giving due importance to the anticipation of the employee who is going to become a member of your business family. Udemy Best Sellers:New Manager Training in Essential SkillsLeadership: Practical Leadership Skills Need for Open Conversation: In case of a small firm or company, it is easy for the manager to have a one on one conversation with each employee to settle his score of grievances then and there. Managers must have an open conversation without room for any ambiguity in the minds of his workers. The manager should try to protect the interest of the employees by representing their demands to the management at the right time. Many employees quit their positions because they have a nagging feeling at the back of their minds that their immediate boss is not the right kind of person to whom they can look up to and ask for support. In big corporates it is not easy to go for a one on one approach. A unique corporate culture that Trains the employees to have an uniform approach to all the systems of routineLed by an effective leader who controls and monitors the behavior and attitude of the workersPossesses sound management practices that make the employees come out with their suggestions freely and induce them to participateProvides satisfactory compensationIncorporates an open door policy catering to the different needs of people and also to the different levels of management, will help the managers to have a healthy relationship with the employees. Human Wants and Needs: Human wants are unlimited and when one want is satisfied, we want more of the same or yet another of a higher order. Approach your workforce to satisfy their craving either in terms of compensation or recognition which will also help to retain your workforce to a greater extent. There should be room for growth, especially for entrepreneurial minds and minds that have parallel thinking. Pic Courtesy: CuteHR Self-Motivation is the Key: Although motivation brings cheer amongst your workforce, self-motivated employees produce better results. Job satisfaction is a relative term; it differs with individuals, some like challenges and some are easily satisfied with an increase in salary quotient. A comprehensive appraisal on the personality of your workforce will give you a clear picture of the IQ (Intelligence Quotient) and EI (Emotional Intelligence) range of your employees which helps in designating employees in the appropriate slots. Such human rationing saves you a lot of time, energy and money as the employees are guaranteed satisfaction in their jobs. Contracts and Agreements: Contracts and agreements bind the employees to the firm only legally. How is that going to help you in terms of productivity? If one of your employees is going to work with discontent, he becomes a problem source spreading the same kind of feeling to others working with him. So it is also necessary for the management to spot out these problem persons either to bring them back into the groove or fire them without any further delay. Rising costs of living and unemployment ratios are really of economic concern, but still we find employees just like that quitting...

Posted by Managementguru in Business Management, Motivation, Organisational behaviour, Principles of Management
on Mar 9th, 2014 | 0 comments
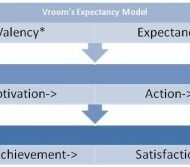
Herzberg and Victor’s Motivation Models Herzberg’s Hygiene Factor Theory Psychologist Fredrick Herzberg asked a basic question to 200 accountants and engineers in firms in and around Pittsburg-“What do people want from their jobs’? He used the critical incident method of obtaining data for analysis. “Think of a time when you felt exceptionally good or exceptionally bad about your job, either your present job or any other job you have had”. The responses obtained were fairly consistent in that, good feelings were associated with job content and bad feelings with job context. The ones on the right side of the table are intrinsic factors leading to job satisfaction and acted as motivators and ones on the left side lead to job dis-satisfaction and were termed as hygiene factors. Hygiene Factors: One has to understand that hygiene factors need not always cause dis-satisfaction; when the managers handle the situation in an amicable manner in terms of company policy, supervision, working conditions, salary and administration, things will be in the right direction but, even if they are adequate, people are never satisfied. These are called Hygiene factors and managers must try to eliminate factors that create discontent among the workers. If we want to motivate people, the real motivators are achievement, recognition, responsibility and growth. We must change the job design in such a way that the work arising out of the job should be challenging, exciting and should offer them a sense of achievement, recognition and growth. HYGIENE FACTORS MOTIVATORS Company policy Achievement Relationship with superiors Recognition Working conditions Work itself Salary Responsibility Relationship with peers Advancement Personal life Growth Relationship with subordinates Status Security CRITICISM: The factors which one particular group of individuals finds to be dis-satisfying may not be applicable for everybody. Factors which are beyond the scope of employees such as policy formulations cannot be considered as hygiene factors. VICTOR H. VROOM’S EXPECTANCY MODEL Valency*Expectancy=Motivation By increasing the positive value of the outcomes through such means as better communication about the outcomes, values and actually increasing them, i.e., the rewards and also by increasing the expectancy of the person by making him believe that the work will really lead him to the desired outcome, organizations can make a strong connection between the work and the...

Posted by Managementguru in Accounting, Financial Accounting, Management Accounting
on Feb 13th, 2014 | 0 comments

Bookkeeping involves organizing and managing all business transactions in a company.
Bookkeeping is the recording, on a day-today basis of the financial transactions and information pertaining to a business. Bookkeeping provides the information from which accounts are prepared but is a distinct process, preliminary to accounting.






